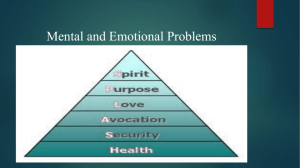
Eating Disorders
advertisement

Mental Illnesses Eating Disorders Depression/Manic Depression/Bi-Polar Anxiety Disorders Suicide Prevention ADHD Schizophrenia Addictive Disorders Bell Ringer #1 Define the following terms using your textbook or your notes: 1. Mental Illness 2. OCD 3. Panic Disorder 4. PTSD Once you have completed this, pick up the handout, Making a Diagnosis, and complete the handout. WRITING Imagine somebody whom you love---parent, brother, sister, boyfriend, girlfriend, etc. Write down everything you love about that person for three minutes. WRITING Imagine that this person was killed/injured by someone with a mental illness, how would you feel? WRITING NOW……Imagine the same person you loved and wrote about developed a mental illness and injured/harmed/killed someone else. How would you feel now? READ ARTICLE: Schizophrenic Man Beheaded Friend Who is Responsible???? EVERYONE has responsibilities to care for those with mental illness (laws, hospitals, family, friends) because people suffering with mental illnesses are limited by what they can do for themselves. We need to start thinking along the lines of…. Stricter laws Better preventative care being instated Family/friends being more vigilant and proactive Schizophrenia Definition: A medical illness that interferes with a person’s abilities to think clearly, to distinguish reality from fantasy, to manage emotions, make decisions, and relate to others. Schizophrenia First signs usually show up in teenage years or late twenties Can be chronic or episodic Does not mean “split personality” Almost all people with schizophrenia are not dangerous or violent towards others when they are receiving treatment. Several stigmas about schizophrenia in society Schizophrenia Diagnosis Difficult Doctor must examine the patient over a course of at least 6 months Symptoms Divided into three categories: Positive, Disorganized, and Negative Symptoms Schizophrenia Positive Symptoms also know as “psychotic symptoms. Delusion and hallucinations Delusions: may cause the patient to believe that people are reading their thoughts or plotting against them, that others are secretly monitoring or threatening them, or that they can control other people’s minds. Hallucinations: causes people to hear or see things that are not there Positve = overt symptoms or characteristics that should NOT be there. Schizophrenia Disorganized Symptoms Confused thinking and speech Behavior that does not make sense Difficulty making sense of every day sights or sounds Negative Symptoms Emotional flatness or lack of expression Inability to start and follow through with activities Negative = lack of characteristics that SHOULD be there. Schizophrenia CAUSE Unknown Scientists have shown that people with Schizophrenia display brain images from MRI or CAT scans that are different from a person who does not have the disorder. Linked to genetics (but genes DO NOT cause the illness) Schizophrenia Treatment No cure, but highly treatable Hospitalization (highly sever cases) Medication Antipsychotic drugs Attempts to correct imbalance of the brain Psychosocial Rehabilitation Program for Assertive Community Treatment (PACT) Support available 24 hrs. 7 days a week Professionals teach people with schizophrenia how to live a life with the disorder Schizophrenic Man Beheaded Friend Everyone has responsibilities to care for those with mental illnesses (law, hospitals, doctors, friends, families) because people suffering with mental illness are limited by why they can do for themselves. This is a caveat PTSD Bell Ringer #2 What is PTSD? Who suffers from PTSD? Use your book to help you find the answer to these questions. PTSD Video http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ghX CrsTVXtc PTSD Activity In a few minutes we are going to read an important selection from a book. To help you better understand it, I’ve prepared a “preview” by cutting out just eight sentences from a longer piece. You will be picking these sentences from a hat. Now that everyone has a piece of the puzzle. If you could see all the sentences other people have, you could probable make a good prediction as to what the who thing is about. That’s what we’re going to do now…. Try to compare your quote with at least 10 other people’s sentences in the next 5 or 6 minutes. GO!!!! PTSD Activity In your notebooks (or discuss in groups of 4), answer the following questions: 1. What do you thing the passage is going to be about? 2. What time and place are depicted? 