Cell Division
advertisement

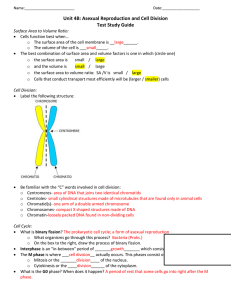
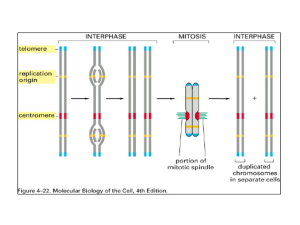
GENETICS GENETICS BRAINSTORM Genetic technology is changing at a rapid rate. Soon humans will have enough knowledge and technology to modify humans. The question is should we? GENETICS The field of biology that involves the study of how genetic material is passed from one generation of organisms or cells to the next generation All cells come from pre-existing cells, therefore, the continuity of life is dependent on the process of REPRODUCTION Stages of the Cell Cycle First Major Stage Interphase: Cell grows, develops into a mature, functioning cell, copies it’s DNA and prepares for cell division. 3 phases:G1 (Growth 1),S (Synthesis) and G2 (Growth 2) G1 = major growth period and synthesizing of molecules S = DNA (chromatin) is copied or replicated. The replicated chromatin coils up and forms double stranded chromosomes G2 = continued growth and preparation for Mitosis MITOSIS Let’s draw the key player of mitosis: coiled chromatin centromere chromosome 2 strands of coiled chromatin = sister chromatids Let’s review the 4 stages of Mitosis Structures of Genetic Material DNA is made up of two long strands that form a spiral shape called a double helix Most of the cell cycle, DNA exists as strands of chromatin fibre. Once mitosis begins, the chromatin condenses into distinct chromosomes Structures of Genetic Material •The basic unit of the DNA molecule is called a nucleotide •Each nucleotide consists of 1. phosphate group 2. sugar group 4 Types A-T 3. nitrogenous base C-G Complimentary Base Pairing Paired Chromosomes Human somatic cells have 46 chromosomes ( 23 pairs) For each pair, one chromosome is from the mother, and the other is from the father One pair = sex chromosomes ( X and Y) XX = female, XY = male All other pairs = autosomes Homologous Pair KARYOTYPE: set of chromosomes that an individual has Homologous Chromosomes Are chromosomes that contain the same sequence of genes as another chromosome Genes = are sections of DNA that contain genetic information for the inheritance of specific traits Homologous chromosomes carry genes for the same traits, such as hair colour, at the same location • Each chromosome carries different forms of the same gene called ALLELES • This difference accounts for the differences in specific traits, such as blue eyes versus brown eyes Homework Pg. 168 # 5, 9, 12, 13, 17