File - Ms Ellis's Website
advertisement

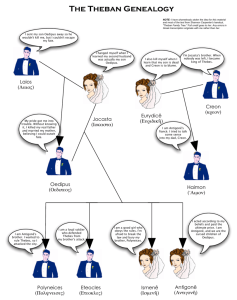
Greek Drama Antigone Cultural Implications Not epic, not lyric, but tragic Only source of entertainment Considered civic responsibility to attend Plays were not performed more than once Performed on a simple, empty stage in an open air amphitheater Tragedy Immediate objective of a tragedy is to arouse pity and fear in the viewers Underlying message was that the audience should learn wisdom from observing the suffering of others…….. And ultimately become a better citizen Usually depicts the downfall of a hero or heroine through a combination of hubris, fate, and the will of the gods Tragic Hero Neither a villain or a model of perfection An overall decent man or woman with a critical flaw or error (hamartia) The hero falls because of some weakness of character, moral blindness or error. The gods may also play a role Plot of a Tragedy All plots have some pathos (suffering) Complex plot includes reversal and recognition Reversal: occurs when a situation seems to be developing in one direction, then suddenly “reverses” to another Oedipus first hears the death of his father, Polybus, which appears to be good news. This is then reversed to be terrible news. Recognition: a change from ignorance to awareness of a bond of love or hate Oedipus kills his father in ignorance and then learns of his true relationship with the King of Thebes. Chorus Greek tragedy contained 2 basic elements: Dramatic, spoken exchanges between 2 or 3 lead characters Choral song Comes from Greek word “choros” = “dance” Chorus sang or chanted the lyric passages of a drama to the tune of a flute or lyre and stylized with choreography Chorus members wore masks to represent a group of people commenting upon the action of the drama (choral response) Strophe and Antistrophe Sophocles 496-406 BC Central Greek Tragedian Wrote 123 plays, we have 7 Was an ambassador, priest, general- fully invested in his city He was concerned with forces of justice, destiny, perspective, pride, and human personality He often has gods as the backdrop of his plays but much more interested in how human beings control their own destiny He was the first to use scenery as a back drop Added a third actor Antigone 442 BC Classical Period Birth of personal awareness Part of the Theban Plays (3 total) All concerned with the fate of Thebes during and after the rein of King Oedipus Characters Antigone: Daughter of King Oedipus and Jocasta Creon: Jocasta’s brother, the new King of Thebes Chorus: the voice of elders in the City of Thebes Haemon: only survivng son of Creon Ismene: sister of Antigone Tiresias: the blind seer of Thebes Eurydice: the wife of Creon