Industrial Revolution
1865-1900 the United States experienced a surge of industrial growth
Marked beginning of second industrial revolution
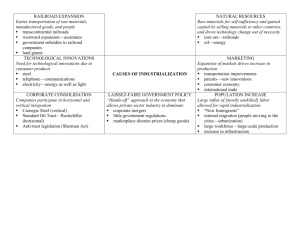
In the late 1800's steel helped spur a second industrial revolution
It was used to build railroad tracks, bridges, and tall city buildings
Steel was around long before the second industrial revolution
Advantages
Strength
Flexibility – could be bent without cracking
problems converting steel from iron ore – removing the impurites
Long slow expensive process
Henry Bessemer in Great Britain and William Kelly in the United
States: Developed new process
Bessemer Process: put out more steel in a day than old technology could in a week
Production required iron ore – most came from the
Iron Range of Minnesota
One of the major consumers of steel were the railroads
Construction
Led to countless other inventions
Automobile
Appliances
Etc.
The development of a process to refine oil also affected industrial practices
Refined crude oil replaced whale oil and could be turned into kerosene
Eventually – gasoline, diesel fuel and many other products
Edwin Drake found oil in
Pennsylvania. It was referred to
Drake’s Folly. Pumped out 20 barrels a day.
Led to intense drilling.
Black Gold
Elijah McCoy made a significant contribution to the industrial use of oil
Invented a lubricating cup that fed oil to parts of a machine while it was running
Innovations in the steel and oil industries lead to a surge of new advances in the transportation industry
This lead to a massive expansion in the railroad network laid the groundwork for air flight and the automobile Workers build the Central Pacific Railroad
Made travel more efficient
Closer contact with each other
It allowed isolated regions to link up with the rest of the United
States
The availability of cheaper steel encouraged railroad companies to lay thousands of miles of new track
This led to a more efficient network of rail transportation
This made it possible to lengthen tracks and make travel a lot less expensive
Transcontinental
Railroad was completed in 1869
Central Pacific and
Union Pacific Railroads were joined
This would allow for towns to spring up and existing towns to transform into lager cities.
The Central Pacific and the Union
Pacific Meet at Promontory Point,
Utah.
Innovations in oil led to development of motors and the creation of a new mode of transportation
Gasoline powered engine led to the creation of a more practical self propelled vehicle
It was limited however since the only ones to have them were the wealthy 1 st practical automobile - 1893
Internal combustion engine
Dec. 17 th 1903 Orville
Wright made the first piloted flight of 12 seconds and 120 feet
This received little public attention
As word spread more people tried their hands in the new technology
Samuel Morse: invented a means of communicating over wires with electricity
Morse Code
Businesses recognized this tool and used it to place orders
Dramatically cut the time necessary to communicate over long distances
Western Union became one of the largest telegraph companies
Western Union Telegraph Office
Patented by
Alexander Graham
Bell
“The Talking
Telegraph”
One of the greatest marvels
Businesses turned their attention to the telephone and replaced the telegraph
Woman with an early typewriter - 1893
Christopher Sholes in
1867
Would quickly produce easily legible documents
His design was the first to be marketed
Provided work opportunity for women in typing pools
Thomas Edison with the 1 st phonograph
Edison made his mark in electricity, light bulbs, phonographs, and early motion picture cameras.
He went into the invention business full time
Made the promise that he and his crew would deliver an invention every ten days
Over 1,000 patents
Business structure
Shares of ownership are sold to raise money for the business
Shareholders receive a percentage of the profits through dividends
Shareholders have limited liability
Very stable as it can last many generations – a corporation does not end when an owner dies
• Carnegie used knowledge of business to reduce production costs.
• Vertical Integration – he owned all phases of the steel production process
• From ore to the finished product – he controlled the whole process
Steel Mill - Ohio
Andrew Carnegie
STANDARD OIL TRUST
Rockefeller used horizontal integration – owned all of one part of the production process
Oil Refining
Was able to control the industry because no one else could refine oil
John D. Rockefeller
Following the civil war, Vanderbilt bought up railroads in the northeast
Used smaller lines to create direct shipping routes between major cities
Owned 4,500 miles of track and was worth
$100,000,000 at his death in 1877 Cornelius Vanderbilt
Made a fortune in the railroad industry
Westinghouse Air Brake
Co.
7000 rail cars were equipped with brakes
He made it possible for trains to carry more as well as travel faster
Another successful railroad tycoon
Designed railcars to be more comfortable for passengers on longer trips
Tried to create a company town
Build a factory and a town around it
Residents grew dissatisfied when he became too controlling Pullman’s sleeping car
People wanted trusts to be outlawed
Trust – a group of companies controlled by one board of directors (created powerful cartels and monopolies)
With no competition the product and prices were not be good for consumers
Sherman Antitrust Act: Outlawed all monopolies and trusts that restrained trade
Many new workers were immigrants
they came to make a living
to provide dowries for daughters purchase land gain work for their sons
African Americans joined them in the workforce
Most of the industries would not offer blacks jobs
-they were stuck in the dirtiest and most dangerous jobs
Most women worked because family needed money
The number of children working also increased for the same reason
It wasn’t hard work but it was monotonous because they would do the same thing all day.
12 hour shifts
1-2 dollars a week wages
Dangerous machines – spinning/moving parts
No sick-leave, vacation, unemployment, workman’s compensation
Workers were viewed as part of the machine
Conditions were worse for unskilled workers
Children sorting and tying tobacco
Labor Union – organization whose purpose is to improve working conditions and pay for its members
Provided one voice in negotiations with management
Taylor strike in New York City
Workers wanted a change
Strike – work stoppage in protest of something
Knights of Labor: White male union. Eight hour work day, equal pay for equal work, and an end to child labor.
Leadership of the Knights of Labor
In 1886 the nation experienced a time period of many intense strikes
Many of these strikes were violent
Haymarket Riot - Chicago
McCormick Harvesting Machine Company
Demand and eight hour work day
Numerous deaths caused by the strike
New union formed by Samuel Gompers
Worked to advance the interests of skilled workers
Plumbers, pipefitters, machinists, carpenters
Workers went on strike in the steel industry.
Guards were hired and the workers would clash with them
Pullman Strike led to people not working and not riding in the trains
Government put a halt to the strike