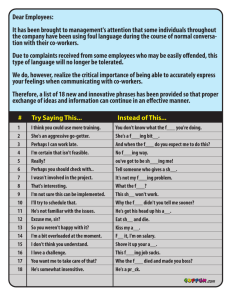
Risk and capital tend to be managed in
advertisement

Financial Conglomerates Koos Timmermans General Manager, Market Risk Management IMF Conference, Washington, 1 June 2005 Table of contents 1. Introduction on ING Group 2. Being a financial conglomerate 3. Risk and capital initiatives 4. Concluding remarks 2 1. Introduction on ING Group 3 ING in a nutshell • Created from a merger in 1991 • Financial Conglomerate: Banking, insurance and asset mgt • Over 50 countries, around 115,000 employees • Strong presence in emerging markets • Market capitalization around EUR 50 billion • Broad international share ownership • Modern corporate governance • Top 100 global brand 4 Top 20 global financial institutions # 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Name Market value in EUR billion as of 25 April 2005 CITIGROUP INC BANK OF AMERICA CORP HSBC HOLDINGS AIG JPM CHASE BERKSHIRE HATHAWAY INC WELLS FARGO ROYAL BANK SCOTLAND UBS WACHOVIA CORP BANCO SANTANDER BARCLAYS ING AMERICAN EXPRESS BNP PARIBAS HALIFAX BANK OF SCOTLAND MITSUBISHI TOKYO FINANCIAL MORGAN STANLEY DEAN WITTER MIZUHO FINANCIAL GROUP BBVA 185.4 138.8 134.9 101.0 95.3 80.2 76.3 74.9 70.4 61.4 57.4 52.7 48.8 47.9 46.6 45.3 43.3 42.1 42.1 41.2 Source : Bloomberg 5 Group organized along six business lines ING Group Insurance Americas Insurance Europe Insurance Asia/Pacific Wholesale Banking Retail Banking Benefits of structure: • • • Simple, clear and transparent Client focus and business logic leads Personal accountability and empowerment • Short and direct reporting lines • Appropriate attention and place for growth engines • Capture the benefits of the Group 6 ING Direct Composition of Group capital base (31 March 2005, EUR bn) Group Net equity Insurance Bank 25.9 Hybrid capital 5.9 Debt 3.2 Total capitalisation/equity 35.0 14.9 20.1 Minorities 1.0 0.5 Hybrid capital 2.5 Other (incl. ING shares) 0.1 Capital base 18.4 7 20.7 2. Being a financial conglomerate 8 What is a financial conglomerate? • A financial conglomerate is a company that combines different types of financial institutions under one roof: • Banking • Insurance • Asset management • The legal structure of the conglomerate is relevant 9 ING believes in the benefit of being a financial conglomerate… • Diversification between bank, insurer and asset manager (regions, activities, clients) • Reduced economic capital • Better ratings, also at holding-level • Cross-balance-sheet utilization • The whole is worth more than the sum of its parts, provided that operations are integrated • • • • • Risk and capital management Back office / systems Distribution channels, branding and marketing HR&MD Culture 10 …however, managing a financial conglomerate also poses challenges • Financial conglomerates are a relatively new phenomenon and not allowed in some countries • Large, complex organization • Different systems, accounting, risk management • Different cultures to combine • Myriad of regulation – often local and specific to banking, insurance or asset management • Basel II for Banks, EU Solvency II Directive for Insurance, IFRS / US GAAP, Corporate Governance (SOX, etc.)… • Lack of external understanding and transparency • Most analysts specialized in either banks or insurers - not both • Not straightforward to quantify and justify diversification benefit 11 3. Risk and capital initiatives 12 To reap the benefit of being a financial conglomerate ING is integrating risk and capital management • Risk and capital tend to be managed in ‘silos’ • Risk silos (credit, market, operational, insurance etc.) • Business silos (bank, insurance and asset management) • Regional / country silos • ING has recently launched two initiatives to gain an integrated view • Group-level risk appetite framework with Board involvement • Integrated Capital Management function 13 The Risk Dashboard is a quarterly report providing Senior Management with a holistic risk view 1. Current risk profile 2. Evolution of risk metrics • Presents current and projected risk profile of ING Group 8. Action tracking 3. Stress analysis Risk Dashboard 7. Limit breaches 4. Threat scenarios 6. Concentrations 5. Key risk trends 14 • • • Aggregate level By risk type By Line of Business • Board-level discussion takes place at least quarterly • Risk issues with Group-level impact are addressed and agreed actions are tracked ING has set up an integrated Capital Management Function • Internally, ING Group uses economic capital as a core management metric • Externally, ING is evaluated on accounting measures: • Integrated Capital Management centralizes the mismatch between internal requirements and external reporting/regulation 15 Future: The role of risk management at ING is expanding Evolution of risk management philosophy Link to strategy #6 High #5 Strategic planning integration • Shareholders care about absolute levels of risk and about the relativity between risk and return #4 Return optimization #3 Medium Risk management #2 Risk measurement #1 • Risk management can provide value-adding input to risk/return optimization and strategic planning (threats and opportunities) Loss minimization Low Compliance Risk controller Balance sheet protection Industry standard (last five years) • Most financial institutions have developed effective mechanisms to control downside risk Risk/return optimization Value creation Industry best practice (next five years) 16 4. Concluding remarks 17 Several themes have triggered a move towards integrating financial management • Benefit of financial conglomerate visible through risk dashboard • First step to risk measurement per risk category • Economic capital = priority in bank & insurance • Integrated capital management deals with regulatory vs economic capital differences 18