Microprocessors Systems: Solutions manual to selected exercises
advertisement

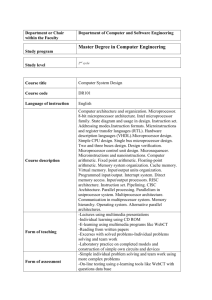
Microprocessors Systems: Solutions manual to selected exercises Mile Stojcev, Tatjana Stankovic 2075 Microprocessor systems Directions: - Electronics, - Communications, - Microelectronics VII semester 2+2+1 VIII semester 2+2+1 2075 Microprocessor systems There are probably almost as many different curricula and syllabi for microprocessor system design as there are schools and instructors in which the subject is taught. The proposed course is suitable for an introduction on microprocessor system design at the junior or senior level, or at an advanced sophomore level. 2075 Microprocessor systems Goal of the course: Microprocessor systems are extremely complex systems consisting of many components whose operation depends on many factors. In order to understand microprocessor systems it is essential that a student should be exposed to the concept of levels in computer architecture. It allows them to see how various parts of the microprocessor system fit into one whole. At the beginning of the course the concept of levels are presented to students. 2075 Microprocessor systems Goal of the course (continued): The students then have a context in which to place various topics as they progress through the course. The course attempts to provide a balanced view of all important elements of microprocessor system design. It is organized so that all the relevant topics are covered at some medium essential level of detail. Additional material is provided to students, in order to overcome certain topics in greater depth. 2075 Microprocessor systems Needed prerequisites: On assume that the student had at least an introductory course in some: High-level programming language such as C, Java, or Pascal, One/two semesters of digital logic design. Many students who have taken a course in digital logic design need to renovate the knowledge concerning synthesis of: FSMs, PLDs (CPLDs & FPGAs), and VHDL as a tool for designing, implementing, and testing complex systems. 2075 Microprocessor systems Organization: We have organized a course so that all relevant topics are covered in two semesters with a fund of 2+2+1. The complete course is composed of: a) 60 classes of teaching; 30 classes per semester, two classes per week b) 60 classes of oral exercises and working in projects; 30 classes per semester, two classes per week c) 30 classes of lab exercises; 15 classes per semester, one class per week. 2075 Microprocessor systems Required course material: 1) RISC, CISC and DSP processors Faculty of Electronic Engineering Nis, 1997. Mile Stojcev 2) Architectures and Programming of Microcomputer Systems Based on IA32 Faculty of Electronic Engineering Nis, 2000. Mile Stojcev, Branislav Petrovic 3) Solution Manual to accompany Microprocessor and Microcomputer Faculty of Electronic Engineering Nis, 1999. Mile Stojcev, Sasa Ristic, Milos Krstic 4) Microprocessors Systems: Solutions manual to selected exercises Faculty of Electronic Engineering Nis, 2003. Mile Stojcev, Tatjana Stankovic 2075 Microprocessor systems Evolution of microprocessor systems: - Earlier generations of microprocessors had almost trivial internal structure. - Present designs contain multiple pipelined functional unit with support for multiple processor and memories. 2075 Microprocessor systems Evolution of microprocessor systems (continued): The appropriate topics for such a course have changed considerably in recent years. The topics of: - pipelined processor design, - the memory hierarchy, and - networks are moving to the center stage in the arena of microprocessor system design. 2075 Microprocessor systems Main topics: Quantitative performance evaluations at both the component and system level, where: - total time to execute a program, - silicon area, - or other hardware/software tradeoffs are considered as dominant performance measures. 2075 Microprocessor systems Main topics (continued): Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) of a microprocessor is involved. The tasks that microprocessor performs are determined. Instructions, internal registers, and other ISA components are specified. 2075 Microprocessor systems Main topics (continued): Register-Transfer-Level (RTL) treatment of the implementation of instruction fetching and execution in a processor is considered. This is followed by a discussion of processor implementation by both hardwired and microprogrammed approaches. 2075 Microprocessor systems Main topics (continued): Memory system is treated. Caches and multiple module memory systems are explained as ways for increasing main memory bandwidth. Caches are discussed in some details including performance modeling. Virtual memory systems and memory management are also presented. 2075 Microprocessor systems Main topics (continued): A detailed coverage of the use of pipelining in the design of high-performance microprocessors is presented. The role of the compiler and the relationship between pipelined execution and instruction set design are explored. 2075 Microprocessor systems Main topics (continued): Instruction-Level-Parallelism (ILP) is considered. The basics of superscalar and VLIW instruction processing by the utilization of multiple functional units are also treated. 2075 Microprocessor systems Main topics (continued): Input/Output organization is considered. The basics of I/O data transfer synchronization are presented. Interrupts and direct-memory access methods are explained, including a discussion of the role of software interrupts in operating systems. Bus protocols and standards are also presented. 2075 Microprocessor systems Main topics (continued): Communication cover network architectures, focusing on: - modems, - local area networks (LANs), - wide area networks (WANs). The emphasis is primarily on network architecture, with accessible discussions of protocols that spotlight key feature of network architecture. 2075 Microprocessor systems Microprocessors Systems: Solutions manual to selected exercises contains 371 plus VII text pages of the B5 format, prepared on PC machine intended for printing. Structure: The book is divided into four Chapters, section Bibliography with 46 cited references, and one Appendix. 2075 Microprocessor systems Microprocessors Systems: Solutions manual to selected exercises Chapter 1 – Written part of the exam tests Exam exercises in the time period from January ’99 until June ’03 are presented. In total there are: - 40 examination periods - 160 solved problems on 150 pages, including 52 pictures and number of tables and short program sequences. 