Distribution
advertisement

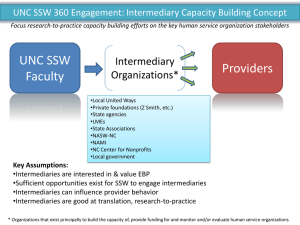
DELIVERING SERVICE THROUGH INTERMEDIARIES AND ELECTRONIC CHANNELS Chapter 13 Donna J. Hill, Ph.D. Fall 2000 Objectives for Chapter 13: Delivering Service through Intermediaries and Electronic Channels • Identify the primary channels through which services are delivered to end customers • Provide examples of each of the key service intermediaries • View delivery of service from two perspectives-the service provider and the service deliverer • Identify the benefits and challenges of each method of service delivery • Outline the strategies that are used to manage service delivery through intermediaries Distribution---Time and Place Utility Availability ---when Access --- easy to conduct transaction Operating Hours Direct channels --no intermediaries Indirect channels --- Service Provider Participants service principal (originator) creates the service concept (like a manufacturer) service deliverer (intermediary) entity that interacts with the customer in the execution of the service (like a distributor/wholesaler) Functions Performed by Intermediaries Co-producing the service Making services locally available Functioning as a link between the brand and the customer Types of Intermediaries Agents selling --- contractual authority to sell purchasing--- purchase for a buyer facilitating --- help with marketing process Brokers --- bring buyers and sellers together Electronic Channels --- do not require human interaction Franchises --- Service outlets licensed by a principal to deliver a unique service concept it had created or popularized. Characteristics of Agents A agent works for the pricipal continuously An agent receives commissions (usually two to six percent of selling price) An agent delivers the rights to services An agent is entrusted with influence over prices, terms, and conditions of sale. Travel Agent (selling agent) Services Intermediaries franchisees e.g., Jiffy Lube, H&R Block, McDonald’s agents and brokers e.g., travel agents, independent insurance agents electronic channels e.g., ATMs, university video courses, TaxCut software Key Issues Involving Intermediaries conflict over objectives and performance conflict over costs and rewards control of service quality empowerment versus control channel ambiguity Exhibit 13-4 Summary of Benefits and Challenges for Franchisers of Service Benefits Leverages the business format to gain expansion and revenues Maintains consistency in outlets Gains knowledge of local markets Shares financial risk and frees up capital Challenges • Difficulty in maintaining and motivating franchisees • Highly publicized disputes and conflict • Possibility of inconsistent quality that can undermine the company name • Control of customer relationship by intermediary Summary of Benefits and Challenges for Franchisees of Service Benefits Obtaining an established business format on which to base a business Receiving national or regional brand marketing Minimizing the risks of starting a business Challenges • Disappointing profits and revenues • Encroachment and franchise saturation • High failure rates and unfair terminations • Lack of perceived control • High fees and rigid contracts • Unrealistic expectations Exhibit 13-6 Summary of Benefits and Challenges in Distributing Services through Agents and Brokers Benefits Challenges Reduced selling and distribution costs Intermediary’s possession of special skills and knowledge Wide representation Knowledge of local markets Customer choice • Loss of control over pricing and other aspects of marketing • Representation of multiple service principals Exhibit 13-7 Summary of Benefits and Challenges in Electronic Distribution of Services Benefits Consistent delivery for • standardized services • Low cost • Customer convenience • Wide distribution Customer choice and • ability to customize • Quick customer feedback • Challenges Customers are active, not passive Lack of control of electronic environment Price competition Inability to customize with standardized services Lack of consistency with customer involvement Security concerns Competition from widening geographies Strategies for Effective Service Delivery through Intermediaries Control Strategies Measurement Review Partnering Strategies • Alignment of goals • Consultation and cooperation Empowerment Strategies • Help the intermediary develop customer-based service processes • Provide needed support • Develop the intermediary to deliver service quality • Change to a cooperative management structure Examples www.garden.com www.ticketmaster.com www.mediconsult.com www.priceline.com www.schwab.com www.starbucks.com Answer these questions Does this represent a direct or indirect channel? If indirect, which type? Describe how each of the following reasons for channel conflict is problematic for these businesses? conflict over objectives and performance conflict over costs and rewards control of service quality empowerment versus control channel ambiguity What is the main benefit the business gets from using this channel? What is the main challenge? Customer-Focused Distribution Identify market segments. Identify benefits sought by customers. Match customer needs to channel and distribution strategies. Manage quality control. Manage corporate growth.