Vacuole
advertisement

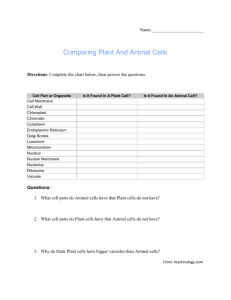
Vacuole By Kurt Smetana Period 2 Types of Vacuoles • Food Vacuoles - formed by phagocytosis • Tractile Vacuoles - pumps excess water out of the cell. • Central Vacuoles - enclosed by a membrane called tonoplast. Functions of Vacuoles • Place to store organic compounds, such as proteins stockpiled in vacuoles of storage cells in seeds. • Plant cell’s main repository of inorganic ions, such as potassium and chloride. • Functions as plant cell’s lysosomal compartment • Disposal sites for metabolic by-products that would be dangerous in cytoplasm More Functions • Help protect the plant against predators because they contains poisonous or unpalatable compounds. • Elongates to absorb water, allowing the plant cell to become larger with a minimal investment in new cytoplasm. Creation of Vacuoles • Developed by coalescence of smaller vacuoles. • These are derived from the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus. Other Important Facts • Is an integral part of the endomembrane system. • Only appears in plant cells. • Some are enriched in pigments that color the cells. • Like vesicles, Vacuoles are membraneenclosed sacs within the cell. Questions • What is the name of the membrane that is around a central vacuole? A. Tonoplast B. Endoplasmic Recticulum C. Golgi Apparatus • Vacuoles are found in… A. The interior of animal cells B. The interior of plant cells C. The cells inside a cow’s intestine Questions • The three types of Vacuoles are… A. Food, Tractile, Phagocytosis B. Tractile, Central, Organic C. Food, Tractile, Central THE END.