ENG708
advertisement
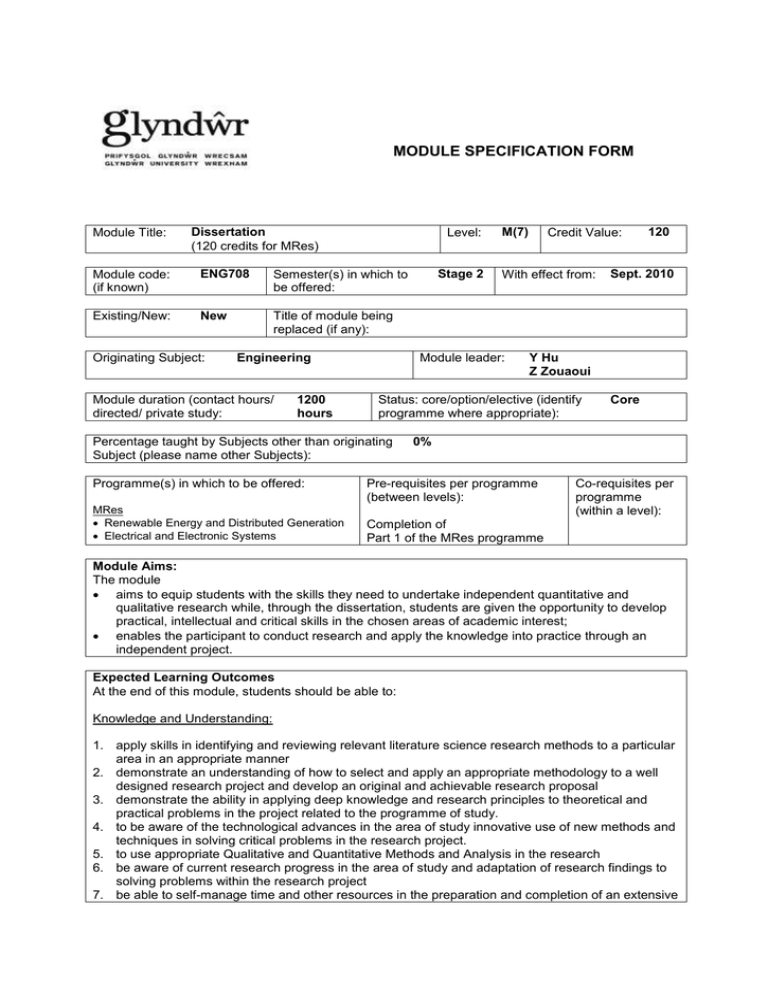
MODULE SPECIFICATION FORM Module Title: Dissertation (120 credits for MRes) Level: Module code: (if known) ENG708 Semester(s) in which to be offered: Existing/New: New Title of module being replaced (if any): Originating Subject: Engineering Module duration (contact hours/ directed/ private study: 1200 hours MRes Renewable Energy and Distributed Generation Electrical and Electronic Systems Credit Value: With effect from: Module leader: 120 Sept. 2010 Y Hu Z Zouaoui Status: core/option/elective (identify programme where appropriate): Percentage taught by Subjects other than originating Subject (please name other Subjects): Programme(s) in which to be offered: Stage 2 M(7) Core 0% Pre-requisites per programme (between levels): Co-requisites per programme (within a level): Completion of Part 1 of the MRes programme Module Aims: The module aims to equip students with the skills they need to undertake independent quantitative and qualitative research while, through the dissertation, students are given the opportunity to develop practical, intellectual and critical skills in the chosen areas of academic interest; enables the participant to conduct research and apply the knowledge into practice through an independent project. Expected Learning Outcomes At the end of this module, students should be able to: Knowledge and Understanding: 1. apply skills in identifying and reviewing relevant literature science research methods to a particular area in an appropriate manner 2. demonstrate an understanding of how to select and apply an appropriate methodology to a well designed research project and develop an original and achievable research proposal 3. demonstrate the ability in applying deep knowledge and research principles to theoretical and practical problems in the project related to the programme of study. 4. to be aware of the technological advances in the area of study innovative use of new methods and techniques in solving critical problems in the research project. 5. to use appropriate Qualitative and Quantitative Methods and Analysis in the research 6. be aware of current research progress in the area of study and adaptation of research findings to solving problems within the research project 7. be able to self-manage time and other resources in the preparation and completion of an extensive research project, including the adaptation of original research plans. 8. to analyse research results and to feed them back the modification and/or further development process of the research plans. 9. to show evidence of an ability to contribute to and develop knowledge and thinking within the field of Engineering. 10. use appropriate techniques in interpreting the ideas and results to produce good quality research. Expected Learning Outcomes (Continued) Transferable/Key Skills and other attributes: Write in an advanced academic manner by following scholarly protocols of organization, citation, and rhetorical presentation (proper diction and style). Communicate research findings appropriately in terms of written and oral presentation. Project management skills. Problem solving skills using selectively available tools and techniques. Decision making in complex and unpredictable situations. Take initiative and personal responsibility Independent learning ability required for continuing professional development Assessment: please indicate the type(s) of assessment (eg examination, oral, coursework, project) and the weighting of each (%). Details of indicative assessment tasks must be included. The participant should show a detailed understanding of informatics, concepts and methods in the chosen subject domain. The project will involve a survey of recent developments in the field, a critical analysis of these developments and a prognosis of future developments. Assessment takes the form of research presentation plus an average 30000 word dissertation on an agreed topic relevant to the programme for those that are undertaking the MRes Degree. The student must also pass a viva-voce examination with a specialist external examiner and a second, internal, examiner. Assessment Type of assessment Assessment