life_science
advertisement

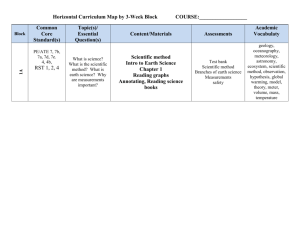
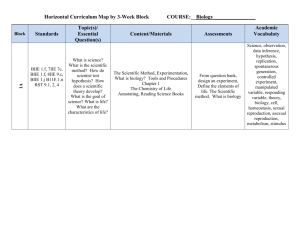
Horizontal Curriculum Map by 3-Week Block 1A Block Standard(s) PE/ATE 7, 7b, 7c PE/ATE 1, 1a, 1f, 2, 2a, 2b, 2e, 5, 5a, 5b, 7a, 3c, 7b, 7d RST 1,2, 4 Topic(s)/ Essential Question(s) What is science? What is the scientific method? Why is science beneficial? How do you design experiments? What tools do scientists do? What is life? Why do organisms need food, water, air and living space? What is atp? COURSE:___Life Science_______________ Content/Materials Scientific method, tools and measurements Chapter 1 and 2 Annotating, Reading Science Books Assessments From bank, scientific method, what is science, tools, characteristics of life, ATP, Academic Vocabulaty Life science, scientific method, hypothesis, factor, controlled experiment, variable, theory, technology, compound light microscope, electron microscope, meter, area, volume, mass, temperature, cell, stimulus, homeostasis, asexual reproduction, sexual reproduction, DNA, heredity, metabolism, producers, consumers, decomposers, proteins, enzymes, carbohydrates, lipids, phospholipids, nucleic acids, ATP 1B Block Standard(s) PE/ATE 6a, 7, 7a, 6, 6a, 6e, 6f, 6g, 7, 7a, 7b, 7d, 7c, PE/ATE 1, 1a, 1b, 1f, 5, 5a, 5b, 7b, 1c, 2, 2e, 4, 4e, WHST 1, 6 Topic(s)/ Essential Question(s) How are electromagnetic waves different from other waves? What are the characteristics of life? How does light relate to life? Content/Materials Light Chapter 3 Cells Chapter 4 Experimentation Writing scientific reports Assessments From assessment bank Electromagnetic spectrum, reflection, absorption, refraction, organization of life, discovery of cells, Eukaryotic cells Academic Vocabulaty Wave, electromagnetic wave, wavelength, frequency, electromagnetic spectrum, reflection, law of reflection, absorption, scattering, transmission, pigment, refraction, lens, convex lens, concave lens, tissue, organ, organ systems, organisms, unicellular, multicellular, population, community, ecosystem, cell theory, cell membrane, organelles, cytoplasm, surface to volume ration, nucleus, prokaryotic, eukaryotic, bacteria, cell wall, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, chloroplast, Golgi complex, vesicles, vacuole, lysosomes, 1C Block Standard(s) PE/ATE 7, 7a, 7c, 1, 1a, 1b, 1d, 3c, 4, 5, 5a, 1e, 1f RST 1, 2, 3 WHST 1,4,5 Topic(s)/ Essential Question(s) How do cells interact with their environment? What is the cell cycle? Content/Materials Cells Chapter 5 Reading for Science specific publications Assessments From test bank Diffusion, cell energy, cell cycle Academic Vocabulaty Diffusion, osmosis, passive transport, active transport, endocytosis, exocytosis, photosynthesis, cellular respiration, fermentation, cell cycle, chromosome, binary fission, homologous chromosomes, centromere, chromatids, mitosis, cytokinesis, 2A Block Standard(s) PE/ATE 7, 7a, 7c, 2b-2c, 5, 5f, 7b7d, 5a, 1, 2, WHST 2, 6, 7 2B PE/ATE 7, 7a, 7c, 2b-2c, 5, 5f, 7b7d, 5a, 1, 2, RST 1, 7, 8 Topic(s)/ Essential Question(s) Content/Materials Assessments What is heredity? What are genes? What is meiosis? What are the building blocks of life? Genetics Chapter 6 Writing for Science From test bank Heredity, Mendel, Meiosis, DNA, genetic engineering What is heredity? What are genes? What is meiosis? What are the building blocks of life? Genetics Chapter 7 Plus evolution, see below Reading Data From test bank Heredity, Mendel, Meiosis, DNA, genetic engineering Academic Vocabulaty Heredity, selfpollinating plant, true-breeding plant, dominant trait, recessive trait, genes, alleles, Punnett square, genotype, probability, sex cells, homologous, chromosomes, meiosis, sex chromosomes, DNA nucleotide, adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine, ribosome, mutation, mutagen, pedigree, genetic engineering, DNA fingerprinting, Human Genome Project DNA nucleotide, adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine, ribosome, mutation, mutagen, pedigree, genetic engineering, DNA fingerprinting, Human Genome Project 2C Block Standard(s) Topic(s)/ Essential Question(s) Why do fossils PE/ATE 7, 7a, 7b, matter? How do 2e, 3, 3a-3c, 3e, organisms change 4, 4a, 4c-4e, 4g, over time? How does 5, 7c, 7d, 2b, 4f, evolution happen? 