narrative - Brianair
advertisement

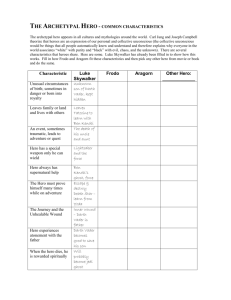
NARRATIVE Film and Media Studies What is Narrative? Latin –NARRE- To make Known Via • Causally related events • Connected • Sequenced • Logically presented Definition 2 “Narrative is a way of organising spatial and temporal data into a cause and effect chain of events with a beginning, middle and end that embodies a judgement about the nature of the events as well as demonstrates how it is possible to know, and hence to narrate, the events. “ Brannigan E. Narrative Comprehension and Film Macro Features of Narrative Structure • • • • Aristotle’s beginning, middle and end. Todorov’s equilibrium>disequilibrium>re-equilibrium Propp’s “functions” Vogler’s “twelve steps” 2. Temporal order,temporal duration, temporal frequency 3. Story and Plot • • • Explicitly presented actions/events Implicitly inferred ationas/events Non diegetic material (captions/titles,drama enhancing music etc.) Micro Features 1. Constructional Devices Cinematography Mise- en- Scene Editing Sound 2. Genre Associations Genre Codes (e.g. Iconography) Genre Conventions 3. Narrative Codes Levi Straus’s Binary Oppositions Barthes Narrative Codes Character Psychology Semiotic Analysis Todorov Initial Situation (Equilibrium) Disruption (Non equilibrium) Restoration (Re Equilibrium) Propp 1928 Morphology of the Russian Folktale 1928 Types of Characters, Specific Forms of Action, function in the Narrative. Thiry One Functions identified. Specific research on narrative • Vladimir Propp • Russian Formalist in the 1930s • He wanted to see if there was a finite number of structures for narrative. He analysied Russian folk tales and found they could be classified into 5 categories. • He also identified seven archetypal characters. Propp’s character archetypes The The The The The The The Villain Donor/giver of knowledge Helper Princess (sought after person) Dispatcher Hero (or victim) False Hero Propp’s character archetypes The The The The The The The Villain Darth Vader Donor Helper Princess (sought after person) Dispatcher Hero (or victim) False Hero Propp’s character archetypes The The The The The The The Villain Darth Vader Donor Obi Won Kenobe Helper Princess Dispatcher Hero (or victim) False Hero Propp’s character archetypes The The The The The The The Villain Darth Vader Donor Obi Won Kenobe Helper Han Solo Princess Dispatcher Hero (or victim) False Hero Propp’s character archetypes The The The The The The The Villain Darth Vader Donor Obi Won Kenobe Helper Han Solo Princess Princess Leah Dispatcher Hero (or victim) False Hero Propp’s character archetypes The The The The The The The Villain Darth Vader Donor Obi Won Kenobe Helper Han Solo Princess Princess Leah Dispatcher R2 - D2 Hero False Hero Propp’s character archetypes The The The The The The The Villain Darth Vader Donor Obi Won Kenobe Helper Han Solo Princess Princess Leah Dispatcher R2 - D2 Hero Luke Skywalker False Hero Propp’s character archetypes The Villain Darth Vader The Donor Obi Won Kenobe The Helper Han Solo The Princess Princess Leah The Dispatcher R2 - D2 The Hero Luke Skywalker The False Hero Darth Vader (Luke’s dad) Basic Plots Romance: Boy meets girl / boy loses girl / boy finds girl(or Vice versa) Bordwell and Thompson (1991) define narrative as “A chain of events in cause-effect relationship occurring in time and space. The Kuleshov Effect: The linear connections we make between shots. Definitions from Bordwell and Thompson (1991) Plot: What we see on screen. Includes extra-narrative things. Story: all that we know about the narrative including seen and unseen. Diegesis: The total world of the story. Parallelism: Parallel development of multiple storylines. Cause and effect: Cause and effect. Causes can come from a character. Chris Vogler 1992 The Writers Journey Archetypes • • • • • • • • Hero Mentor Shapeshifter Trickster Herald Allies Shadow Threshold Guardians The Hero’s Journey • • • • • • • • • • • • Ordinary World Call to Adventure Refusal of the Call Mentor First Threshold Tests, Allies, Enemies Approach to the Inmost Cave Ordeal Reward (seizing the sword) The Road Back Resurrection Return with the Elixir Levi Strauss Binary Opposites (Macro) • Protagonist/Antagonist • Action /Inaction Binary Opposites (Micro) • Good looking / Ugly • Witty / Humourless Barthes Audience Decodes • Enigma Code (sets up a question to be answered later) • Semic Code (How characters, actions ,events, settings etc. take on meaning within a culture. • Symbolic Code - Binary Oppositions or Psychological symbols • Action Code - understood by cross reference to other narratives in our culture • Cultural Codes - understood through our interaction with the wider world.