Classification - De Anza College
advertisement
MICROBIOLOGY Introduction & Classification Topics • • • • • • • Classification Methods of Microbiology Nutrition & Growth Microbial Structure Metabolism Host parasite relationships Control of Growth Types of Microorganisms • Bacteria – Gram positive & gram negative • Viruses – RNA & DNA • Fungi – Yeasts & molds • Protozoa History • Robert Hooke – Described units in cork as cells Anton van Leeuwenhoek-1667 – Made lenses or simple microscopes Spontaneous Generation • Abiogenesis-living matter arising from nonliving matter • Redi –maggots & meat • Pasteur et al disproved abiogenesis Pasteur • Fermentation – Yeast ferment grape juice –alcohol – Bacteria ferment grape juice-acids • Pasteurization Germ Theory of Disease • Koch – Koch’s postulates – Developed pure culture techniques – Discovered TB agent Immunology/Chemotherapy • Jenner and smallpox vaccine – Used cowpox virus Antiseptics • Semmelweis • Lister Fleming • Discovered penicillin Taxonomy • System of cataloging organisms – Identification: characterization of organisms – Classification: arrangement of organisms into similar groups – Nomenclature: assign names Binominal Nomenclature • Genus-capitalized ; collection of species • Microbes – species can be subdivided into strains • Strains have small genetic differences Rules • Both genus & species underlined or italicized • Strain-subdivision of species – ID by name, number or letter – Example- Escherichia coli- E. coli K12 Classification • Wittaker-5 kingdoms – Plants – Animals – Fungi – Protista – Monera or Prokaryote Domains • Carl Woese-1980s • Based upon modern techniques – Sequence of rRNA in ribosomes • Three cell types based upon ribosomes Three Domains • Domains above kingdom level • Bacteria or Eubacteriae – Prokaryotes with peptidoglycan in cell wall – Divide by binary fission – Motile by flagella or cilia – Sensitive to antibiotics Archaea • Ancient prokaryotes – Cell wall present, not peptidoglycan – Live in extreme environments – Have unusual metabolic processes – Not sensitive to antibiotics Archaea • Methanogens -strict anaerobes – Produce methane from CO2 + H2 – Live in anaerobic mud lakes – Intestine of cows Archaea • Halophiles – Require high concentration of salt • Maintain cell wall – Spoilage of food-salted fish – Salt lakes Archaea • Thermophiles – Live in hot sulfurous waters or acidic water – Nucleic acids/proteins do not function at low temperatures – Volcanic vents in ocean Eukarya • • • • • • All eukaryotes Cell wall varies in composition Not sensitive to antibiotics Fungi-yeasts and molds Protists-slime molds, protozoa, & algae Plants & animals Endosymbiotic Theory • Eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes • Supported by similarities between prokaryotes & organelles in eukaryotes • Mitochondria & chloroplasts same size as prokaryote cell – Contain DNA, 70S ribosomes • Endosymbiont-organism that lives within another Support for Theory » • • • • • Prokary DNA circular Histones No Ribosomes 70S Growth binary Cyanophora Eukary linear Yes 80S mitosis Mitoch & Chloro circular No 70S binary Viruses • Obligate intracellular parasites • Not cells so non living agent • No ribosomes • Classification is different Viroids & Prions • Viroids – Single short piece of RNA – Cause disease in plants – ? In humans • Prions – Protein – Cause neurodegenerate diseases – Humans & animals – CJD & mad cow New Challenges • Antibiotic resistance – MRSA, VRE & ESBL • Emerging diseases – SARS & Avian Influenza • Bioterrorism – Anthrax, smallpox, plague, botulism
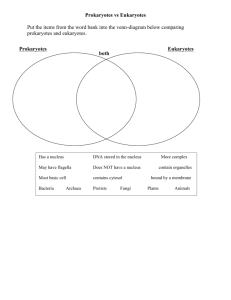
![Cell Game Board [10/16/2015]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007063627_1-08082c134bbc8d8b7ad536470fbed9dc-300x300.png)





