Chapter Two
The Evolution of
Business
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Introduction to Business
© 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., All Rights Reserved.
Division of Labor in a Tribe
Figure 2.1
2-3
The Emergence of the Hierarchy
• Hierarchy of authority
- the ranking of people according to their
relative rights and responsibilities to control
and utilize resources
2-4
Hierarchy and Property Rights
• Property rights
- the right of people to own, use, or sell
valuable resources
• Aristocracy
- people given the right by a ruler to control a
country’s resources, including its land and
labor
2-5
The Hierarchy of English
Aristocrats
Figure 2.3
2-6
Feudalism
• Feudalism
- the business or economic system in which
one class of people, aristocrats, controls
the property rights to all valuable
resources, including people
2-7
Feudalism, Mercantilism, and
Capitalism
Figure 2.4
2-8
From Barter to Money
• Double coincidence of wants
- each person has to want the product that
the other person has to offer for the
exchange to be successful
• When people agree to use money to buy
and sell products it increases the
profitability of trade
2-9
Money as a Standard of Value
Figure 2.5
2 - 10
From Money to Capital
• Interest rate
- the price at which capital will be loaned
• Risk
- the possibility of incurring future financial
losses because of one’s investment
decisions
See current interest rates at
money-rates.com
2 - 11
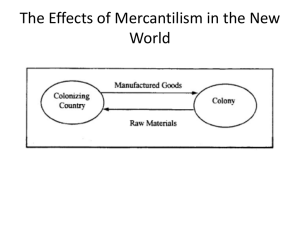
Mercantilism: Trade and Enterprise
• Mercantilism
- the business system in which a product’s
price differences are exploited by trading
the product across markets and countries
2 - 12
Feudalism, Mercantilism, and
Capitalism
Figure 2.4
2 - 13
The Growth of Enterprise
• Merchant
- a trader who uses the discrepancy between
the value and price of a product in one
market and another to trade goods for profit
• Bankers
- the people who estimate the risks
associated with a new venture and
determine the way profits from a venture
should be shared
2 - 14
Craft Guilds and Occupational
Specialization
• Craftspeople
- workers or artisans with the skills to
produce higher-quality goods and services
• Craft guild
- a group of skilled artisans organized to
control and govern different aspects of its
trade
2 - 15
The Industrial Revolution
• Industrial Revolution
- an era in the 18th and 19th centuries that
marked improved production and trade
brought about by advances in technology
2 - 16
Capitalism, Unionization, and the
Modern Class System
• Capitalism
- the economic or business system in which
the private ownership of resources
becomes the basis
for the production
and distribution of
goods and services
2 - 17
Feudalism, Mercantilism, and
Capitalism
Figure 2.4
2 - 18
Capitalism, Unionization, and the
Modern Class System
• Capitalists
- people who personally own or control the
physical capital of industrial production
such as machinery, factories, distribution
networks, raw materials, and technology
2 - 19
Capitalism, Unionization, and the
Modern Class System
• Proletariat
- the class of unskilled workers who have no
capital and only possess the rights to sell
their own labor
• Trade union
- an organization that lobbies on behalf of its
members (workers) to increase their
bargaining power in work-related
negotiations
2 - 20
Capitalism, Unionization, and the
Modern Class System
• Class system
- a social ranking of people based upon the
amount of their capital and wealth, and
because of factors such as heredity,
kinship, fame, and occupation
2 - 21
The Class System in Capitalism
Figure 2.6
2 - 22
Changing Forms of Business
Organization
Figure 2.7
2 - 23
The Partnership and Sole
Proprietorship
• Partnership
- two or more skilled professionals who
agree to pool their talents and capital to
establish a company in which they are the
stockholders and owners
• Sole proprietorship
- a non-incorporated business entirely owned
by one person
2 - 24