McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Copyright © 2013 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
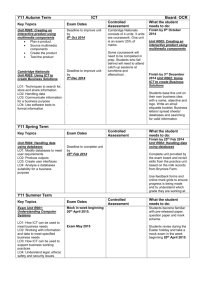
LEARNING OBJECTIVES (LO)
AFTER READING CHAPTER 12, YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO:
LO1
LO2
Explain what is meant by a marketing
channel of distribution and why
intermediaries are needed.
Distinguish among traditional
marketing channels, electronic
marketing channels, and different
types of vertical marketing systems.
12-2
LEARNING OBJECTIVES (LO)
AFTER READING CHAPTER 12, YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO:
LO3
LO4
Describe factors that marketing
executives consider when selecting
and managing a marketing channel.
Explain what supply chain and
logistics management are and how
they relate to marketing strategy.
12-3
CALLAWAY GOLF: DESIGNING AND DELIVERING
THE GOODS FOR GREAT GOLF
12-4
FIGURE 12-1 The variety of terms used
for marketing intermediaries that vary in
specificity and use in consumer and
business markets
12-5
LO1
NATURE AND IMPORTANCE OF
MARKETING CHANNELS
THE VALUE CREATED BY INTERMEDIARIES
Marketing Channel
Functions Performed by Intermediaries
• Transactional Function
• Logistical Function
• Facilitating Function
Utilities Received by Consumers
12-6
FIGURE 12-2 Marketing channel
intermediaries perform three functions,
each consisting of different activities
12-7
CHANNEL STRUCTURE & ORGANIZATION
LO2
MARKETING CHANNELS FOR
CONSUMER PRODUCTS AND SERVICES
Direct Channel
Indirect Channel
• Retailers
• WholesalersRetailers
• AgentsWholesalersRetailers
12-8
FIGURE 12-3 Common marketing channels
for consumer products and services by the
kind and number of intermediaries
12-9
CHANNEL STRUCTURE & ORGANIZATION
LO2
MARKETING CHANNELS FOR
BUSINESS PRODUCTS AND SERVICES
Direct Channel
Indirect Channel
• Industrial Distributor
• Agents
• AgentsIndustrial Distributors
12-10
FIGURE 12-4 Common marketing channels
for business products and services by the
kind and number of intermediaries
12-11
CHANNEL STRUCTURE & ORGANIZATION
LO2
ELECTRONIC & DIRECT MARKETING CHANNELS;
MULTICHANNEL MARKETING
Electronic Marketing Channels
Direct Marketing Channels
Multichannel Marketing
12-12
FIGURE 12-5 Consumer electronic
marketing channels are similar to those for
consumer products and services
12-13
CHANNEL STRUCTURE & ORGANIZATION
LO2
DUAL DISTRIBUTION &
STRATEGIC CHANNEL ALLIANCES
Dual Distribution
Strategic Channel
Alliances
Honey Nut
Cheerios Ad
12-14
MARKETING MATTERS
LO2
Nestlé and General Mills—
Cereal Partners Worldwide
12-15
FIGURE 12-6 Three types of vertical
marketing systems: corporate, contractual
(most popular), and administered
12-16
LO2
CHANNEL STRUCTURE & ORGANIZATION
VERICAL MARKETING SYSTEMS
Vertical Marketing Systems
Corporate Systems
• Forward Integration
• Backward Integration
Contractual Systems
• Wholesaler-Sponsored Voluntary Chains
• Retailer-Sponsored Cooperatives
12-17
LO2
CHANNEL STRUCTURE & ORGANIZATION
VERICAL MARKETING SYSTEMS
Contractual Systems
• Franchising
Manufacturer-Sponsored Retail Franchises
Manufacturer-Sponsored Wholesale Franchises
Service-Sponsored Retail Franchises
Service-Sponsored Franchises
Administered Systems
12-18
LO3
CHANNEL CHOICE AND MANAGEMENT
CHANNEL CHOICE CONSIDERATIONS
Target Market Coverage (Density)
• Intensive Distribution
• Exclusive Distribution
Gucci
• Selective Distribution
12-19
LO3
CHANNEL CHOICE AND MANAGEMENT
CHANNEL CHOICE CONSIDERATIONS
Buyer Requirements
• Information
• Convenience
• Variety
• Pre- or Post-Sale
Service
Profitability
12-20
LO3
Jiffy Lube and Petco
What buyer requirements have been satisfied?
