NoS – Lesson Powerpoint
advertisement

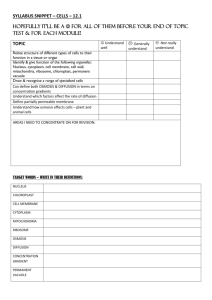
Today’s Class Review of Chapter 8.1 Membrane Properties (small quiz). Lab: Transport across a semi-permeable membrane Passive transport: OSMOSIS Lab Conclusion: Observation and results 8.2 Transfer Across Cell Membranes 1 Molecules crossing the cell membrane are distinquished by 3 things? 2 All matter is in a constant state of motion. The amount (rate) of motion is dependent on? 3 Motion of particles results in a net movement toward areas of lower concentration of those particles. The difference in concentration between two areas is called a? Diffusion Lab: 8.2 – part A This lab will reinforce what we have learned about passive transport across semi-permeable membranes Please work in bench groups of 4 Please practice SAFE LAB PROCEDURES! Each student must hand in a description and explanation of any movement you observed. The description may be in the form of a data table. 3 Diffusion Lab: 8.2 – part A Purpose: To investigate diffusion (Passive Transport) across a semi-permeable membrane. Materials: Rubber gloves, safety goggles, lab apron, 500ml beaker, tap water (300ml), 1 10cm dialysis tube, 2 elastics, paper towels, starch solution, plastic spoon, iodine solution (Lugol’s). 4 Procedure: 1. One person from each group will gather the materials. Carry the materials in a safe manner. 2. Pour 300ml of lukewarm tap water into the 500ml beaker. 3. Submerge the 10cm dialysis tube into the water for 1-2 minutes. Remove the tube and constrict one end of the tube using an elastic. 4. Add a few drops of the iodine solution to the beaker of water so the colour of the water is pale yellow. 5. Open the other end of the tube by rolling it between your fingers. Using the plastic spoon, gently scope the starch solution into the tube until it is ¾ full. 5 Procedure: 6. Constrict this end of the tube using an another elastic 7. Wash the sealed tube off under gently running lukewarm water. Pat dry the tube with paper towels. 8. Weigh the tube and it’s contents. Record the initial mass in your group table. 9. Submerse the tube in the beaker. Add more water if needed. Let the product sit for 25 minutes. 6 1 2 3 4 7 Data table Mass of Volume tube and of water starch in the beaker Initial Final Colour of Colour of water tube Chapter 8 Dynamic Cells http://kentsimmons.uwinnipeg.ca/cm1504/Image127.gif Passive Transport Movement of materials across membranes without the input of energy is called passive transport. There are 3 types of passive transport 1. Diffusion 2. Osmosis 3. Facilitated diffusion 1. Diffusion http://www.williamsclass.com/SeventhScienceWork/ImagesCellBricks/Diffusion.gif http://gotoknow.org/file/somluckv/Cell_membrane02.jpg Diffusion Across Membranes Molecules diffuse across cell membranes. Very small molecules can move between the phospholipid molecules from one side of the membrane to the other. Cells do not expend any energy during this process. Eg: O2 is always being used by the cell the concentration of O2 is always lower inside the cell compared to outside the cell. 2. Osmosis – Diffusion of Water Most of the molecules that fill and surround cells are water (H2O). The diffusion of water across a membrane is called osmosis. Osmosis – Diffusion of Water http://i77.photobucket.com/albums/j48/annahybrid/normal_osmosisweb.jpg Osmosis – Diffusion of Water Water molecules move from areas of high concentration of water to areas of low concentration of water across a semi-permeable membrane. Osmosis http://www.biologycorner.com/resources/osmosis.jpg Osmosis Passive Diffusion of Water If one solution has a high concentration of H2O and a low concentration of solutes relative to another solution it is called HYPOTONIC. Hypotonic http://www.williamsclass.com/SeventhScienceWork/ImagesCellBricks/hypertonic.jpg Osmosis Passive Diffusion of Water If one solution has a low concentration of H2O and a high concentration of solutes relative to another solution it is called HYPERTONIC. Hypertonic http://www.williamsclass.com/SeventhScienceWork/ImagesCellBricks/hypotonic.jpg Osmosis Passive Diffusion of Water If the concentration of water is equal on both sides of a membrane the solutions are called ISOTONIC. Isotonic