IAFNR.NR.4.PP.3.0 - NAAE Communities of Practice
advertisement

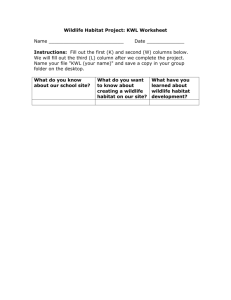
Fish and Wildlife IAFNR MODULE 4 N AT U R A L R E S O U R C E S Wildlife • Living things that are neither human nor domesticated, especially mammals, birds, and fish. – In this lesson, we refer to the higher forms of life as wildlife (vertebrates or non-plant life) • Wildlife is considered a Natural Resource – Wildlife allowed the survival of early American pioneers The Wildlife Population • In order to survive, any species must reproduce – Must be done quicker than an animal dies in nature • Expected population increase • Species require an appropriate habitat – An area that a species can find shelter, food, water, and safety • The Limiting Factor – A shortage of some element of the system—results in restriction of population (Ex. Water availability and presence of predators) • Carrying Capacity – Who remembers this from before? What is Carrying Capacity? The Wildlife Population • Extinct-species no longer exists • Rare-very small population of species exist • Endangered-in danger of extinction • Threatened-species likely to become endangered Image retrieved from: Top-Bottom L-R http://dinosaur-archives.boards.net/thread/64/bighorn-sheep-ovis-canadensis-pictorial; http://www.polarbearsinternational.org/our-work/international-polar-bear-day; http://ecowatch.com/2012/08/31/wyoming-wolves/; http://famebiography.net/wp-content/uploads/1685_puma.jpg; https://pgcpsmess.wordpress.com/2014/03/26/bald-eagle-in-mid-airflight/; http://animals.nationalgeographic.com/animals/birds/whooping-crane/ Wildlife Management Image retrieved from: http://toodalootravels.com/category/nationalwildlife-refuges/ Muscatatuck National Wildlife Refuge in Seymour, IN. Habitat Requirements • The basic requirements of a species habitat – Food • Game animals are typically classifies by the type and amount of food they eat – Cover • A place that provides protection from predators and harsh weather conditions – Water • Most important requirement if wildlife – Home Range and Territory • Home Range: area traveled by game and used for breeding • Territory: area and animal will defend Management Practices Image retrieved from: http://patch.com/california/imperialbeach/chula-vistapreschool-receives-wildlife-habitat-certification • Game Refuges • Habitat Development and Improvement • Coordinating Resources • Hunting Regulations • Predator Control • Artificial Stocking We’ll be covering Game Refuge and Hunting Regulations in more detail Game Refuges • Setting aside land for the protection of wildlife species – Provides the basic needs for survival without the threat of hunters • Muscatatuck National Wildlife Refuge – Over 7,000 acres of refuge land area near Seymour, IN – More than 280 species of birds found there – Highlighted Wildlife at Muscatatuck • Wood Ducks • River Otters • Bald Eagles Hunting Regulations • Hunting Regulations were put into place as early as the 1600’s – Bison faced extinction because of overhunting • Hunting is now controlled on both public and private lands – Used mainly to control overpopulation • Populations are dependent upon: reproduction rates, climate, disease, habitat, and predators – Experts track year-to-year populations to determine regulations like bag limits, hunting season lengths, and closed seasons Freshwater Fishery Management Image retrieved from: https://www.visitstmarysmd.com/activities-attractions/fishing-hunting/ The Habitat Lakes Farm Ponds • Three zones • Uses – Littoral • Shallow zone that contains rooted vegetation (lilies and cattails) • Most aquatic life located in this zone – Phytoplankton present – Limnetic • No rooted vegetation • Photosynthesis reaches the bottom of this zone • Fish also present in this area – Phytoplankton present – Profundal • Bottom zone, no sunlight • Warmest in winter and coolest in summer • Bacteria thrive in this zone – Water Livestock – Recreation – Fire Protection – Fish Production • Important to manage farm ponds properly Common Freshwater Game Fish • Largemouth Bass • Bluegill • Channel Catfish Image retrieved from: Top-Bottom: https://www1.maine.gov/ifw/fishing/species/identification/largemouthbass.htm ; http://www.shelbyfishfarm.com/Our-Fish.htm; http://www.agfc.com/youth/Pages/YouthGetStartedFishingCatfish.aspx Management • Vegetation – Provides food, shelter, oxygen, and area for nesting and spawning – Overabundance can cause problems in fish populations • Controlled biologically and chemically • Sampling – Tracking fish species and growth • Population Removal or Adjustment – Procedures to remove or lessen unwanted species of fish • Fishing Regulation – Commonly a limit of fish taken from public waters • Water Quality – Essential for fish production – Checking levels of temperature, oxygen, pH, and clarity Go FishIN! • Would you like to go fishing? • Indiana DNR has a new urban fishing program! – City Lakes are supplied with rainbow trout and catfish for recreational fishing – 17 and younger DO NOT need a fishing license – 18 and older DO need a fishing license • FishIN in Indianapolis – Fort Harrison State Park – Riverside Park Aquaculture • Propagation or rearing of aquatic organisms in controlled or selected environments for commercial use including food, recreation, or other public purposes • Most of the seafood consumed in the US is imported • Wouldn’t it be nice if we could produce seafood right here in our own backyard? Image retrieved from: http://followgreenliving.com/eco-friendly-aquaculture/ Indiana Aquaculture • Indiana produces 1.5 million pounds of fish per year from about 40 farmers estimated at a value of $15 million • Fish grown in Indiana – tilapia, yellow perch, prawns, shrimp, bait fish, catfish, hybrid striped bass, bluegill and decorative fish. • Indiana farmers are replacing fish meal with soybean meal in fish feeds to be more sustainable Image retrieved from: http://www.indianasoybean.com/strategic-programs/indianaaquaculture/42-strategic-programs-aquaculture/79-indiana-aquaculture-producers References • Camp, W., & Heath-Camp, B. (2009) Managing our Natural Resources. New York: Delmar. • Indiana Soybean Alliance. (N.D.) Indiana Aquaculture. Retrieved from: http://www.indianasoybean.com/strategicprograms/indiana-aquaculture • U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service. (2015, Feb. 19). Muscatatuck. Retrieved from: http://www.fws.gov/refuge/Muscatatuck/