electromagnetic spectrum notes bk
advertisement
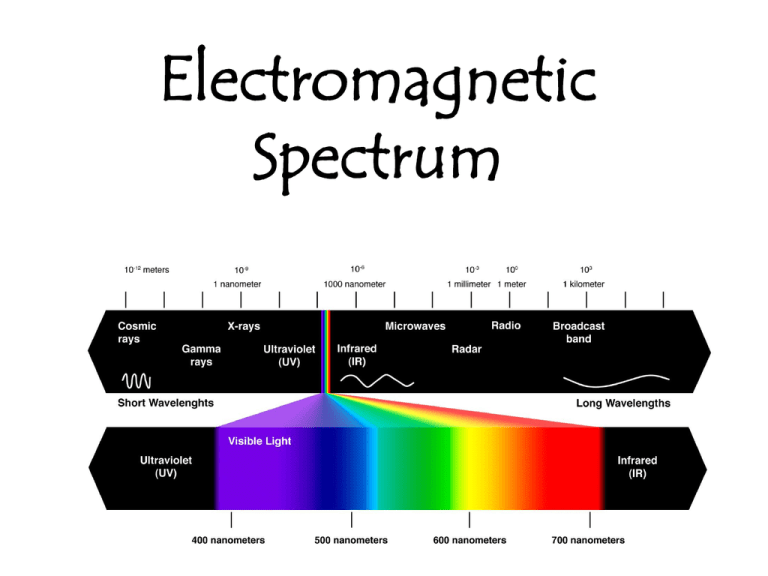
Electromagnetic Spectrum Radiation – energy moving from a source as a wave Light is a combination of electric and magnetic energy. Light can behave as both a particle and a wave. The particle is a packet of light called a photon. Two main properties of light: Brightness (intensity) - amount of energy carried by light - determined by the height (amplitude) of the wave OR - the number of photons Color Color Color of light is determined by its wavelength (λ). Wavelength – the distance from crest to crest Frequency – the number of crests passing a given point in a second (measured in cycles per second OR Hertz -Hz) Amplitude – distance from the center of the wave to the crest or trough Velocity (speed) of a wave: The velocity of a wave can be calculated using the formula: V= ν λ Where V = velocity ν = frequency and λ = wavelength The speed of light is 3.0x10-8 m/s. This is actually the speed of ALL wavelengths of all of the different types of radiation- including light. Because the velocity is the same, as wavelength increases, frequency decreases. Electromagnetic Spectrum The electromagnetic spectrum spans longer and shorter than the visible spectrum. Types of Radiation Gamma Rays (γ) - High Energy radiation- The “dangerous” radiation from nuclear decay, nuclear reactors, and bombs. - Gamma radiation can be stopped by several feet of concrete, or many inches (7-8 or so), of lead. X Rays • X rays go through “stuff” such as skin, and clothing. Depending on the density of the “stuff” film is exposed in different amounts. • From the following x-rays- you can see the skin ( barely) bones ( quite well) and even metal- (very clearly) as X rays do not pass easily through very dense objects- such as metal, etc. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation What is the most important source? The Sun What protects the earth from UV radiation? The ozone layer U.V. radiation is bad because it causes: Skin cancer Visible Spectrum Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo, Violet ROYGBIV Red – longer wave length Blue – shorter wavelength White light is a mixture of all colors. Infrared Radiation Infra- beyond Infrared is a larger wavelength than red. We can’t perceive it, but some animals such as snakes can. Infrared radiation I.R. is used in remote control devices and heat lamps. This way McDonalds can cook a hamburger 4 hours ago, and keep it hot for you! Microwaves Microwave radiation has been used in communication as well as … Cooking popcorn! Microwaves cause water molecules (in food) to vibrate and thus heat up. Radar Radars send out a signal, it hits an object and reflects back to the sender. Knowing that the signal travels at the speed of light (really fast!) a computer can determine how fast an object is moving based on the time it takes for a signal to get back to the receiver. “Stealth” planes use radar absorbing substances on their surfaces, and lots of funky angles to prevent radar signals from getting back to the receiver, thus making it hard to detect. Television Analog signals Use a typical electromagnetic radiation beamed from a TV station to a tower, or a satellite, then beamed to your rabbit ears antennae. Radio waves Radio waves come in a large range of sizes. They can be produced by stars, galaxies, nebulae, and black holes, therefore radio telescopes can be used to study stars and galaxies. • Several types of radio signals • Shortwave- perhaps still used by amateur radio operators • FM radio - Frequency Modulation • AM radio - Amplitude Modulation