http://www.williamsclass.com/SeventhScienceWork/ImagesCellBricks/isotonic.jpg Osmosis in Living Cells Maintaining water balance across the cell membrane is essential to survival. If the concentration of water outside the cell is greater than inside the cell water will flow into the cell (cells in distilled water). Water Movement A C B D http://www.kscience.co.uk/resources/ks5/as/cells/osmosis/Plasmolysis_and_recovery.jpg Osmosis in Living Cells In plant cells, the cell’s contents swell (turgid) but the cell walls keep the cell from exploding. http://leavingbio.net/OSMOSIS%20AND%20DIFFUSION_files/image021.gif Osmosis in Living Cells In animals cells, (with no cell wall) the cell will explode or rupture. http://www.wadsworth.org/chemheme/heme/cytoheme/hemepix/slide092.jpg Osmosis in Living Cells If the concentration of water outside the cell is less than inside the cell, water will flow out of the cell (cells in salt water) Osmosis in Living Cells In plant cells, the cell contents will lose water, shrivel and pull away from the cell wall (plasmolysis). In animals cells (no cell wall) the cell contents will lose water and shrivel (crenated) Crenated Red Blood Cells http://labmed.hallym.ac.kr/hematol/Hematol-Cell-Lists/crenatedrbcs.jpg Membranes at Work Water Purification Reverse osmosis Water is filtered, by pressure, through a membrane with pores that only allow water through. All substances larger than water cannot pass through These systems are used in houses where well water is too salty or larger systems can provide clean water during disasters or war. http://enr.construction.com/images2/2005/08/050815-20.jpg Membranes at Work Kidney Dialysis Blood is pumped through a synthetic semi-permeable tubing called dialysis tubing. The dialysis tubing is immersed in a saline solution similar to blood. Wastes in the blood move from the tubing into the solution by diffusion. Because the salts and water are in equilibrium with the blood, there is no loss of salts and water from the blood. http://biomed.brown.edu/Courses/BI108/BI108_2008_Groups/group04/images/ppf/girl.png Membranes at Work Controlled delivery of medication. Semi-permeable membranes deliver medications in a safe, controlled manner. Transdermal patches on the skin use a semi-permeable membranes to deliver the medication at a constant rate. This delivery method is used to deliver drugs that counter motion sickness, and nicotine to aid in stopping smoking. Artificial vesicles called Liposomes can be used to transport medicines to specific sites in our bodies. Test Questions: TRUE or FALSE? 1. The amount (rate) of motion is dependent on the nature of particles, its state (gas, solid, liquid), and temperature. 2. Movement of materials across membranes with the input of energy is called passive transport. 3. In a crenated cell the turgor may cause the cell to swell and rupture. 4. If one solution has a low concentration of H2O and a high concentration of solutes relative to another solution it is called HYPERTONIC. Water molecules move from areas of _______ concentration of water to areas of _______ concentration of water across a semi-permeable membrane to maintain a (an) ______ condition. A. High; Low; Hypertonic B. Low; High; Hypotonic C. High; Low; Isotonic D. Low; High; Isotonic Diffusion Lab: 8.2 – part B Observe the colour of the water in the beaker and the colour of the dialysis tube. Record observations on the data sheet. One student weighs the tube and another records it on the data sheet. Students to take note of any change in mass to help answer the lab questions. As a group they are to complete 3 questions on the back of the data sheet and submit at the end of the class. 38 Data table Mass of Volume tube and of water starch in the beaker Initial Final Colour of Colour of water tube Diffusion Lab: Questions As a group, answer all questions on the back of your group’s Data Sheet. Submit at the end of the class 1. Is iodine moving through the membrane osmosis or diffusion? 2. Did the water move into the dialysis tube through the membrane? How can you explain this? 3. Did the starch move out of the dialysis tube through the membrane? How can you explain this? 40 Next Class Review of Chap. 8.2 Transport Across Cell Membrane Introduction of the next lesson: Facilitated Diffusion