Weeks 5 and 6 - Performance Management
advertisement

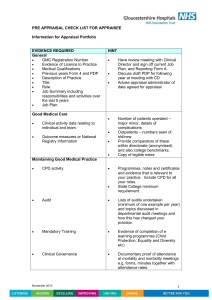
Human Resource Management 2 Performance Management and Appraisal interviewing Nick Kinnie 1 Objectives To recall why performance management is important – in theory and practice To understand the purpose and nature of the appraisal interview in the performance management process To examine the different approaches and styles of appraisal interviews To give an opportunity to gain experience in the practical aspects of appraisal interviewing 2 Performance Management and Appraisal interviewing Introduction – recall the uses, objectives and problems of Performance Management Performance appraisal - what is appraised? Appraisal interviewing - styles, structure and skills Interviewing practice - some guidelines Summing up 3 Introduction Performance Management … has a critical role to play in organisational performance is widespread (found in nine out of ten firms) is vital to all employees is increasingly carried out by line managers is one of the most difficult tasks managers have to carry out (Torrington et al 2005; Grint, 1993; McGregor, 1957; Meyer, 1965) 4 What do we mean by performance management? ‘the policies, procedures and practices that focus on employee performance as a means of fulfilling organisational goals and objectives’ (Lowry (2002) in Marchington and Wilkinson (2005: 187-8)) ‘establishing a framework in which performance by individuals can be directed, monitored, evaluated and rewarded, and whereby the links in the cycle can be audited’ (Mabey and Salaman (1995) in Torrington et al (2005: 261)) 5 Performance Management: why is it used? Key role in linking the goals of the organisation to the individual (vertical integration) Gives a synergy with other HR practices eg reward systems (horizontal integration) Seeking to improve performance at an organisational and individual level Ritualistic aspects 6 How does a performance management system look? Organisational objectives Departmental/team objectives Individual competencies Setting of performance standards Monitoring and Assessment Development Reward Career planning 7 Objectives of Performance Management Systems Set objectives and review performance against objectives/standards Personal development: identify training and development needs and potential Linking team and organisational objectives Source: Performance Management Survey Report September 2005 CIPD 8 Performance Management: some problems Conflicting purposes: judge/coach dilemma Role of the appraiser: competence, motivation and values Role of the appraisee: promotion and development Appraiser/appraisee relationship: quality is key Validity of the criteria: are they related to the job? What is the quality of the data collected? Impact of performance appraisal on performance 9 Conflicting aims Organization Individual Seeking the development of individuals through coaching Seeking valid performance feedback for development Seeking information on which to base reward and promotion decisions Seeking rewards and promotion = conflict 10 Performance Appraisal: What is appraised? Non-criteria or evidence based – personal evaluation Rating traits – personal characteristics Objectives – performance compared with targets Competencies/behaviours – displayed and desired 11 Types of interaction Enquiry Exposition Selection Attitude survey Health screening Joint problem solving Presentation Lecture Briefing Conflict resolution Appraisal Counselling Discipline Negotiation Arbitration Torrington et al (2005: 71) 12 Performance Appraisal: interviewing styles Tell and sell: appraiser acts as a judge – tells the appraisee the result and how to improve Tell and listen: communicates outcomes and listens to reactions Problem solving: appraisee encouraged to discuss problem areas and consider solutions (Maier, N. (1976) The Appraisal interview – the three basic approaches) 13 Performance Appraisal: interview structure Preparation Both parties need to prepare Appraiser: What style to adopt? gather the evidence from all parties Appraisee: self assessment Structure Purpose and rapport – agree purpose and structure Factual review – of the known facts 14 Appraisee views – comments on the last time period (gone well/what could be improved/likes and dislikes) Appraiser views - asks questions, offers views and comments Problem solving – how can any differences be resolved? Objective setting – what actions should be taken, by whom and on what time scale (Torrington et al, 2005: 343) 15 Performance appraisal: interviewing skills Ask the right questions: open, probing, follow up and reflective Engage in active, careful listening to all forms of communication Provide feedback based on evidence and examples Avoid: a focus on failure, control by the appraiser, ends with disagreement (CIPD Performance Appraisal Fact Sheet at cipd.co.uk) 16 Ideally an appraisal meeting is where… Appraisees do most of the talking Appraisers listen actively and provide feedback Scope for reflection and analysis – an exchange of views Performance is analysed not personalities Whole period is reviewed not just isolated incidents – evidence based Achievement is recognised and reinforced Identify areas for improvement – set agree objectives Ends positively with agreed action plans to improve performance (CIPD Performance Appraisal Fact Sheet at cipd.co.uk) 17 Summing up Key strategic and individual role of performance management – new developments Key task for line managers but difficult to carry out successfully Powerful influence on behaviour – both positive and negative Requires careful support and implementation by line managers 18 Features of Performance Management Systems % use % effective Individual annual appraisal 65 83 Objective setting and review 62 82 Personal development plans 62 81 Career management 37 47 Coaching 36 46 Performance related pay 31 39 Competence assessment 31 39 Self appraisal 30 53 19 % use % effective Twice yearly 27 38 360 degree 14 20 Continuous 14 20 Subordinate 11 17 Rolling 10 21 Peer 8 12 Competence related 7 11 Team 6 10 Contribution 4 6 Team pay 3 5 Source: Performance Management Survey Report September 2005 CIPD 20