3. Any guesses about who wrote this? PTSD Activity Read excerpt from Soldier’s Heart Discussion If Charley survived the war-which we cannot tell from this passage-how do you think he would do? Would he be able to go right back to normal life, or do you think he might have had to struggle with his memories? Do you think Charlie suffers from PTSD? (refer back to your definition) Mental Illnesses Bell Ringer: PTSD ARTICLE Read article and T4 it! Fill out handout that accompanies article. (10-15 minutes) Activity Now everyone is going to get a chance to read an article of their own choice to learn more about PTSD. Today we have four choices. The first two are very intense accounts from a battlefield. Activity continued…. A Soldier’s Letter Home from WWII-This was written by an American GI serving in the Pacific, graphically telling his parents about the combat casualties he had seen. “The Forever War of the Mind”: Max Cleland, who served as head of the Veterans Administration, recounts how he lost an arm and both legs in battle-and describes the mental anguish that accompanied his physical wounds. “Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder”: Basic problems associated with PTSD. Blog Post-”Daddy’s Home”: Written by the wife of a decorated soldier who suffers from PTSD, this article offers tips for families in the same situation. Activity continued…. Once you have selected your articles, sit with small groups (3-4) with students who have picked the same article. In your groups discuss and write the answers to the following questions: What struck you about the piece you chose? What are some things family members and friends can do to help someone suffering from PTSD? Make a list of specific actions. RECONVENE AS A CLASS-DISCUSS EATING DISORDER BELL RINGER QUESTION #3 What is an eating disorder? What’s the most common eating disorder? Who is mainly affected by eating disorders? Why? Article “The Real Skinny” Eating Disorders Affect ~5 million Americans every year 90% affected are female Disturbance in eating & excessive concern about body shape or weight Types: Anorexia Nervosa Bulimia Nervosa Binge-Eating disorder & others Anorexia Nervosa Refusal to maintain normal body weight Characterized by selfstarvation Fear of weight gain or being fat despite being underweight Distorted body image Subtypes: restricting; binge-purging Anorexia Nervosa Anorexics use starvation to feel more in control through tension, anger and anxiety More than 90% are female Ballerinas Fashion models Gymnasts actresses Anorexia Signs/Symptoms Loss of menstrual cycle Skin is dry and yellow Bones becomes brittle Always complain they are “cold” body compensates by growing fine hair called “lanugo” Are deficient in potassium, mineral needed for healthy heart Anorexia Behavior Clues… Preoccupation with weight and food Hides foods Cuts foods into small pieces Excessive calorie counting Exercises a lot Wears baggy clothes to hide appearance Weighs her/himself many x a day. Binge Eating Disorder Recurrent binge eating (2 days per week for 6 months) Marked distress Eat rapidly Uncomfortably full Eating when not hungry Eating alone Feeling disgusted or guilty after binging Bulimia Nervosa Recurrent binge eating episodes Eating in discrete times (2 hrs) where the amount of food is larger than what others would eat in a similar circumstance Lack of control Recurrent behavior to prevent weight gain Vomit, laxatives, water-pills, enemas, fasting, exercise Anorexia Clues Cont… Talks about weight and food all the time Usually makes excuses for not eating Acts moody or depressed Bulimia Nervosa Binge-purge episodes occur twice a week for months, even years Self-evaluation mainly influenced by weight/shape Subtypes: Restricting; Binge-Purging Average binge = 1200 calories Bulimia Nervosa Onset in teens or early adulthood Extreme concern with weight and shape Eating patterns: skipped meals, restrained eating, binge-purge episodes Majority in normal weight range Dietary restraint and negative emotions promote binging and purging Eating Disorders: Cultural Factors Beauty considered central to femininity Thin is considered beautiful for women When relationships fail, women more likely blame themselves Men emphasize physical appearance in relationships Perceived pressure to be thin Body dissatisfaction Becoming more prevalent in AsianAmericans? Eating Disorders: Complications Many Medical Complications Underweight, obesity Menstrual irregularities Osteoporosis Heart disease Erosion of digestive tract & teeth Electrolyte imbalance, seizure, anemia Dry skin/hair, hand abrasions Depression, anxiety Other medical and psychiatric disorders Family Influence & Settings Perfect Family 1. High expectations 2. Threatening atmosphere 3. Overly critical parents 4. Overprotective parents Social Personality Traits 1. Leader 2. Competitor 3. Popular 4. Performer 5. Studious 6. Perfectionist 7. O. C. D. Media Influence People in Hollywood 1. Models 2. Actresses TV/Movies 1. Actors/Actresses 2. Underlying message 3. Ads/Commercials Media Influence Continued… 1. 2. 