Assessment & Intervention Strategies for Behavior FBA & BIP
advertisement

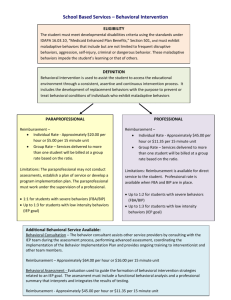
Assessment and Intervention Strategies for Behaviors: Part 1 Functional Behavioral Assessment (FBA) & Behavioral Intervention Plan (BIP) Development January 2008 Revised July 2010 Bette Greer Betsy Stanwood What Should We All Know About Behavior? 1. There is a significant learned component in most forms of challenging behavior and what has been learned may be “unlearned”. 2. Challenging behavior almost always means something. 3. Understanding the behavior helps us to change it. Challenging behavior and autism Making Sense-making progress Philip Whitaker Why? When? Would a School Team Consider Starting the FBA/BIP Process? Required: To access certain system supports (i.e. Lake Forest Academy) To seek entitlement for special education services To meet IDEA process requirements (i.e. Manifestation Determination, Change in Services, Functional Behavioral Assessments, and Behavioral Intervention Plans) Recommended: To assess & address significant behavior problems in a school setting Student Student Student Student Student Student not motivated to participate in school activities does not complete tasks has poor peer relationships has poor self esteem has heightened levels of anxiety does not comply to adult requests Functional Behavioral Assessment (FBA) What is a “Functional Behavioral Assessment”? A method of identifying the social, affective, and environmental factors that reliably predict and maintain behaviors that interfere with learning. Its purpose is to determine a target behavior that will be the focus of intervention on a Behavioral Intervention Plan. Steps in the FBA Process 1. Collect Data 2. Analyze Data • Antecedent • Behavior • Consequence • Target Behavior 3. Identify Function of Target Behavior 4. Develop Hypothesis 1. Collect Data FREQUENCY DATA SHEET Student: ______________ Date 6/14/ 04 Time 10:30 to 12:25 Behavior of Concern Exhibited EXAMPLES: -Refuses to work -Talks out -Out of seat Teacher: _________________ Location/Activity Regular class/ Math lesson Presence of Others, Peers, Adult(Specify) EXAMPLES: -Students (all class) -TA (CM) -T (BS) NHCS PBIS 3 Tool Adult Response/ Action TA walks to student prompts verbally “Get Busy” Other Factors EXAMPLES -After fire drill -Day after return from holiday -No medications 2. Analyze Data Identify antecedent or factors noted prior to the behavior Summarize behavior, noting level of intensity and specific patterns, using information from Frequency Data Sheet (NHCS PBIS 3) Identify consequences or events that follow the behavior Define the target behavior (NHCS PBIS 4) Considerations when Analyzing the Data Are there patterns? Are there specific locations,times, subjects or people? (Triggers) Are there physical signals of impending problems? Are there home concerns? Divorce? Death? Illness? Transition? How often do the behaviors occur? (frequency) How long do behaviors last? (duration) How severe or damaging are the behaviors? (intensity) Can the student continue with their school day when behavioral episode is over? Consider that a Target Behavior is . . . • a specific behavior that needs to be replaced OR • a cluster or combination of behaviors that are related to one another and are a part of the target behavior 3. Identify Function Attention? Power? Escape/Avoidance? Self Stimulation Self Stimulation? Identifying Functions The function and purpose of the behavior can be… To tell us that they want more of something pleasant = Power and Control or Attention To tell us that they want to get away from something that they consider unpleasant = Escape and Avoidance To obtain something pleasant at a sensory level = Self-Stimulation Functions of Behavior Target Behavior Pos Reinf Attention From: Peers Staff Preferred Adult Power For: Control Intimidation Vengeance Escape/ Avoidance Neg Reinf Self Stimulation Of: To reduce: Person Activity Classroom Anxiety Fear So, It Is Important To Determine the “REAL” function of the behavior and the “REAL” message being communicated. Once you establish the function of a behavior, you need to determine how the ADULT might be contributing to the problem. Just how does she think I contribute to THEIR behavior? Do you mean that I have to change so the student will change? Do you contribute? Are you guilty of saying any of these? “I tried that visual stuff and she still won’t do her work!” “He understands, I had him repeat my directions.” “He knows what he is doing and he is just being manipulative.” “She just sits there and waits for me to tell her what to do.” “I wrote it on the board" “He understands, he did the work yesterday.” 