Ecology Worksheet: Biomes, Food Webs, and Biodiversity
advertisement
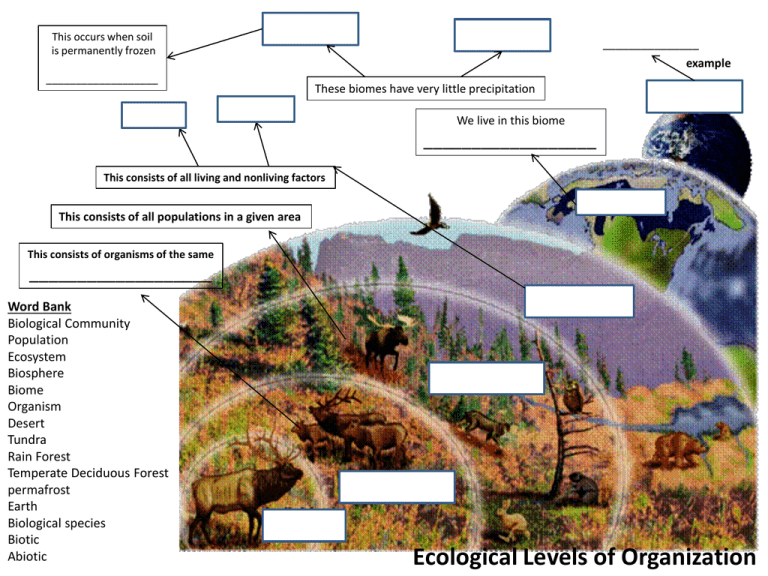
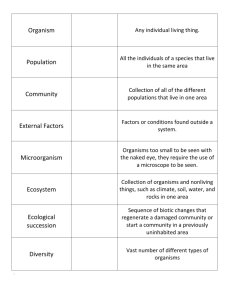
This occurs when soil is permanently frozen _______________ example ___________________ These biomes have very little precipitation We live in this biome __________________ This consists of all living and nonliving factors This consists of all populations in a given area This consists of organisms of the same ___________________ Word Bank Biological Community Population Ecosystem Biosphere Biome Organism Desert Tundra Rain Forest Temperate Deciduous Forest permafrost Earth Biological species Biotic Abiotic Ecological Levels of Organization Word Bank: Relationship Mutualism Commensalism Parasitism Host Parasite Where an organism lives Pollination ______________ Habitat Niche Examples of _______________ Both organisms benefit An organism’s job __________ One organism benefits, The other is neither harmed nor helped Symbiosis A very close ________________ Between 2 organisms One organism Benefits, The other is harmed Examples Examples Harmed Helped Food Chains show only _________ energy pathway Eats plants and other heterotrophs Eats dead things Make its own food Eats only plants Eats other heterotrophs 4 types Primary ___________ Can not make their own food using photosynthesis This is the First ____________ Word Bank: Consumer Producer Autotroph One All Trophic level Heterotroph Carnivore Omnivore Herbivore Detritivore Primary __________ Secondary ____________ 3rd Level ____________ Food Web & Food Chains Food Webs are different from food chains because Food Webs show __________ energy pathways Evaporation of water from leaves of plants Nitrogen Cycle Used to make ___________ Nitrogen gas Some Nitrogen Fixing Bacteria are __________ Can also cause Soil erosion Symbiotic relationships With plants (legumes) waste waste Water Cycle Matter Cycles Phosphorus Cycle Used to make __________ ___________ Word Bank Transpiration Run-off Nitrogen fixation Precipitation Fossil fuels Evaporation Bacteria Mutualistic Greenhouse Effect Climate Change Cellular Respiration Photosynthesis Rock Mitochondria Hereditary Material Condensation Chloroplast DNA RNA Protein Carbon Oxygen Cycle Natural Layer of CO2 Occurs here Oxygen burning Carbon Dioxide Occurs here P Use food chain to answer Energy Pyramid Is Ruled by 90% of energy Is lost as 0.1% energy Problem: If the primary producer makes 150,000 units of energy, how Many units of energy are transferred To each level? (use boxes next to pyramid) __________ At each level _________ Problem: (use above units) How many units of energy are lost As heat by the secondary consumer? ______________ Show work for 2nd Problem: Ultimate energy source for every ecosystem Numbers Pyramid There are _______ There are _______ Than Than Word Bank 10% Rule Heat Sun More Less Fewer Greater Primary producer Primary consumer Secondary consumer Tertiary consumer Biomass Pyramid The total mass of The total mass of Ecological Pyramids Is _______ than Is _______ than Population Dynamics Word Bank J-Curve S-Curve Logistic Growth Graph Exponential Growth Graph Exponential growth phase Lag phase Carrying Capacity Limiting Factors Abiotic Factors Biotic Factors Density Dependent Factors Density Independent Factors Drought Disease Food availability Tsunami Realistic Examples Shape of the curve This type of growth Curve is not _____________ These are considered Which can be non-living Because they are not dependent On the # of organisms in the area Determined By Which can be living Shape of the curve These are considered Because they are dependent On the # of organisms in the area Examples Ecological Succession Word Bank: Primary Secondary Soil Rock Volcanic Eruption Glacier Melt Forest Fire Clearing of Land Pioneer Species Lichen Caused by: Caused by: 2 Types First organisms to get established Example Variety of Species Excessive use due to high economic value ___________ Threats to Biodiversity Permanent loss of a species ____________ Variety of Genes __________ Variety of Life Run-off of chemicals, fertilizers, sewage into water ___________ Biodiversity & Conservation increasing concentration of toxic substances a measure of human demand on the Earth‘s ecosystems _________________ Disease resistant crops Economy Importance of Biodiversity Extracts used to make Healthy _______ Word Bank: Biodiversity Extinction Biosphere Genetic diversity Species diversity Overexploitation Pollution Biological Magnification Acid Precipitation Eutrophication Introduced Species Renewable Nonrenewable Drugs (medications) Ecological Footprint Transgenic Organisms Rain with a pH below 7 Loss of Natural Resources Clean Air & Water Fossil Fuels & Mineral Deposits