3. Internet Weight loss emails Ads Pro-eating disorder websites Eating Disorders Treatments Psychotherapy Medication Weight restoration for anorexia Multidimensional approach most effective For bulimia, 60-80% reduction in purging if treated. Lower in Anorexia Refer to physician. Which version is more attractive? Victim #1 Kate Bosworth Which version is more attractive? Victim #2 Lindsay Lohan Which version is more attractive? Victim#3 Nicole Richie Which version is more attractive? Victim #4 Mary Kate Olsen Food for thought…How pretty are these mobile skeletons? DEPRESSION Bell Ringer Question #4 What is depression? Why do people get depressed? Can they control this? Why/Why Not? Depression Depression: An emotional state characterized by exaggerated feelings of sadness, melancholy, dejection, worthlessness, emptiness, and hopelessness that are inappropriate and out of proportion to reality. Depression can appear at any age and is the major cause of suicide in this country. Diagnosis: Requires at least 5 of the following to be present Depressed Mood Loss of Interest or pleasure in all or most activities Weight Changes Sleep Changes Fatigue or Loss of Energy Feelings of worthlessness Diminished ability to think or concentrate; indecisiveness Thoughts of suicide or suicide attempts Causes of Depression Heredity Environment Background and Personality Biochemical Factors Physical Illness Common Myths of Depression Depression is just a feeling Only a few “crazy” people really get depressed Depression only occurs when bad things happen It’s easy to make yourself feel better There’s nothing you can do to treat depression Medicines like Prozac and Zoloft are “happy pills” More Common Myths Therapy’s just lying on a couch talking about your childhood Antidepressants can help anybody with depression There are no outward signs of depression People dealing with depression never experience extreme highs. Only adults suffer from depression ANXIETY DISORDERS BELL RINGER #5 Is anxiety normal? When does anxiety become a problem? What do you think people should do to “treat” their anxiety? ANXIETY DISORDERS Anxiety is a normal part of life, but when the fear becomes irrational and starts to interfere with daily life than you may be suffering from some form of anxiety. They are broken down into 5 categories. 5 CATEGORIES 1. General Anxiety Disorder 2. Phobic Disorder 3. Panic Disorder 4. Obsessive Compulsive Disorder 5. Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) OCD Clip http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=44DCWslbsNM Howie Mandel http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dSZNnz9S M4g Suicide Prevention Most people don’t want to die, they just want to end the emotional pain they are suffering. Life can seem extremely stressful, especially one with low self-esteem. A person under great stress experiences a crisis. Life seems UNBEARABLE!!! Suicide Prevention When a person is depressed an event that at other times would be tolerable might seem impossible to deal with. Suicidal Mind Set: The feeling that suicide is the ONLY solution to life’s problems. **Suicide is a PERMANENT response to what is usually a TEMPORARY problem. Suicide Prevention Possible Reasons for an Increase Teenage Suicide: Rising divorce rates People relocate more often Pressure to succeed in school and future careers. Increase in alcohol/drug use. Lack ability to solve problems. Physical, sexual, emotional abuse. Suicide Prevention Warning Signs: Verbal Direct statements: “Life isn’t worth living anymore.” “I’d be better off dead.” Indirect statements: “They’ll be sorry when I’m gone.” “I just feel sad and lonely all the time.” Suicide Prevention Warning Signs: Behavioral Signs Prior suicide attempts. Withdrawal from family and friends. Change of mood. Significant losses or change in environment. Change in school performance. Problems at home Suicide Prevention Warning Signs: Behavioral Signs Giving away possessions or making a will. Not taking care of personal appearance. Abusing alcohol or drugs. Problems with the law. Family/Friend has attempted suicide. Unwanted pregnancy. Breaking up with a significant other Suicide Prevention 90% OF PEOPLE WHO ATTEMPT OR COMPLETE SUICIDE GIVE WARNING SIGNS AS A CRY FOR HELP!!!!! Suicide Prevention How can you help? Take ANY threat seriously. Establish how serious the treat is. Ask the person: How serious are you? Has the person found a means to use? How lethal is the method? How detailed is the plan? Had that person talked to anyone else. Suicide Prevention How can you help? Look for other clues. Show the person that you care. Encourage the person to talk to a professional. Take charge!! Never keep it a secret…Tell someone! Remain with the person until help arrives. QPR Question, persuade, refer REVIEW What has been the most interesting information you have learned related to mental illness? How will you use this information that you’ve learned in the future or throughout your life?