4. Develop the Hypothesis When Johnnie is in small group instruction and/or gym and does not get his way he typically responds by shoving and/or using threatening language to gain attention. A hypothesis statement summarizes the team’s analysis of the behavior. It is a statement of what the student is doing and why the student is doing it as framed in the FBA tool. Other Considerations Related to the FBA Process Use the alternate autism FBA Functional Behavioral Assessment for Students with Autism when students have a diagnosis of autism/autism spectrum disorder Use the alternate autism FBA when students demonstrate social and communication deficits demonstrate a strong visual learning channel demonstrate sensory integration deficits FBA Pitfalls Failure to use FBA process proactively Failure to collect data efficiently Failure to summarize data for analysis Failure to analyze data efficiently Failure to see or look for patterns Failure to utilize the process to identify the function of the behavior Accessing the Tools All tools related to the FBA/BIP process can be located at New Hanover County Schools, Special Education & Related Services Manual. Look in the Positive Behavioral Interventions & Supports Chapter. Frequency Data Sheet (PBIS 3) Analysis of Data (PBIS 4) FBA/BIP Autism FBA The FBA Process Collect Data Analyze Data Identify Function Develop Develop Hypothesis Hypothesis Behavioral Intervention Plan (BIP) What is a “Behavioral Intervention Plan”? A plan generated by a team based on the information gathered from a FBA. This tool is a “lesson plan” for teaching replacement behaviors. “Recipe” for a Successful Behavioral Intervention Plan 2 Part Focus of a BIP Replacement /Desired Behavior Rewards Proactive Focus Teaching Plan Documentation Consequences Reactive Focus Crisis Plan Must be specific in describing the behaviors. Can everyone see them? BIP Instructional Considerations “I want Joe to follow directions in class.” How? Who? Documentation? Consequences? When? Replacement/Desired Behaviors ”I want Joe to follow directions for task completion in class.” Progressive Steps must be taught to reach desired behaviors. Complete entire task Complete ½ sheet Complete 1 problem Work with peer Request help from teacher Behavior Management and Reinforcement ALL students need strong reinforcement to change their behavior. Reinforcement is equally as important to get them to comply to your request when they perceive the task too difficult or repetitive. IN OTHER WORDS, They have to decide if it is worth doing X to get Y. Just because an adult tells them to do something or threatens to “drop their boat” isn’t going to alter the behavior if there isn’t a strong reinforcer. Avoid These Pitfalls When Using Reinforcement Don’t forget to teach the behavior you are trying to reinforce, you will need to provide instruction and reinforce close approximations of the goal behavior. Be sure to tell the student what they CAN DO to earn a reinforcer NOT what they can’t do. Make sure you are reinforcing what you truly want to reinforce. For example, make sure that the bulk of the attention paid to children is for desired behaviors rather than undesired behaviors. Keys for Effective Rewards and Consequences •Get information regarding the student’s interests and motivators •Get student’s “buy in” regarding rewards system – give at least 5 reward choices •Make sure your consequence doesn’t really reward the student •Utilize a variety of consequences that offer a more positive outcome such as restitution BIP Pitfalls Failure to use the tools to guide the decision making Failure to include a teaching plan Failure to identify reinforcers that are effective with the child (inconvenient for adults) Failure to review the BIP Additional Pitfalls Don’t Get Caught “Failing” to . . . -Evaluate the plan’s effectiveness after collecting data - Agree on the number of weeks to implement the plan - Schedule a date to review and revise the plan -Explain all aspects of BIP to student and team members - Document BIP as an accommodation in IEP (if the student has an IEP) The BIP Process Activity A Case Study of Sponge Bob Case Study #1 Sponge Bob Repeating kindergartner Diagnosis of ADHD – Inconsistently taking Ritalin Becomes agitated when presented with an academic task, usually math Becomes agitated when work is marked incorrect Refuses to comply when redirected to correct his work Further redirection increases his level of agitation, possibly to the point of outward aggressive behavior (such as, crumpling paper, throwing items, destroying property) OR presents non-compliant, shut-down behavior, refusing to follow directions Following the shut-down behavior, student may exhibit aggressive behavior towards peers (such as, kicking or shoving a student) Case Study #1 Sponge Bob When debriefing with the student he will refuse to accept ownership for his behavior and will blame peers as having prompted the behavior (i.e., perceived students making fun of him, staring at him, talking about him) Analysis of observational data indicates behavior occurs typically during math or in the afternoon as well as when items have been taken from the student Interventions to date have included bouncing to the IBS class - 3 episodes lasting approximately 1.5 hours Parent