4d, 1c, 4b What is natural RST 1, 2, 7 selection? Content/Materials Evolution (overlap with above) Chapter 8, 9 Comparing sources Assessments From exam bank Natural selection, adaptation, process of evolution, eras of geologic time scale, human evolution Academic Vocabulaty Adaptation, species, evolution, fossil, fossil record, vestigial structures, trait, selective breeding, natural selection, mutation, generation time, speciation, paleontologist, fossil, rock cycle, relative dating, absolute dating, half-life, geologic time scale, extinct, mass extinction, Pangaea, plate tectonics, Precambrian time, prokaryote, anaerobic, ozone, eukaryote, Paleozoic era, Mesozoic era, Cenozoic era, primate, hominid, prosimian, australopithecine, Neanderthal, CroMagnon 3A Block Standard(s) PE/ATE 7, 7c, 7e, 3, 3a-3d, 4, 4e, 7b, 1, 1b-1d, 4d, 5, 5a WHST 1,2, 4,5 ,6 3B PE/ATE 3e, 7, 7a, 7c, 3, 5, 5f, 7b, 5, RST 1,2, 8, 9 Topic(s)/ Essential Question(s) Why do we need to classify? What are the six kingdoms? What are ecosystems? Why are they important? What are the different biomes? What makes up the ocean? What are the differences between ocean and freshwater ecosystems? Content/Materials Classification Chapter 10 Observation writing Ecology Chapter 17 Evaluating scientific arguments Assessments From Exam bank, levels of classification, scientific names, six kingdoms From exam bank, land ecosystems, marine ecosystems, freshwater ecosystems Academic Vocabulaty Classification, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species, taxonomy, dichotomous key, bacteria, Archaebacteria, Eubacteria, Protista, Plantae, Fungi, Animalia Abiotic, biome, deciduous, conifer, diversity, savanna, desert, tundra, permafrost, marine, phytoplankton, zooplankton, Sargassum, estuary, tributary, littoral zone, open-water zone, deep-water zone, wetland, marsh, swamp 3C Block Standard(s) PE/ATE 7, 7a, 7b, 3e, 7c, WHST 2, 7 4A PE/ATE 7, 7c, 1b, 1d, 2a, 2b, 3c, 5, 5a, 5f, 6f, 7b WHST 1, RST 1,2, 4 Topic(s)/ Essential Question(s) How do humans change their environment? Why is conservation important? What makes a plant a plant? How are plants structured? What is the purpose of seeds? How do plants reproduce? How do they make food? How do plants respond to the environment? How do plants grow? Content/Materials Ecology Chapter 18 Writing scientific arguments Plants Chapter 11, 12 Writing observations Assessments From test bank Pollution and conservation From test bank Plant structure Academic Vocabulaty Pollution, pollutant, toxic, radioactive waste, renewable resource, nonrenewable resource, alien, overpopulation, biodiversity, deforestation, biodegradable Cuticle, sporophyte, gametophyte, nonvascular plant, vascular plant, gymnosperm, angiosperm, xylem, phloem, epidermis, taproot, fibrous root, stomata, sepals, petals, stamen, pistil, stigma, ovary, dormant, chlorophyll, cellular respiration, stomata, transpiration, tropism, phototropism, gravitropism, evergreen, deciduous, hormones Block Standard(s) 4B PE/ATE 7, 7a, 7c, 7e. 1, 1b, 2a, 2b, 5, 5a, 7b, 2c, 3, 3a,3d, 2a, RST 2, 6, 7 WHST 2,4, 6, 7 Topic(s)/ Essential Question(s) What are the characteristics of animals? What is the difference between learned and innate behavior? How do animals communicate? Content/Materials Animals, Invertebrates Chapter 13, 14 Scientific Arguments Assessments Test bank Vertebrate, Invertebrate, animal behavior, communication Academic Vocabulaty Vertebrate, invertebrate, multicellular, embryo, tissue, organ, consumer, predator, prey, camouflage, innate behavior, learned behavior, migrate, hibernation, estivation, biological clock, circadian rhythm, navigate, landmark, bilateral symmetry, radial symmetry, asymmetrical, ganglia, gut, coelom, medusa, polyp, parasite, host, exoskeleton, compound eye, antennae, mandible, metamorphosis, endoskeleton, water vascular system, Block Standard(s) 4C PE/ATE 7, 7a, 7d, 5, 5c, 2a, 4e, 5a, 6, 7, 7b, 7c, 3, 3c, 4, 4e, 5, 5c, 3a, RST 2, 6, 7 WHST 2,4,6, 7 Topic(s)/ Essential Question(s) What is a chordates? What are fish? What is the difference between amphibians and reptiles? Why are birds like reptiles? What are characteristics of mammals? Content/Materials Fish and Birds Chapter 15, Chapter 16 Arguments Assessments Test bank Vertebrate, classification of fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, mammals, Academic Vocabulaty Endotherm, ectotherm, fins, scales, lateral line system, gills, external fertilization, internal fertilization, denticles, swim bladder, lung, tadpole, metamorphosis, therapsid, amniotic egg, down feather, contour feather, preening, lift, brooding, precocial chick, altricial chick, therapsid, mammary glands, diaphragm, monotreme, marsupial, placental mammal, placenta, gestation period, carnivore, primate