Key 10-6 worksheet
advertisement

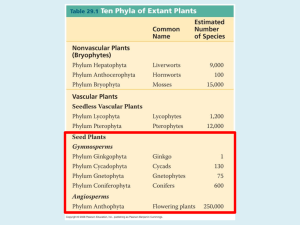
1. Explain what a megaspore and a microspore is, where they come from and what they produce. Megaspore-product of the megasporangia that develops into the female gametophyte which produces large gametes called eggs. Microspores-produce of the microsporangia that develops into the male gametophyte which produces small gametes called sperm. *A plant that produces these is heterosporous. 2. Explain the gymnosperm life cycle A sporophyte (2n) produces cones called the microsporangia and the megasporangia. The microsporangia divides by meiosis to produce microspores (n) that divide by mitosis to form pollen grains (n) The megasporangia divides inside of a mother cell that divides by meiosis to form a megaspore (n) that undergoes mitosis to from the female gametophyte containing egg cells (n). The pollen grains are delivered by wind or animals to the female gametophyte and delivers its sperm to fertilize the egg. This becomes the embryo (2n) that matures inside a seed. The seed becomes dispersed and grows into a new sporophyte (2n). Repeat. 3. Explain the angiosperm life cycle A sporophyte (2n) includes a flower with stamens and carpels. The stamens contain the anthers where the microsporangia (n) develops by meiosis. The carpel contains the ovary (fruit) which contains the ovules, which produce the megasporangia (n) by meiosis. The pollen grains are delivered to the carpel, and the two pollen grains undergo double fertilization in the ovule. One sperm fuses with the egg to form the diploid zygote (2n). The second sperm fuses with 2 nuclei in the female gametophyte to form a triploid nutritive tissue called endosperm (3n). The seeds are dispersed and grow into a new sporophyte (2n). Repeat. 4. Why does this video relate to the direct-pollination hypothesis? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GV0oLYLgSJs Terms: Gynmosperm (life cycle) Angiosperm (life cycle) Heterosporous Megaspores Microspores Pollen grains Flower Stamens Anthers Carpel Ovary Double fertilization Endosperm Directed pollination hypothesis Pollination syndrome Fruit Monocotyledons (monocots) Dicotyledons (dicots) Cotyledons Ginkgophyta Cycadophyta Pinophyta Gnetophyta