input indicates aggressive episodes have increased at home even with medication Student’s strengths include articulating his feelings, complying when given one on one support. He also has artistic abilities. FBA Information Activity #1: In teams, complete FBA Activity #1(a): In teams, complete FBA hypothesis statement. Presenter will direct which activity DISCUSSION AND SHARE Sponge Bob FBA Hypothesis When Bob is given an assignment (most often with math) and is asked to make corrections or complete an assignment he typically responds by refusing to complete task or shuts down to gain escape and avoidance of the task. BIP Development Activity #2: In teams, brainstorm a list of appropriate replacement/desired behaviors for Sponge Bob. Activity #3: In teams, brainstorm a list of possible rewards for Sponge Bob. DISCUSSION AND SHARE In Session 2 we will work with Teaching Strategies - The How! Teaching Plan New Hanover County Schools Behavioral Intervention Plan (BIP) Replacement/ Desired Behaviors How? Sponge Bob 1. 2. 3. Utilize appropriate de-escalation strategies Request academic assistance Accept responsibility for behavior Who? When? How will teaching time be documented? EXAMPLES: Classroom teacher Peer School Staff Counselor Parent Volunteer Reading Teacher IBS Teacher EXAMPLES: 1 time a week Daily Weekly During resource period At the end of the day EXAMPLES: Data Collection Sheet Self- Monitoring Tools Behavior Contract . 1.Teach how to use visual gauge Use visual gauge to indicate level of frustration Choose a de-escalation activity from a menu of activities 2. Teach how to use visual cue card Use a visual to request assistance Participate in academic tutoring 3.Engage in problem solving discussion with adult - Complete Problem Solving tool and identified preferred, acceptable alternate behavior What rewards will be provided when the desired behaviors are demonstrated? EXAMPLES: Extra time for identified preferred activity Homework/classroom Pass Mystery Motivator Reduction of task expectations Time with a preferred adult Good Report Home Extra “Special Activity” time * Who will implement the rewards? EXAMPLES: Classroom teacher Peer School Staff Counselor Parent Volunteer Reading Teacher IBS Teacher How will the desired behavior data be collected? EXAMPLES: Behavior Point Chart Data Collection Forms/Tools * “Reinforcers are carefully tailored to the child’s strengths and interests. This is an important factor in developing successful BIPs. The one size fits all approach to reinforcers is not nearly as effective as the individualized approach.” Bateman & Golly BIP Crisis Plan (Mild, Moderate, Severe) Activity #4: In teams, brainstorm descriptions of MILD, MODERATE, AND SEVERE behaviors for Sponge Bob. DISCUSSION AND SHARE In Session 2 we will work with Teaching Strategies - The How! Crisis Plan Sponge Bob New Hanover County Schools Behavioral Intervention Plan (BIP) What? . Describe the target behavior from FBA. What Consequences will be enforced? Mild: Shut down Refusal to follow directions Moderate: Crumpling paper and throwing items Severe: Kicking or shoving peers Destroying property Who? Data Describe the responsibilities of each team member, including school staff, family and student. Explain how and when data will be recorded. List the type of data collection tool that will be used. Mild: 1.Cue student to use visual to request assistance or de-escalation break Mild: 1.Classroom teacher will allow enough time for a response Moderate: 1.Send home work that has been crumpled or not completed for homework 2.Write an apology to the teacher & classmates for interrupting instruction and endangering their safety 3.Bounce to alternate, non-preferred location Severe: (including components of a crisis plan) 1.Remove class from setting 2.Call first responders 3.Utilize communication de-escalation strategies (Verbal but may be more visual for students with communication delays.) 4.Refrain from interaction to allow student to de-escalate 5.Physical restraint 6.Contact parents 7.Team considers student’s level of deescalation and potential to remain in school. 8.Team decision will be made to determine need to send student home Moderate: 1.Teacher 2.Student 3.Teacher or other staff EXAMPLES: Data Collection Sheet Self- Monitoring Tools Behavior Contract Severe: 1.Teacher or other staff 2.Teacher or other staff 3.Personnel trained in Mindset communication de-escalation 4.Teacher or other staff 5.Personnel trained in Mindset physical restraint procedures/In an emergency other staff until trained staff arrive 6.Teacher or other staff 7.Administration & team 8.Administration & team Activity A Case Study of Wile E. Coyote Case Study #2 Wile E. Coyote 5th Grader Diagnosis of ADHD and Bi Polar Takes medication routinely Becomes agitated when asked to transition from preferred activity Has poor self-esteem and thinks he must “know” all the answers Often will not attempt a task he is unsure of or will begin as if he knows what he is