Organization
advertisement

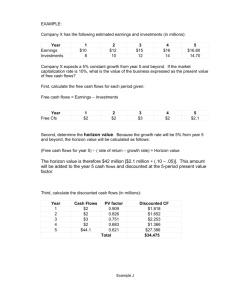
Prepared by group No. 2: Natalia Trunova (M004610026) Domingo Lee (M994610011) Libby Shun-Chi Chiang (M014020007) Chapter content Company’s profile Integrative module • Top management role in Organization Direction, Design, and Effectiveness • Porter’s Competitive Strategy • Miles and Show’s strategy typology • Organizational Effectiveness • Overview of the company • Core competencies • External environment • Horizon Analysis: Miles and Show’s & Porter’s Strategy • Effectiveness • Influence of structure on company’s design The primary responsibility of top management is to determine an organization’s goals, strategy, and design, thereby adapting the organization to a changing environment External Environment CEO Top management Strategic Intent Organization Design Internal Situation Effectiveness Outcomes Opportunities Threats Uncertainty Resource availability Strengths Weaknesses Distinctive competence Leader style Past performance Define mission Official goals Select operational goals Competitive strategies Structural form Learning Efficiency Information and control systems Production technology Human resource policies, inventives Organizational culture Interorganizational linkages Goal attainment Resources Efficiency Strategic constituents Differentiation • Focus on Uniqueness Low-Cost Leadership • Focus on efficiency Competitive Scope Competitive Advantage Low Cost High Cost Broad Overall Cost Leadership Differentiation Narrow Cost Focus Defferentiation Focus Source: http://www.vectorstudy.com/management_topics/strategy_typology.htm Source: http://www.vectorstudy.com/management_topics/strategy_typology.htm Source: http://www.emeraldinsight.com/journals.htm?articleid=1411048&show=html Bad strategy • It fails to define the problem; • It is based on weak or fussy objectives; • It is mostly fluff. Good strategy • Diagnosis; • A guiding policy; • Coherent action steps. Environment Culture Organizational structure and design Size / life cycle Strategy Technology Definition Effectiveness degree to which an organization realizes its multiple goals. Efficiency the amount of resources used to produce outputs. Overall effectiveness is difficult to measure in organizations. 4 approaches to the measurement of organization effectiveness Goal approach Resource-based approach Internal approach Strategic constituents approach Exhibit 3.9 Strategic Constituents Approach Employees Owners Government Customers Suppliers Community Creditors Resource Input Organization Internal Activities & Processes Product and Service Outputs Resource-based Internal Process Goal Approach Approach Approach Consists of identifying an organization’s output goals and assessing how well the organizations has attained those goals. Activities the organization is really performing. E.g. output, profit, or client satisfaction Indicators – operative goals – easy to measure Evaluates the ability of the organization to obtain valued resources from the environment. Indicators bargaining position, ability to correctly interpret properties of the environment, ability to use resources to achieve superior performance, ability to respond to environmental changes. An evaluation of human resources and their effectiveness is important. internal organizational health and efficiency Indicators Positive corporate culture and work climate Confident between employees and management Operational efficiency Communication Growth and development of employees Coordination among organization’s parts measures efficiency by focusing on satisfaction of key stakeholders. e.g. owners, employees, customers, creditors, community, suppliers, government Indicators - Criteria of constituents groups Usefulness - Constituencies have powerful influence on the organization, and it has to respond to demands Developed by R. Quinn and J. Rohrbaugh Tries to balance a concern with various parts of the organization rather than focusing one part. Combines several indicators into a single framework. NASA example – different viewpoints Competing values model Exhibit 3.10 Case study: Horizon Business concept/strategy Core competencies Customers Competitors Future perspective John Lu founded Horizon Yacht in 1987 Horizon has endeavored to create and build yachts that embody each client’s dreams. Integrated Company Structure. Horizon Group Management Center functions by supervising the Horizon Group network: delivery center; mold center; human resources center; marketing center and IT center. Source: Horizon Company’s