Group #6 - s3.amazonaws.com
advertisement

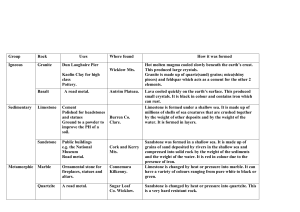
Geology of Southern Oklahoma Group #6 Ronnie Miller Amy Miller Kim Scott Kristi Birdsong Hannah Benson Amy Benson Reina Womack Tammara Cook Brenda Wright Lee Vertrees Sedimentary Rocks of Bryan County Quaternary Period • Alluvium • 20-30 ft deep • Sediment that will eventually form conglomerate rocks • 10,000 years –present • Qt Cretaceous Period Dexter Sandstone • • • • • 85-90 ft thick Kwd Shallow ocean formation Natural Aquifer Yellow brown, iron containing sedimentary rock Bennington Limestone • 7-13 feet thick • Kb • Deep Ocean Formation • Hard limestone w/fossil • Blue-gray, very dense, fossilized limestone Fossilized Bennington Limestone • • • • • 7-13 feet thick Kb Deep Ocean Formation Hard limestone w/fossil Blue-gray, very dense, fossilized limestone Pawpaw Sandstone • 40-45 feet thick • Kbp • Youngest of the Bokchito Formation Evidence of Sandstone • Sandstone is permeable to water. Natural Aquifer • Plant Growth – – – – Willow Trees Mimosa Tres Cat tails Horse tail rush Soper Limestone • • • • 0-2 feet thick Kbs Deep Ocean Deposit Gray, fossilized limestone Caddo Formation • 150-160 feet thick • Kc • Alternating layers of limestone and shale • Cream colored limestone, gray colored shale Kiamichi Formation • 30-40 feet thick • Kk • Deep Ocean Formation • Dark-gray to black limestone • Fossilized with ammonites Geology of Johnston County Antlers Sandstone • 250-600 feet thick • Ka • Poorly cemented, unfossilized, white to yellow sandstone • Used by Cardinal Glass in Durant • Also used as frac sand by oil companies Wapanuka Formation • • • • Limestone and Shale interbedded Shallow Ocean formation Calcium Carbonate from coral reefs Crinoids fossils abundant Springer Formation • Limestone on the ground • Lichens tend to grow on limestone giving them a darker appearance • Found at the edge of the ArbuckleSimpson Aquifer Woodford Shale • Dark colored shale • Presence of phosphate nodules • Natural gas deposits are found in Woodford shale • MDsw • Deep Ocean Deposit • 360-408 million years Dolomite • Thick deposit of Magnesium Carbonate • Ocm • 438-500 million years Granodiorite • P€gr • Medium-grained hornblende-biotite Troy Granite • P€tr • Medium-grained pink granite Tishomingo Granite • 1.37 billion years • P€ti Granitic Gneiss • 1.39 billion years • P€gg Trip Through the Arbuckles Anticlines • Form when convergent forces in the earth fold rock layers upward. • Causing the oldest layers at the core with younger layers progressing outward from the core Synclines • Form when convergent forces in the earth fold rock layers downward. • Causing the oldest layers at the core with younger layers progressing outward from the core Faults • Occur where forces inside earth have caused layers to break and fall at different angles. Collins Ranch Conglomerate • IPcr • 3000 ft thick est. Woodford Shale • MDw • Blake shale Viola Group • Limestones that form steep resistant ridges • Ov • 684 feet thick Oil Creek Formation • Basal Sandstone • Ooc • 747 ft thick Joins Formation • Thin bedded, fossiliferous light gray limestone • Oj • 294 feet thick West Spring Creek Limestone • 284 ft thick • Ow • Mostly gray to tan limestones Butterly Dolomite • Oldest member of the upper Arbuckle group • Ob Sylvian Shale • Mostly olive green plastic to fissile clay shale • Os • At contact zone with Keel Limestone of the Hunton Group Kindblade Formation • Gray, fine grained limestone • Ok • 1440 feet thick Royer Dolomite • Only Cambrian sample • Pink to gray massive dolomite • Cry