12-21
USING MARKETING DASHBOARDS
LO3
Channel Sales and Profit at
Charlesburg Furniture
12-22
LO3
CHANNEL CHOICE AND MANAGEMENT
CHANNEL RELATIONSHIPS
Sources of Channel Conflict
• Vertical Conflict
• Disintermediation
• Horizontal Conflict
12-23
LO3
CHANNEL CHOICE AND MANAGEMENT
CHANNEL RELATIONSHIPS
Channel Captain
Channel Influence
• Economic
• Identification
• Expertise
• Legitimate Right
12-24
LO4
CHANNEL CHOICE AND MANAGEMENT
CHANNEL RELATIONSHIPS
Legal Considerations
• Dual Distribution
• Tying Arrangements
• Vertical Integration
• Full-Line Forcing
• Exclusive Dealing
• Refusal to Deal
• Resale Restrictions
12-25
FIGURE 12-A The Clayton Act and Sherman
Act place legal restrictions on specific
marketing channel strategies and practices
12-26
LO4
LOGISTICS & SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT
KEY CONCEPTS
Logistics
Supply Chain
Logistics
Management
Supply Chain
Management
• Customer
Requirements
• The Automotive
Supply Chain
• Cost-Effective Flow
• Customer Service
12-27
FIGURE 12-7 Relating logistics
management and supply chain management
to supplier networks and marketing
channels
12-28
FIGURE 12-8 The automotive supply chain
includes thousands of firms that provide the
5,000 or so parts in a typical car
12-29
LO4
LOGISTICS & SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT
SUPPLY CHAIN MGMT & MKT STRATEGY
Aligning a Supply Chain with
Marketing Strategy
• Understand the Customer
• Understand the Supply Chain
• Harmonize the Supply Chain
with the Marketing Strategy
12-30
MARKETING MATTERS
LO4
IBM’s Integrated Supply Chain—
Delivering a Total Solution for Its Customers
12-31
LO4
LOGISTICS & SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT
SUPPLY CHAIN MGMT & MKT STRATEGY
Dell: A Responsive Supply Chain
Wal-Mart: An Efficient Supply Chain
• Cross-docking
12-32
LO4
TWO CONCEPTS OF LOGISTICS
MANAGEMENT IN A SUPPLY CHAIN
Total Logistics Cost Concept
Customer Service Concept
12-33
FIGURE 12-9 Supply chain managers
balance five total logistics cost factors
against four customer service factors
12-34
LO4
KEY FUNCTIONS IN A SUPPLY CHAIN
CUSTOMER SERVICE FACTORS
Time
• Lead Time
Order Cycle Time
Replenishment Time
• Quick Response
• Efficient Consumer Response
12-35
LO4
KEY FUNCTIONS IN A SUPPLY CHAIN
CUSTOMER SERVICE FACTORS
Dependability
Communication
Convenience
• Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI)
12-36
LO4
KEY FUNCTIONS IN A SUPPLY CHAIN
TOTAL LOGISTICS COST FACTORS
Third-Party Logistics Providers
Transportation Mode Service Criteria
• Cost
• Dependability
• Time
• Accessibility
• Capability
• Frequency
12-37
FIGURE 12-B Advantages and
disadvantages of five transportation modes
12-38
LO4
KEY FUNCTIONS IN A SUPPLY CHAIN
TRANSPORTATION MODES
Railroads
• Unit Train
• Intermodal Transportation
Piggyback or
Trailer on Flat Car
Containers
12-39
LO4
KEY FUNCTIONS IN A SUPPLY CHAIN
TRANSPORTATION MODES
Motor Carriers
(Trucks)
Air Carriers and
Express Companies
Freight Forwarders
12-40
LO4
KEY FUNCTIONS IN A SUPPLY CHAIN
TRANSPORTATION MODES
Pipelines
Water Carriers
12-41
LO4
KEY FUNCTIONS IN A SUPPLY CHAIN
WAREHOUSING AND MATERIALS HANDLING
Storage Warehouses
Distribution Centers
Materials Handling
12-42
LO4
KEY FUNCTIONS IN A SUPPLY CHAIN
ORDER PROCESSING
Stages of Order Processing
Electronic Data Interchanges (EDI)
Extranet
12-43
LO4
KEY FUNCTIONS IN A SUPPLY CHAIN
INVENTORY MANAGEMENT
Reasons for Inventory
Inventory Costs
• Capital Costs
• Storage Costs
• Inventory
Service Costs
• Risk Costs
12-44
LO4
KEY FUNCTIONS IN A SUPPLY CHAIN
INVENTORY MANAGEMENT
Supply Chain Inventory Strategies
• Just-in-Time (JIT) Concept
12-45
LO4
CLOSING THE LOOP:
REVERSE LOGISTICS
Reverse Logistics
UPS Video
12-46
MAKING RESPONSIBLE DECISIONS
LO4
Reverse Logistics and Green Marketing
Go Together at Hewlett-Packard: Recycling e-Waste
12-47