DNA
advertisement

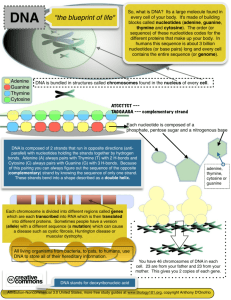
DNA The Blueprint of Life Nucleic Acids (Remember the macromolecules back in Chapter 2?) Nucleic Acids - store the genetic instructions for all life Two types of nucleic acids: RNA and DNA DNA • Stands for: Deoxyribonucleic Acid • Type of sugar: Deoxyribose • # of strands of nucleotides: 2 (Double Stranded) “double helix” • Function: stores genetic material RNA • Stands for: Ribonucleic Acid • Type of sugar: Ribose • # of strands of nucleotides: 1 (single stranded) • Function: Transfers genetic material DNA is made up of small repeating units (monomers) called nucleotides. Nucleotide has three parts: • 1. A phosphate group • 2. A sugar (called deoxyribose) • 3. A Nitrogen Base – There are 4! – Adenine “A” – Thymine “T” – Guanine “G” – Cytosine “C” Slide # 3 Components of DNA DNA is made up small, repeating units called nucleotides. Nucleotide has 3 parts 1 . Phosphate group 2. Deoxyribose sugar 3. Nitrogen base (4 different bases) – – – – Adenine Thymine Cytosine Guanine Adenine Guanine Thymine “A” “T” “C” “G” Phosphate group Go to Section: Cytosine Deoxyribose DNA Structure: Two strands of nucleotides bonded together at the nitrogen bases (with hydrogen bonds) and twisted. flat twisted What is DNA Made Of? DNA is made of four building blocks called nucleotide bases; adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C). Each strand of DNA is made up of long strings of these nucleotides arranged in a specific order. Two strands stick together and twist to form a helix. Slide # 6 Rosalind Franklin: The Famous Picture Taker 1.1952: Rosalind Franklin: an expert in x-ray crystallography. 2.She took the x-ray picture of DNA -shows DNA is a double helix. 3.1958: Franklin died (37 years old) Watson and Crick Are responsible for the 1st model of DNA and described its shape as a double helix (twisted ladder) • The two sides of the DNA ladder are made up of sugar and phosphate groups. • The “steps” (center) of the DNA ladder are made up of base pairs : adenine+thymine Hydrogen guanine+cytosine bonds Hydrogen bonds Chargaff’s Rule = A-T G-C A (Adenine) bonds to T (Thymine) and C (Cytosine) bonds with G (Guanine). FYI !!!! Base pairs are weakly joined together by hydrogen bonds to form each step of the ladder. Erwin Chargaff The KEY!!!! The sequence (order) of the 4 base pairs determines the genetic instructions or ‘code’ for life. DNA Replication – replica = copy creating two identical DNA molecules by copying the original DNA strand DNA Replication Steps: DNA Polymerase 1. DNA unwinds 2. DNA unzips DNA polymerase (an enzyme) break the weak hydrogen bonds holding the base pairs together splitting the DNA ladder down the middle. DNA Replication 3. Enzymes hydrogen bond new nitrogen bases onto the original DNA ½ ladders using Chargaff’s basepairing rule (A-T and G-C). 4. Finally, sugar and phosphate groups covalently bond to the new nitrogen bases and to each other to finish off the two new DNA strands. Results: two identical DNA strands made up of ½ of the original strand and ½ of the new strand. Parent strand: gray Daughter strand: red When does DNA copy itself? The cell replicates its DNA right before cell division. When two new cells are produced in cell division, each new cell needs its own copy of the DNA. (Identical Copy!) What happens to the Cell after DNA Replication? After DNA replication, the cell will divide in half (cell division) and give each new cell a copy of the DNA. Chromosomes As humans, we have 46 chromosomes in each of our cells. Each chromosome has millions of base pairs storing the codes that make up our bodies. ***Your genetic code depends on the sequence “order” of the bases in your DNA. Chromosome coiled DNA and protein “spacers” called histones. Histones keep the chromosome from getting tangled. DUPLICATED CHROMOSOME A chromosome that has gone through DNA replication and has an identical “sister” DNA copy attached to it. We call each copy of this duplicated chromosome a sister chromatid.