One: Learning Outcomes to be met outcomes 1, 2, 4, 6 Weighting Interim presentation covering progress and plans for completion 10% Assessment Two: outcomes 1 - 10 Dissertation 70% Assessment Three: outcomes 1 - 10 Viva voce examination 20% Duration (if exam) Word count or equivalent if appropriate 30 mins 30000 Or equivalent 30 mins Learning and Teaching Strategies: Seminar / workshop, Independent study, Individual supervision Students will be guided towards the choice of an appropriate research topic during the delivery of the Research Methods module. This may be a current research topic of a member of staff, a topic suggested by industry or a topic of particular interest to a student or his or her employer or sponsor. Prior to the start of the project students have to write a project proposal containing an introduction, background to the proposal, outline of the proposal, conclusion and a bibliography. A presentation, covering the progress and plans for completion of project work and dissertation, takes place half-way through the project. Regular timetabled meetings will be held between students and supervisors to discuss the development and progress of the research project and dissertation. Syllabus outline: Supervised independent work leading to the submission of a dissertation of 30,000 words in average, based on innovative research and development work conducted with an awareness of current scholarship. Conduct of the Dissertation Project Supervision: There will be individual supervisor in specialist knowledge to supervise the general conduct and progress of the project. Each student will be required to maintain a Research log folder and to consult with his/her supervisor regularly, normally every week. The Dissertation is assessed by two tutors on the programme. A senior member from the course will be involved in the case there is any discrepancy. Assessment: Successful completion of the Dissertation will demonstrate that the student has the ability: 1. to use together relevant concepts and theories in dealing with particular problems; 2. to design and carry out a coherent piece of research drawing upon an appropriate methodology and using appropriate methods; 3. to deal with theoretical, conceptual, experiments and empirical results in interpreting research findings and generating new knowledge; 4. to present and defend arguments based on theories, concepts, experiments and empirical evidence in project development; 5. to demonstrate the capacity for reflective and analytical thought; 7. provide evidence of a substantial piece of research carried out 8. to present the research process and outcomes effectively, logically in a scholarly manner. The external examiner will be invited to confirm the final grading. Each student will be required to attend a viva voce to defend to dissertation and answer examiners’ questions. Sample Dissertation/Project Topics (MRes) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Hysteresis control of PMSG for wind turbine applications Converter control for Wind Power Plant connect to Grid dsPIC wireless communication; central control system with sub-remote systems Wireless data aquisition and processing using Zigbee Sinusoidal Control of PMSM Motors with dsPIC Field Oriented Control (FOC) of an AC Induction Motor. Bibliography Essential reading: Sage. Salkind, N. J, (2008) Exploring Research, 7th Ed. (Prentice Hall) Sharp et al (2002), The Management of a Student Research Project, (Open University) Other indicative reading: Barrass, R. (2002), Scientists must write: A guide to better writing for scientists, engineers and students, 2nd edition (Routledge0 Beer, D and McMurrey, D. (1997), A guide to writing as an engineer, (John Wiley). Davis, M. (1997), Scientific papers and presentations, (Academic Press) Goodlad, S. (1996) Speaking technically: A handbook for scientists, engineers and physicians on how to improve technical presentations, (Imperial College Press) Holtom, D. and Fisher, E. (1999), Enjoy writing your science thesis and dissertation: a step by step guide to. (Imperial College Press) Houp K.W., et al. (2002), Reporting technical information,10th edition, (Oxford University Press)







