Cold War Terms Review - Waterford Union High School
advertisement

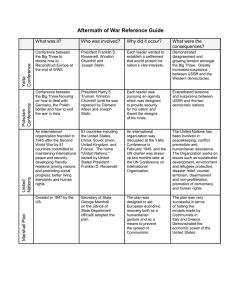
Ch. 27, Section 1 The Beginning of the Cold War The “Big Three” leaders at the Yalta Conference near the end of WWII Winston Churchill (GB), Franklin Roosevelt (US), and Joseph Stalin (USSR) February 1945 Three things agreed upon by the Allied leaders at the Yalta Conference • Free elections in Eastern Europe • The Soviet Union would help with the defeat of Japan after Germany defeated • An international organization to solve world problems would be created (would become known as the United Nations) Potsdam Conference in July 1945 (Near Berlin) LEADERS PRESENT: • Winston Churchill and Clement Atlee (Great Britain) • Harry S Truman (US) • Joseph Stalin (USSR) Potsdam Conference in July 1945 (Near Berlin) Berlin • The leaders agreed Germany and the city of Berlin would be divided into 4 zones of occupation • The US, USSR, Great Britain and France each would control one of the zones War Crimes Trials • Nuremburg Trials – highranking Nazis put on trial for “crimes against humanity” in November 1945 by Allied leaders • 19 Nazi leaders were found guilty and 12 were sentenced to death • Another set of war crimes trials took place in Japan and their wartime leader, Hideki Tojo, was convicted and sentenced to death with 7 others Principle Establish by War Crimes Trials • The trials in Germany and Japan helped establish the principle that individuals must be held responsible for committing war crimes, even when acting on behalf of a government Hideki Tojo on trial in Japan → United Nations U.N. Meets in New York • As agreed to at the Yalta Conference an international organization dedicated to resolving international conflicts was created – the U.N. • 5 Security Council nations with a veto power were: – United States – Great Britain – France – Soviet Union – China U.N. in Cold War and Today • U.N. unable to resolve problems of the Cold War as either the U.S. or the Soviet Union would veto any related action • Today the U.N. works to avoid wars and provides disaster relief, prevents hunger and disease, and combats international terrorism Palestine Mandate • Many Jews moved back to their ancient homeland after WWII • Arab Palestinians lived there • One of the UN’s first actions was to divide Palestine into separate sections for Jews and Arab Palestinians Creation of Israel • Jewish leaders announced the creation of the nation of Israel in May 1948 • The US quickly recognized the new nation • 5 neighboring Arab nations attacked Israel • With US aid, Israel drove them back and took more land than given by the UN • Other wars have been fought since, and tensions have remained high all the way to the present • A term originated by Winston Churchill which refers to the line in Europe following WWII separating the communist nations in Eastern Europe from the democratic nations of Western Europe • In the same speech Churchill warns of Soviet ambitions to keep control of the nations of Eastern Europe and to force them to submit to Soviet control Iron Curtain Winston Churchill giving his “Iron Curtain” speech when visiting the US in 1946 Iron Curtain U.S.S.R. ◄ BALTIC SEA ◄ Stettin ◄ Trieste ADRIATIC SEA ► “From Stettin in the Baltic to Trieste in the Adriatic an Iron Curtain has descended across the continent” -- Winston Churchill The Cold War Churchill, Truman, and Stalin at the Potsdam Conference in the summer of 1945 • A conflict between the US and the Soviet Union, without direct confrontation on the battlefield, that lasted from after WWII until 1991 • It began as Soviet leader Joseph Stalin broke his promise from the Yalta Conference to have free elections in Eastern Europe and instead set up communist dictatorships in these nations • It caused nations of the world to choose what side they would be on, and led to the fear of nuclear war Sources of Distrust between US and USSR that led to the Cold War • Different political and economic systems (US democratic and capitalist and USSR communist) • Disagreement in WWII over when the US would start a second front against Germany • US didn’t tell USSR about our atomic bomb program • Soviet Union broke Yalta Conference pledge to allow free elections in Eastern Europe Truman Stalin Containment Telegram from a U.S. State Dept. official in Moscow, George Kennan, which described the need to contain the spread of Soviet influence • U.S. foreign policy under Pres. Truman to stop the spread of communism to any places that were not already communist during the Cold War • It meant that the U.S. would stop the spread of communism even if it meant going to war (which it did in places like Korea and Vietnam) Truman Doctrine • Policy of the U.S. under Pres. Truman which promised aid to people resisting threats to their democratic freedom • U.S. aid helped defeat communist overthrow attempts in Greece and Turkey • Showed other nations that we would back up our containment policy President Truman giving the speech before Congress in 1947 that outlined his Truman Doctrine and asked for aid to help Greece and Turkey Marshall Plan Green nations received aid, and the red bars show how much in comparison to other nations • Plan created by U.S. Secretary of State, George Marshall, which sent $13 billion in aid to western and southern Europe to help them rebuild after WWII • The plan was to help our democratic allies to handle post-war problems before communism could threaten to take over in their nations Division of Germany after WWII • The division of Germany was first agreed to by Allied leaders at the Yalta Conference, and the exact borders were set at the Potsdam Conference after Nazi Germany was defeated • Later the British, French, and American zones would combine to become the democratic nation of West Germany British zone Soviet zone U.S. zone French zone Division of Berlin • The German capitol city of Berlin was also divided into 4 occupied zones • The French, British, and American sectors of the city combined and became known as West Berlin West Berlin became a democratic zone in the middle of communist East Germany Berlin Airlift Flight paths to West Berlin during airlift • After the Soviet Union blocked access to West Berlin in 1948, Truman responded by airlifting food, fuel, and equipment to West Berlin for nearly a year with non-stop flights until the Soviet Union called off its blockade • Prevented WWIII and showed U.S. would uphold containment ◄ C-47s unloading at Tempelhof Airport in Berlin. Up to 102 of these planes were flying during the first three months of the Berlin Airlift West Berlin citizens watch ► a plane take off from Tempelhof Airport, which was the central point of a massive U.S.-led airlift in 1948 of the city. North Atlantic Treaty Organization • N.A.T.O. was the defense alliance created in 1948 by the democratic nations of Western Europe and North America to prevent against Soviet or communist threats • As United Nations couldn’t solve Cold War problems (as the Soviet Union would veto any U.S.-backed proposals) this alliance was necessary Warsaw Pact • A Treaty signed in Warsaw, Poland in 1955 that set up an organization of communist states in Central and Eastern Europe. • The treaty was an initiative of the Soviet Union and was in direct response to West Germany joining NATO in 1955. • As such, it was the Sovietsponsored communist counterpart to NATO The nations in red above were members of the Warsaw Pact communist alliance G.I. Bill of Rights • Returning veterans flooded the job market • To assist them, the GI Bill of Rights was passed by Congress which provided veterans: – One year of unemployment pay – Four years of college tuition – Low-interest loans for homes, farms, or businesses