2075 Microprocessor systems Microprocessors Systems: Solutions manual to selected exercises Written part of the exam tests – Layout 2075 Microprocessor systems Microprocessors Systems: Solutions manual to selected exercises Written part of the exam tests - Layout (cont.) 2075 Microprocessor systems Microprocessors Systems: Solutions manual to selected exercises - Written part of the exam tests - Layout (cont.) 2075 Microprocessor systems Microprocessors Systems: Solutions manual to selected exercises - Written part of the exam tests - Layout (cont.) 2075 Microprocessor systems Microprocessors Systems: Solutions manual to selected exercises - Written part of the exam tests - Layout (cont.) 2075 Microprocessor systems Microprocessors Systems: Solutions manual to selected exercises Written part of the exam tests – Criteria for evaluation - Each exam consists of four problems. - All problems are pointed equally. - Maximal number of points 100. - Minimal number of points to pass the written part of the exam test is 50 points. - Criteria for pointing problems: - correct answer 25 points - correct answer but error in computing/program presentation 20 points - correct idea and concept well defined, only, 15 points - correct idea but non optimal hardware-software solution 10 points - correct idea but badly documented 5 points. 2075 Microprocessor systems Microprocessors Systems: Solutions manual to selected exercises Chapter 2 – Selected problem Collection of distinctive problems from the field of computer architecture and organization. Hot topics refer to RISC processors, pipelining, superscalar, VLIW concepts, ILP cash memory, etc. In total there are: - 76 pages - 107 problems illustrated by 41 figures, a great number of tables and short program sequences. The aim of the presented problems, is to, in an indirect way, bring closer and explain contemporary concepts of processing instructions. 2075 Microprocessor systems Microprocessors Systems: Solutions manual to selected exercises Chapter 2 – Selected problem - Typical problem 2075 Microprocessor systems Microprocessors Systems: Solutions manual to selected exercises Chapter 2 – Selected problem - Typical problem – (cont.) 2075 Microprocessor systems Microprocessors Systems: Solutions manual to selected exercises Chapter 2 – Selected problem - Typical problem 2075 Microprocessor systems Microprocessors Systems: Solutions manual to selected exercises Chapter 2 – Selected problem - Typical problem (solution) 2075 Microprocessor systems Microprocessors Systems: Solutions manual to selected exercises Chapter 3 – Oral part of the exam - 16 sets of questions - totally 150 questions, presented on 14 pages - the writing part consists of 10 questions selected from different topics - criteria for evaluation - a correct answer to the question ……….. 1 point - incomplete correct answer ………………. 0.7 point - presentation of the main idea …………… 0.5 point - partially correct answer ………………….. 0.3 point - no answer ………………………………… -0.3 point - incorrect answer …………………………. -0.5 point - maximal number of points ……………… 10 points - minimal number of points for pass ……… 5 points - final number of points is determined as arithmetic means of the written and oral parts of the exam. 2075 Microprocessor systems Microprocessors Systems: Solutions manual to selected exercises Chapter 3 - Oral part of the exam - Layout of a typical set 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) Describes the differences between a trap instruction and a subroutine call. Concerning disc, define the terms seek time, rotational delay, access time, and transfer time. What is the difference between DRAM and SRAM in terms of characteristic such as speed, size, and cost? What is the distinction between spatial locality and temporal locality? What are the typical elements of a machine instruction? 2075 Microprocessor systems Microprocessors Systems: Solutions manual to selected exercises Chapter 3 - Oral part of the exam - Layout of a typical set (cont.) 6) What is the distinction between instruction level parallelism and machine parallelism? 7) What is the difference between a hardware pipeline and a software pipeline? 8) What is the difference between horizontal microinstruction and vertical microinstruction? 9) Briefly define indirect addressing. 10) What are the advantages of the geometric mean over the harmonic and arithmetic means when combining normalized execution rates? 2075 Microprocessor systems Microprocessors Systems: Solutions manual to selected exercises Chapter 4 – Selected test problems - 555 different selected test problems - given in 119 pages - depending on how a problem difficult is, the questions are divided into three groups: - standard questions, devoted to everyone, are not marked - questions which the students should know if they want to get a higher mark (>8) are marked with one asterisk - difficult questions, intended for graduate students, are marked with two asterisks. 2075 Microprocessor systems Microprocessors Systems: Solutions manual to selected exercises Chapter 4 – Selected test problems - Layout of standard questions - What types of locations can hold source and destination operands? - What is a difference between big endian and little endian? - What general roles are performed by CPU registers? - What is a program status word? - Give a simple definition of precise interrupts/exceptions? 2075 Microprocessor systems Microprocessors Systems: Solutions manual to selected exercises Chapter 4 – Selected test problems - Layout of questions marked with one asterisk - Define the crucial differences between microcontrollers and microprocessors? Explain the differences among the following program defined exceptions: a) illegal instruction b) non-implemented instruction c) privileged instruction d) arithmetic error. For the example of a conditional jump statement if C then I1 else I2 explain the concepts of branch prediction and speculative execution. 2075 Microprocessor systems Microprocessors Systems: Solutions manual to selected exercises Chapter 4 – Selected test problems - Layout of questions marked with two asterisks - - Define the basic characteristics of the following benchmark programs: Dhrystone, Whetstone, Livermore Loops, and Linpack. Define briefly what kind of relationship exists between the sequential model of execution and the precise processor state. What kind of similar and conceptually different activities perform the linker and loader? 2075 Microprocessor systems As conclusion Microprocessors Systems: Solutions manual to selected exercises, by M. Stojcev and T. Stankovic, published by Faculty of Electronic Engineering Nis 2004. contains a collection of problems and theoretical questions, useful to students for preparing the major Microprocessor systems exams, and at the same time shows new trends of development in the field of computer architecture. 2075 Microprocessor systems Thanks to all for stated attention and patience to follow this presentation!