Levels of Abstraction (Views of Data )
advertisement

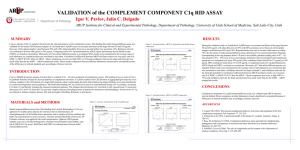
Levels of Abstraction (Views of Data ) • Physical level: describes how a record (e.g., customer) is stored. • Logical level: describes data stored in database, and the relationships among the data. type customer = record customer_id : string; customer_name : string; customer_street : string; customer_city : integer; end; • View level: application programs hide details of data types. Views can also hide information (such as an employee’s salary) for security purposes. View of Data An architecture for a database system DATA MODELING AND ITS COMPONENTS Data Modeling • In computer science, data modeling is the process of structuring and organizing data. • These data structures are then typically implemented in a database management system. • In addition to defining and organizing the data, • data modeling may also impose constraints or limitations on the data placed within the structure • Managing large quantities of structured and unstructured data is a primary function of information systems. • Data models describe structured data for storage in data management systems such as relational databases. • They typically do not describe unstructured data, such as word processing, documents, email messages, pictures, digital audio, and video. Data model • Data model fall into three different groups. 1.Object based logical model. 2.Record based logical model. 3.Physical model Object based logical model • object based logical model are used in describing data at the logical and view level. • They are characterized by the fact that they provide fairly flexible structuring capabilities and allow data constrains to a specified explicity. Record Based Logical Model • • • Record based logical model used in describing data at the logical and view level. In contrast to object based data models they are used both to specify the overall logical structures of the data base and to provide a higher level description of the implementation. Record based models are so named because the database is structured in fixed format records of several types. Each record type defines a fixed number of fields, or attributes, and each field is usually fixed length The three most widely accepted record based data models are 1. 2. 3. Relational Model Network Model Hierarchical Model. RELATIONAL MODEL • Relational model uses a collection of tables to represent both data and the relationship among those data. Each table has multiple columns and each column has a unique name. Table Name: Student Student code name k101 raja s102 geeta Table Name: Course Course code Course name C21 agronomy C32 maths C33 economics C50 extension C81 horti C86 pathology NETWORK MODEL • Data in the network model are represented by collection of records and relation ship among data are represented by links, which can be viewed as pointers. • The records in the database are organized as collection of arbitary graphs. K101 Rajat Kataria 96 56 S102 69 88 92 c math 3 s C34 c AG 2 R C33 AEX Geet a Subr ama nian 76 89 82 92 C81 C50 ENT AEC 96 C86 PAT HOR HIERARCHICAL MODEL. • Hierarchical model is similar to the network model in the sense that data and relationship among data are represented by records and links, respectively. • It differs from Network model in the records are organized as collection of trees rather then arbitrary graphs. • Student code stu.name k101 raja Course code , cou.name, marks C21 c32 agro 88 maths 96 c33 nom economics 69 c34 extension y c50 entomology 56 76