Week 3
advertisement

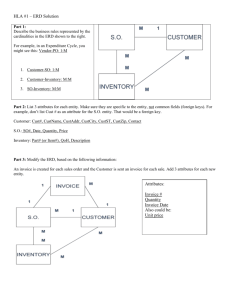
Database Design Sections 4 & 5 Subtype, Supertype, Mutually exclusive, non-transferability, transferable, 1:1, 1:M, M:M, Redundant, Intersection entity, Barred relationship, CRUD analysis 1 DJs on Demand – Partial ERD 2 Reserved Words A reserved work is one that has a specific meaning and function in the computer system, language, or database. Examples: NULL DATE DISTINCT 3 Video Store – example next slide Identify business rules Construct ERD Class activity 4 Video Store example Read the given business scenario and walk through the steps below. 1. Examine the nouns. Are they things of significance? 2. Name each entity. 3. Is there information of interest about the entity that the business needs to hold? 4. Is each instance of the entity uniquely identifiable? Which attribute or attributes could serve as its UID? 5. Write a description of the entity. 6. Diagram each entity and a few of its attributes. Remember, entity names are always singular. 7. Identify the relationships and draw them on the ERD. 5 Video ERD •TAPE/DVD a copy of number format on MOVIE id title category the feature of rented by the renter of CUSTOMER membership number last name first name phone number featured in ACTOR stage name real name 6 Use Source Documents Source document assist in identifying entities, attributes, and relationships 7 Subtype A subtype: inherits all attributes of the supertype inherits all relationships of the supertype usually has its own attributes or relationships is drawn within the supertype never exists alone may have subtypes of its own is also known as a "subentity“ 8 Subtype & Supertype Supertype (entity) can be subdivided into Subtypes Example: JOB manager clerk sales support 9 Attributes Supertype can have attributes at supertype level Attributes at supertype level are for all subtypes Subtypes can have own attributes for only that attribute 10 Example EXAM takes STUDENT taken by #number *description *weight *date *grade for written component MIDTERM *grade for BONUS QUESTIONS oral presentation FINAL included in *extra pts for opt. paper QUIZ include 11 Global Fast Food Employees STAFF is an entity with supertypes What are the attributes of STAFF? #id *first name *last name *DOB *salary What subtypes exist in STAFF? ORDER TAKER *overtime COOK *training OTHER Are there any attributes in any of the subtypes? 12 Example: an incorrect subtypes in the illustration. AUTOMOBILE subtypes are not mutually exclusive AUTOMOBILE possible solution BUILDING subtypes have problem of not being exhaustive, should be minimum of 2 types 13 Subtype Needs Exhaustive: Every instance of the supertype is also an instance of one of the subtypes. Treating all parts or aspects without omissions. 2 or more items Mutually exclusive: Every instance of the supertype is of one and only one subtype. A relationship that presents choices which are unable to be true at the same time. 14 Correctly identify subtypes When considering supertypes and subtypes, you can use three questions to see if the subtype is correctly identified: 1. Is this subtype a kind of supertype? 2. Have I covered all possible cases? (exhaustive) 3. Does the example fit into one and only one subtype? (mutually exclusive) 15 Nested subtypes 16 Documenting Business Rules Source documents assist in identiying: entities attributes relationships Some business rules are “implemented by programming” 17 Business Rules Recognize if Business rule is implemented by the data model or by programming Example: Only an employee with a title of manager can manage other employees The event planner must contact the customer before the DJ can be assigned Business rules can be changed as society changes or business leaders feel change is needed 18 Business rule types Structural Must be entered at time of initial data entry Example: When ORDER entered a staff id must be entered Does not require code written to enforce Procedural Work flow related Programmed validation is procedural constraint Generally need to write code Example: Commission can not be > 25% of salary 19 Structural Business Rule examples: 20 Procedural Business Rule example: 21 Discussion Students must have studied algebra and geometry in order to sign up for trigonometry. Could you represent this in the ERD? • How would you implement this with programming? • If the student had taken the subjects, can you think of an additional business rule that a school may want in this scenario? 22 Each entity has Name Optionality Cardinality Transferability Example on next slide. 23 Relationship Transferability 24 Relationship transferability Rules established for the purpose such as safety, efficiency, or increased profit Example: Airline tickets can be transferable or non-transferable? Non-transferable means also not updatable symbol used to denote nontransferable blood type is non-transferable 25 Non-transferable relationship place CUSTOMER ORDER placed by Orders are non-transferable Resolution would be to cancel order and create new order 26 Example 5.1 exercise 1 a Each town may be the birthplace of many people. Each person must be born in one and only one town. birthplace for PERSON TOWN born in 27 Relationship types One to One (1:1) One to Many (1:M) Many to Many (M:M) 28 One to One relationship 29 One to One relationship Usually few of these relationships Often mandatory at one side If mandatory at both ends be aware, it might be a error. Possible should be only one entity not two ride PERSON ridden by BYCYCLE 30 One to One relationship 31 One to Many relationship 32 One to Many Most common type are mandatory on one side and optional on the other Mandatory at both ends models entities that cannot exist without each other ORDER TYPE ORDER 33 One to Many example TAX RETURN composed of entered in BAND composed of TAX REPORT LINE MUSICIAN belong to 34 Many to Many relationship 35 Many to Many Often common in initial version of ERD Later stage of design converted to other type learn from TEACHER STUDENT educate 36 Redundant relationship Redundant relationship is one that can be derived from another relationship in the model 37 Many to Many Relationship Resolution All M:M relationships must be changed to a set of 1:M and M:1 relationship Insert a transition entity between Occurs when you go from conceptual model to design model 38 Example: M:M with Intersection Entity COURSE STUDENT REGISTRATION 39 Resolving M:M with Intersection Create an intersection entity If you can’t find a good intersection entity create one by concatenate two entities together 40 Example EVENT PARTNER WORK ASSIGNMENT (PARTNER_EVENT) 41 CRUD analysis Create ER models that reflect all business rules gathered during the interview process Identify the create, retrieve, update, and delete (CRUD) requirements of the business Validate your ER model by performing a CRUD analysis 42 CRUD requirements CRUD analysis will help you: Translate between the consultant and the client. Provide a guideline for the DBA who will eventually build the database. Check that you haven’t missed any entities or relationships in your data model. Check to make sure that you haven’t modeled anything that the business does not require. 43 What is CRUD? CRUD is an acronym for create, retrieve, update, delete. Check for completeness and accuracy. 44 Create keywords Look for these words when you interview the client. INPUT ENTER LOAD IMPORT RECORD CREATE 45 Retrieve keywords Look for: VIEW REPORT BRING UP PRINT FIND READ LOOK UP 46 Update keywords Look for: CHANGE MODIFY ALTER UPDATE 47 Delete keywords Look for: DISCARD REMOVE TRASH PURGE DELETE 48 CRUD analysis If you have a business function that has no entity to CRUD against, then your data model may be incomplete. Similarly, if you have entities in your ERD that are not touched by any CRUD (there is no business function that creates, retrieves, updates, or deletes from it), then you may not need that entity in your model. 49