File
advertisement

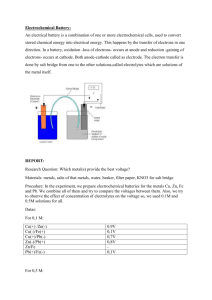
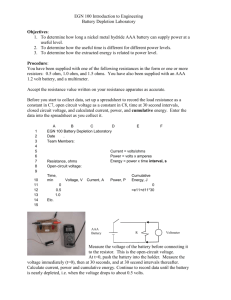
Ch. 8: Ohm’s Law Current, Voltage & Resistance 8.1 Electric Potential Energy & Voltage • Electric potential Energy increases when unlike charges move further apart • Electric potential difference (voltage) is the change in electric potential energy per coulomb of charge • Voltage is measured in volts (V) • Electrical energy depends on the amount of charge and voltage • Electrochemical cells (batteries) are a common source of voltage • Voltmeters measure potential difference (voltage) Battery An electrochemical cell Electrochemical cell Converts stored chemical energy into electrical energy Battery Terminals Positive or Negative End points where a connection can be made Battery Terminals Electrochemical cells/Batteries • have separate positive and negative charges • the negative terminal has excess electrons • the positive terminal has less electrons Typical household battery (C, D, AA & AAA) • potential difference of 1.5 Volts (V) Wall sockets • potential difference of 120 to 230 Volts (V) Voltaic Pile Invented the first battery in 1799 Alessandro Volta The Volt (V) was named in his honour Kinetic & Potential Energy Energy • The ability to do work Kinetic Energy • Energy a moving object has because of its motion Potential Energy • energy stored in an object Electric Potential Energy • Potential Energy: energy stored in an object • Electric Potential Energy: Electrical energy stored in a battery Potential Energy & Potential Difference The potential energy in a battery is due to … 1. The amount of charge that has been separated (coulombs) 2. The potential difference/voltage (volts) The potential energy in a battery is due to … 1. The amount of charge that has been separated (coulombs) 2. The potential difference/voltage (volts) 1. The amount of Charge that has been separated (Coulombs) • Electrochemical cells (batteries) separate positive & negative charges • The greater the difference, the greater the amount of charge (Coulombs) in this battery The potential energy in a battery is due to … 1. The amount of charge that has been separated (coulombs) 2. The potential difference/voltage (volts) 2. Potential Difference (Voltage) The pushing force of water (electricity) is due to the …height difference (potential difference/Voltage) Voltage - like a “pushing force” of electricity - measured in volts (V) Which has greater potential difference (voltage)? Electric Potential Energy & Electric Potential Difference The potential difference (voltage) in a battery is like… the height of the stairs The amount of potential energy (charge/Coulombs) separated in a battery is like… the mass moved up the stairs If this person were to fall from top of the stairs, in A or B, the potential difference (height) is the same However, there’s more potential energy in B than in A because more mass (charge/Coulombs) have been separated A B The Voltmeter Measures Electric Potential Difference Voltmeters are a device that measures the amount of potential difference between 2 locations of charge separation In this image, The battery’s voltage is measured Volt (V) is the unit for measuring voltage Batteries: Wet Cells or Dry Cells Electrolyte: Substance that conducts electricity Dry cell – moist paste Wet cell – battery solution Producing Voltage Electrodes • the 2 terminals of a battery • 2 different metals (usually) Electrolyte • Substance that conducts electricity • Acid, base or salt In Figure 8.6 the acidic electrolyte… • pulls atoms off the Zinc and leaves electrons on electrode • pulls electrons off the Copper electrode Sources of Electrical Energy 1. Friction 2. Piezoelectric Crystals 3. Photo-electrochemical cells 4. Thermocouples 5. Generators