5 DNA Notes - Solon City Schools
advertisement
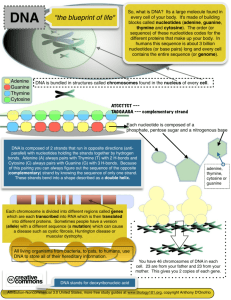
GETTING TO KNOW DNA: As you may already know, DNA stands for…. DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID Functions of DNA • Contains the code for making proteins Types of Nucleic Acids 1. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid): *double-stranded *deoxyribose sugar 2. RNA (ribonucleic acid): *single-stranded *ribose suger Nucleic Acid Structure • The monomer units of DNA are known as nucleotides • All nucleotides have three “parts” in common: a. Phosphate b. Pentose sugar a. (ribose or deoxyribose) c. Nitrogen base Deoxyribose Sugar (DNA) • Has 5 carbons • Carbon atoms are numbered 1', 2', 3', 4', and 5' • 5'-carbons link to the phosphate groups • 3'-carbons link to the hydroxyl groups • Notice what’s attached to the 5’ end And the 3’end Antiparallel • DNA is antiparallel because one strand runs upside down from the other. (If one strand ends with a phosphate (5’), the other strand will end with a sugar (3’)) Is DNA a monomer or polymer 8.33E-021. 92% Monomer 2. Polymer Table What does it mean to be a monomer? What does it mean to be a polymer??? What type of reaction is being shown below? O 78% O 0 17% Counter eh tio n iz a is ly m er Po yd ra tio n Sy nt he s ro ly s is 0% yd H D t xi da O al en ov 4% tio n 0% C 1. Covalent 2. Oxidation 3. Hydrolysis 4. Dehydration Synthesis 5. Polymerization Response Table The molecules marked “Y” and “W”: 86% 0% 0% 0% 14% 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Polymers and monomers Water and polymer Water and monomer Water and water Monomers and polymers Table What two functional groups will be involved in joining nucleotides? 19% 76% 0% 4.76E-02 0% 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Phosphate and amine Phosphate and hydroxide Amine and amine Phosphate and phosphate Amine and hydroxide Table The monomer units of DNA are known as…. NUCLEOTIDES All nucleotides have three “parts” in common. They all contain…. One of FOUR different NITROGEN BASES Phosphate Group Sugar= Deoxyribose PLEASE UNDERSTAND, A NUCLEOTIDE IS A VERY COMPLEX STRUCTURE. IF WE REPRESENTED ALL OF THE ATOMS, IT WOULD LOOK LIKE THIS… The four different Nitrogen Bases for DNA are abbreviated using the following letters…. A Adenine T Thymine G Guanine C Cytosine Let’s Practice How to Form DNA! We will use our hands to represent a nucleotide. PHOSPHATE NITROGEN BASE SUGAR Using your two hands, please show how you think two nucleotides will/should bond together. Did you put your hands like this??? Time to find out why this is wrong!!! Adenine and Guanine are larger molecules known as… PURINES LOOK! TWO RINGS!!! b. Purines: combination of a pentagon shaped ring and a hexagon shaped ring 1. Adenine 2. Guanine THYMINE and CYTOSINE are smaller molecules known as… PYRIMIDINES LOOK! Only one ring!! Nitrogen Base Pairing • Adenine and Thymine must form two hydrogen bonds to be stable while Guanine and Cytosine must form three – Makes the base pairing system an extremely simple: the A-T and C-G pairs are the only ones physically possible Now, when using our hands to represent the nucleotides, we must modify the nitrogen base in order to represent these PURINES and PYRIMIDINES. How would you represent a large PURINE? How would you represent a small PYRIMIDINE? Full Finger Half Finger In DNA, a PURINE always bonds with a PYRIMIDINE when forming a “rung” of the DNA ladder. LOOK! A long finger pairs with a short finger! In other words, a purine pairs with a pyrimidine. In DNA, Adenine always pairs with Thymine (using two hydrogen bonds.) A T A AND T AT THE ATOMIC LEVEL In DNA GUANINE always pairs with CYTOSINE (using three hydrogen bonds.) G C G AND C AT THE ATOMIC LEVEL THE ENTIRE MOLECULE AT THE ATOMIC LEVEL Time to use your brain and hands in order to review nucleotide structure and type. USING YOUR HAND, SHOW ME THYMINE USING YOUR HAND SHOW ME ADENINE SHOW ME CYTOSINE SHOW ME HOW CYTOSINE AND THYMINE BOND TO FORM A RUNG ON THE LADDER THEY DON’T OK Now that you recognize nucleotide type and structure, it’s time to start building the polymer from these monomers. In order to make a molecule of DNA, you would need to create many rungs to the DNA ladder. Look. Many Rungs. Etc… What part of the nucleotide alternates to form the sides of the DNA ladder? Sugar, Phosphate. Sugar, Phosphate. Sugar, Phosphate. Etc… Etc… What makes up the “RUNGS” of the ladder? The Nitrogen Bases Go Ahead! Stack you hand on top of your partners hands building two rungs of the DNA ladder. Why is this WRONG???? The sides of the DNA ladder “run” in opposite directions. One side is actually flipped and the nucleotides are upside down! TRY IT!!! Because the sides of the DNA “run” in opposite directions, DNA is said to be ANTIPARALLEL. In this DNA molecule, the THUMB part or better known as the PHOSPHATE GROUP, is said to be the 5 prime (5’) end. 5 prime 5 prime The “hand” or sugar part of the DNA molecule makes up the 3 prime (3’) end of the DNA ladder. 