The Israelites
advertisement
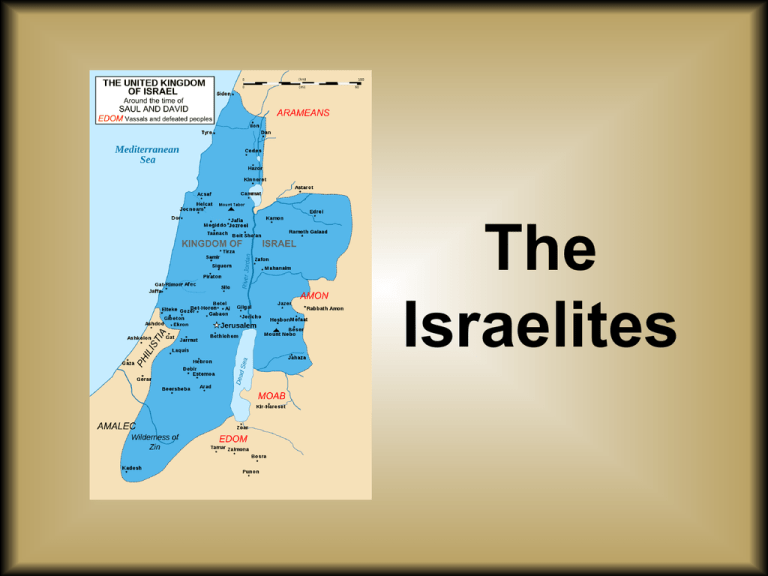
The Israelites Geography and Demography • Extends from the western edge of the Assyrian Empire to the “Upper Sea” • Negev and Sinai Desert Wastelands • Hills of Shephelah and Galilee • Relatively fertile • Jordan River and The Dead Sea • Land also known as Palestine and Canaan • Peoples called Israelites, Hebrews, and Jews • Crossroads linking Anatolia, Egypt, Arabia, and Mesopotamia • Place of significance throughout history • Few natural resources Geography and Demography • Hebrew – Semitic Language • Related to Phoenician & Aramaic Languages • Language parallels ethnic relations Historical Documentation and Discoveries • Archaeological excavations • The royal annals of Egypt and Assyria • The Hebrew Bible contains information about the history of Israel compiled from many sources – Different interpretations of past events – Orally transmitted until the 6th century BCE – Canonical text first appears around the 5th century BCE • Some text added later but very little • Reflects the views of those in control of The Temple • Accuracy can be debated but few other options exist History and the Hebrew Bible • Hebrew Bible tells the story of Abraham, Isaac, and Jacob • Israel promised to Abraham by Yahweh – Story of Abraham may compress the journey of generations to who moved through the grazing lands between the Tigris & Euphrates and the Mediterranean • Other stories may also parallel the conflict between the newly arrived Israelites and the settled peoples of the area – Cain and Abel as well as Sodom and Gomorrah History and the Hebrew Bible • According to the Hebrew Bible many Israelites were taken as slaves by the Egyptians – Biblical account skips over the period of time when the Hyksos ruled over Egypt • Rise and fall of the Hyksos in Egypt possibly connected to the enslavement of Israelites – Egyptian records mention Apiru slaves • Class rather than ethnicity – Coincided with ambitious building projects • Moses leading the freed Israelites from Egypt, although filled with folklore, could be the result of oral stories of the emigration evolving over time History and the Hebrew Bible • The freed Israelites , led by Joshua, attacked and destroyed Jericho and other Canaanite Cities – 1250-1200 BCE – Unified Israelite attack on Canaan is a point of contention among scholars • Some believe that it is more likely the Israelites and other groups simply took advantage of a period of widespread decline in cities in the region History and the Hebrew Bible • The new peoples of the area created a common ancestry in “The Children of Israel” – Common at the time • Land split between 12 Tribes Descended from the sons of Joseph and Jacob – Each tribe had one or more chiefs – Judges – A class of charismatic figures, War heroes, or Skilled arbitrators who transcended tribal boundaries – Tribes bound together by access to the shrine at Shiloh that housed the Ark of the Covenant History and the Hebrew Bible • As the Israelites arrived in their new home the Mediterranean area was in a period of Chaos • The Philistines and Israelites fought frequently – Wars immortalized in biblical stories like those of David and Samson History and the Hebrew Bible UNIFICATION • Saul’s throne handed over to David who unified the Israelites under a monarchy – Capital city moved to Jerusalem along with the Ark – Jerusalem becomes a unified center for politics and religion • David created “cities of refuge” where people could flee from retribution and blood feuds • Record keeping and government innovations • Expanded Israel’s borders through military victories History and the Hebrew Bible UNIFICATION • Peak of ancient Israel civilization came under King Solomon – Created Alliances with neighboring cultures – Built and deployed a fleet of ships to bring treasure, materials, and exotic animals to Israel – The Mythical visit from the Queen of Sheba reflects the trade relationship with Seba and the people of the Horn of Africa – First Temple completed in 960 BCE CULTURE • Lived with extended family under the authority of the eldest male • Marriages were arranged • The brother of a sonless man was expected to marry his brother’s wife should he die • Women provided many vital services and were regarded with respect – Relatively equal status with their husbands • Some restrictions: Divorce, Inheritance, extra-marital affairs – Deborah the Judge fought alongside men and led troops against the Canaanites • Women could be educated • The reality of women’s rights in Israel obscured by male bias in biblical text • Urbanization diminished women’s status Division and Fall • Split in to two kingdoms after the death of Solomon – Israel in the north and Judah in the south – Sometimes at war and other times allies • Syria and Israel united in response to Neo-Assyrian aggression – Israel destroyed and its people deported – New ethnicities were brought in and Israel was stripped of much of the religion and culture of the Israelites – Would be separated from the Jewish people and their culture for much of history Division and Fall • Judah survives the Neo-Assyrians – The Temple destroyed by Nebuchadnezzar of the Neo-Babylonian empire in 587 B.C.E. • The Jewish Diaspora originates at this time – Synagogues and other institutions allow the Jewish People to maintain connections and keeps their religion and culture alive • Babylonian Jews returned to Jerusalem and rebuilt the Temple (The Second Temple) in 515 BCE – Established the Deuteronomic code – Hebrew bible compiled – With Isolation came a strong sense of community that survives today