doing and puts any answer to fill in the blanks Will not ask for help Case Study #2 Wile E. Coyote Analysis of observational data indicates behavior occurs typically when new skills are introduced Interventions to date have included prior notice of instructional topics for pre-teaching at home Parent input indicates frustration at home when he cannot grasp concepts or indicate when he doesn’t know or comprehend info Student’s strengths include vocabulary and significant factual/rote information FBA Information Activity #1: In teams, complete AU-FBA Activity #1(a): In teams, complete FBA hypothesis statement. Presenter will direct which activity DISCUSSION AND SHARE Wile E. Coyote FBA Hypothesis When Wile is in an educational setting and is asked to transition when he isn’t finished he typically responds by presenting verbal refusal or destroying materials to gain escape and avoidance of the adult request. BIP Development Activity #2: In teams, brainstorm a list of appropriate replacement/desired behaviors for Wile E. Coyote. Activity #3: In teams, brainstorm a list of possible rewards for Wile E. Coyote. DISCUSSION AND SHARE In Session 2 we will work with Teaching Strategies - The How! Teaching Plan New Hanover County Schools Behavioral Intervention Plan (BIP) Wile E. Coyote Replacement/ Desired Behaviors 1. Communicate appropriately with staff regarding his needs or concerns . How? 1. Student will use visual help flip card - “I need help card.” to indicate a need for help or to ask for an opportunity for additional time to complete a task. What rewards will be provided when the desired behaviors are demonstrated? Sticker reward system to be traded in for school rewards and/or at home towards larger incentive Tickets as a part of reinforcement system Computer time Homework Pass Visit to other classes to act as helper Free time to listen to music Who? When? How will teaching time be documented? 1. Resource teacher to develop and pre-teach “Help card procedure. Student will need multiple opportunities to practice/role play the use of the card system. School staff to implement the procedure. EXAMPLES: 1 time a week Daily Weekly During resource period At the end of the day EXAMPLES: Data Collection Sheet Self- Monitoring Tools Behavior Contract Who will implement the rewards? School Personnel EVERY TIME HE COMPLIES TO RULES/EXPECTACTIONS/ PROCEDURES, EVEN DURING A CONSEQUENCE, STUDENT GETS REINFORCED REINFORCEMENT SHOULD ACCOMPANY APPROXIMATIONS How will the desired behavior data be collected? EXAMPLES: Behavior Point Chart Data Collection Forms/Tools * “Reinforcers are carefully tailored to the child’s strengths and interests. This is an important factor in developing successful BIPs. The one size fits all approach to reinforcers is not nearly as effective as the individualized approach.” Bateman & Golly BIP Crisis Plan (Mild, Moderate, Severe) Activity #4: In teams, brainstorm descriptions of MILD, MODERATE, AND SEVERE behaviors for Wile E. Coyote. DISCUSSION AND SHARE In Session 2 we will work with Teaching Strategies - The How! Crisis Plan Wile E. Coyote What? Describe the target behavior from FBA. Mild: Shut down Refusal to follow directions States OK, in a minute Moderate: Verbal refusal – “I ‘m not going to do that Crumpling paper and throwing items Yelling out inappropriate comments to teacher or students Refusing to leave class Severe: Throws himself on the floor Leaves assigned area without permission Pushes, hits, throws inappropriate objects, grabs New Hanover County Schools Behavioral Intervention Plan (BIP) What Consequences will be enforced? Who? Data Mild: 1.Cue student to use visual to Communicate his needs/concerns Mild: 1.Classroom teacher will allow enough time for a response Moderate: Moderate: 1.Teacher 2.Student 3.Teacher or other staff EXAMPLES: Data Collection Sheet Self- Monitoring Tools Behavior Contract Severe: (including components of a crises plan) 1. Remove other students from Severe: 1.IF REFUSING TO COMPLY present visual cue card that says, “If you don’t stop (or start) ____ then you will go to Ms. X’ room. When student complies then he return to class if calm room 2. Call Administrator 3. Administrator will present next choices: “You can walk with me to my office or, I will take you to my office”. 4. Parents notified. Student makes choice of consequence with parents to be implemented the following day, Describe the responsibilities of each team member, including school staff, family and student. 1.Teacher or other staff 2.Teacher or other staff 3.Administrator 4.Administration & team Explain how and when data will be recorded. List the type of data collection tool that will be used. Resources - NHCS Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports Training Modules NHCS Student Support & Intervention System Manual Why Johnny Doesn’t Behave by Barbara Bateman & Annemieke Golly Web Resources http://dpi.wi.gov/sped/ebdbluepri.html http://www.interventioncentral.com/ http://www.pbis.org/main.htm