3 Prime 3 Prime • Direction of the nucleotides in one strand is opposite to their direction in the other strand: the strands are antiparallel. • Asymmetric ends of DNA strands are called the 5′ (five prime) and 3′ (three prime) ends – 5' end having a terminal phosphate group – 3' end having a terminal hydroxyl group If you link enough nucleotides together, the DNA molecule begins to take on the characteristic shape known as the Double Helix Let’s make a candy version of our DNA You Need… •Two Pipe cleaners •Two red twizzlers •One black twizzlers •Many toothpicks •Four different colored marshmallows The marshmallows represent the nitrogen bases. Let’s decide as a class what colors will represent the following nitrogen bases. ADENINE= CYTOSINE= THYMINE= GUANINE= Person One Cut the black twizzlers into 1.5 cm pieces. These will represent the phosphate groups Person Two Cut the red twizzlers into 3 cm pieces. These will represent the sugars. Add the twizzlers to the pipe cleaners. Remember, you need to alternate SUGAR (red) AND PHOSPHATE GROUPS (black). When you are finished, your strand should not end in the same color you started with! Did you and your partner make the same number of nucleotides on the sides of your ladder? If not, FIX IT!!! Time to put together the two sides. Using the toothpicks and marshmallows, you are to add the nitrogen bases to the sides of the ladder. Remember, the nitrogen bases “come off” the sugar part of the nucleotide. As a result, they should be coming off of the red twizzler. Please use two of the same color marshmallows to represent one ADENINE and GUANINE. The BIG purines. Please use only one marshmallow to represent THYMINE and CYTOSINE. The small pyrimidines. Following your teachers directions, let’s build one long strand of DNA A Particular strand of DNA contains 10 adenine molecules. How many thymine will it contain: 0% 0% 0% 0% 1. 2. 3. 4. 5 10 20 Not enough information Table A strand of DNA is 20% Guanine molecules. What is the percent of thymine in the strand of DNA? 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 10 20 30 40 Not enough information Table A particular strand of DNA is 40% guanine. What is the percent of adenine in the same strand? 0% 1. 10 2. 20 0% 3. 30 0% 4. 40 0% Table The molecule at the location identified by the arrow: 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Adenine Guanine Sugar Phosphate thymine Table The molecule at the location identified by the arrow: 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Adenine Guanine Sugar Phosphate thymine Table The molecule at the location identified by the arrow: 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Adenine Guanine Sugar Phosphate thymine Table The end of the molecule identified by the blue arrows: 0% 0% 1. Five prime 2. Three prime Table The end of the molecule identified by the red arrows: 0% 0% 1. Five prime 2. Three prime Table Because the sides of the DNA ladder run in opposite directions, DNA is said to be… 0% 0% 0% 0% 1. 2. 3. 4. Parallel Nonparallel Antiparallel proparallel Table What do you notice about all the DNA molecules in the room? • They are all different! If your DNA ladder contains 28 red segments of licorice, how many nucleotides would your DNA ladder contain? 1 14 28 42 56 Table 0% 56 0% 42 0% 28 0% 14 0% 1 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What name is given to the reaction that was used to create this candy molecule? 1. Hydrolysis 2. Fertilization 3. Dehydration Synthesis 4. Crossing over ov si ng ro s C Sy n yd ra tio eh er is nt he s iz a rt il Fe D H yd ro ly s is tio n 0% 0% 0% 0% Table In the diagram below, how will these two molecules join together? OH HO If you were making our candy molecule in a cell where would you be found? 1. Cytoplasm 2. Endoplasmic Reticulum 3. Golgi Body 4. Nucleus 5. Vacuole En do pl ol e cu Va N uc le u s y ol gi Bo d um G et ic ul R as m ic C yt op la s m 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% Table Looking around the room you noticed that a particular strand of DNA contains 20% adenine marshmallows. What percentage of Thymine can be expected in that piece of DNA? 1% 10% 20% 40% 80% % 0% 80 % 0% 40 20 10 0% % 0% % 0% 1% 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Table If a DNA molecule contains 30% Guanine, then you would expect it to have how much Adenine? 15% 20% 30% 40% 60% % 0% 60 % 0% 40 % 0% 30 % 0% 20 % 0% 15 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Table What is a GENE?