official presentation materials Taiwan Australia China Europe Greece/Cyprus Hong Kong Japan New Zealand Russia Singapore South Korea Turkey United States Source: Horizon Company’s official presentation materials Advanced Technology Sophisticated Craftsmanship Extraordinary Design Excellent Engineering Quality Assurance State-of-the-art Facilities 2006 Awarded “Best Asian Super Yacht” Award and “Best Asian Yacht Builder” Award at the Christofle Asia Boating Awards 2006 2007 Awarded “Best Asian Yacht Builder (under 100 feet)” by Christofle Asia Boating Awards 2007 2007 Won the “2007 Taiwan Superior Brand” competition 2010 Horizon E88 motoryacht and SC46 solar power boat won the “Taiwan Excellence 2010” Awards 2011 Awarded “Best Asian Motor Yacht Builder ( 81 feet and up)” by Asia Boating Awards 2012 Awarded “Best Asian Yacht Builder (15-30 meter)” by Asia Boating Awards Source: Horizon Company’s official presentation materials Main competitors Top 20 Builders 2012 Rank Company Total (m) Total (ft) Projects Avg. (ft) 1 Azimut-Benetti (Italy) 2,640 8,661 75 115 2 Ferretti Group (Italy) 2,427 7,961 76 105 3 Sanlorenzo (Italy) 1,413 4,635 42 110 4 Lürssen (Germany) 753 2,471 7 353 5 Sunseeker (UK) 649 2,127 21 101 6 Feadship (Netherlands) 567 1,860 8 233 7 Westport (USA) 548 1,798 16 112 8 Heesen Yachts (Netherlands) 535 1,754 11 159 9 Horizon (Taiwan) 519 1,704 17 100 10 Amels (Netherlands) 495 1,625 8 203 11 Fipa Group (Italy) 482 1,581 15 105 12 Overmarine (Italy) 461 1,512 13 116 13 Trinity Yachts (USA) 432 1,417 8 177 14 Perini Navi Group (Italy) 426 1,398 8 175 15 Princess Yachts (UK) 378 1,239 13 95 16 Palmer Johnson (USA) 303 993 5 199 17 Christensen (USA) 259 848 6 141 18 Proteksan-Turquoise (Turkey) 257 843 4 211 19 Kha Shing (Taiwan) 240 787 8 98 20 Dream Ship Victory (Turkey) 238 781 3 260 Dedicated to customer satisfaction. Horizon strives to improve and advance upon every aspect of the boat building process. Horizon also invests in the future, developing new models and series (focus on environmental friendly designs). Perception of environment unstable Prospector Horizon efficiency innovation Defender stable Underlying values Dimensions Horizon’s reality Stable market • Ability of customization within smooth production process. •Yachts of average 100 ft. on European (40%) and Australian (26%) markets. New market •Risk diversification, creating more markets. •Recently, plans have been made to expand to India. •Expand into China through dealership. Emphasis on efficiency •Employment of high-quality talent. •Ability of group specialization and integration. •Strengthen services. Emphasis on innovation •CNC (Computer numerical control) milling system •SCRIMP (Seemann’s Composites Resin Infusion Molding Process) for producing one -piece yacht hull (longest in the world in 2006). •Yachts equipped with solar-power panels . The competitive advantage of Horizon is customization. stability and equilibrium. Growth and resource acquisition Productivity, efficiency Invests in the future, integrated enterprises to Horizon Group Co. - Open Systems Model Improve process, developed internal communication - Internal Process Model STRUCTURE FLEXIBILITY F O C U S Human Relations Emphasis INTERNAL Horizon Yachts Internal Process Emphasis CONTROL Open Systems Emphasis EXTERNAL Rational Goal Emphasis Internal Process Emphasis Horizon Group Horizon Yachts Since: 1987 Employees:340 Atech Composites Since: 2000 Employees: 250 CNC Mold Workshop Since: 2005 VISION Yachts Since: 2001 Employees: 250 PRIMIER Yachts Since: 2003 Employees: 110 Horizon Furniture Since: 2000 4 Yacht Factories Total employees: 1000 Open Systems Emphasis Customers Customer Service Center Marketing Center Yachts Manufacture Factories Market information Fast service Orders /Need joint marketing Horizon Group Professional Task Force Center Think tank Purchasing Dep. Information Technology Center R&D Financial Dep. Suppliers Knowledge Management Center Human Resource Center United Delivery Center US. → Europe Market OEM → OBM 80~110ft → 120 ft Customize (High Value add) Differentiation Ex. BMW motor MIT = Made in Taiwan Manufactory base – High Quality Relatively low cost ( vs. Italy) Low Cost Competitive Advantage External Environment - Decline of US market - OEM limitation - 120ft Yacht CEO Top management Internal Situation - Weak of Design - No brand image - Low Cost & High Quality Strategic Intent - Branding - EU market - Customize - Risk diversification Organization Design -Efficiency but Flexible Effectiveness Outcomes - Top 10 Brand