GIS 1001 Introduction to Geographic Information Systems
advertisement

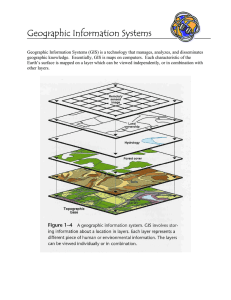
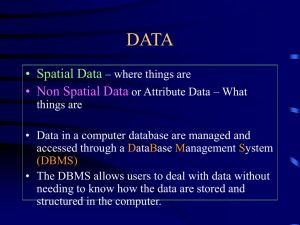
GIS 1001 Introduction to Geographic Information Systems Instructors Jeff Fesperman: B309, 224-0356 Mike Phillips: B318, 224-0394 Texts Concepts & techniques of Geographic Information Systems Getting to Know ArcView GIS Organization Lecture Lab Exercises Projects Course Outline & Schedule http://www.ivcc.edu/phillips Chapter 1 Introduction to Geographic Information Systems Definitions “…a system of hardware, software, and procedures designed to support the capture, management, manipulation, analysis, modeling, and display of spatially referenced data for solving complex planning & management problems” (Rhind, 1989) Definitions “…a computer system capable of assembling, storing, amnipulating, and displaying geographically referenced information…” (USGS, 1997) “…a set of computer-based systems for managing geographic data and using those data to solve spatial problems” (Lo & Yeung, 2002) Definitions a computer system that allows the analysis and display of data with a spatial component (Phillips, 2002) Definitions data: collection of facts/figures information: data in useful form knowledge: what you have intelligence: what you use Information System allows the transformation of data into information via: structuring formatting conversion modeling GIS: transforms data with a spatial component Geographic Data spatial data referenced to “geographic space” coordinate system • grid • other projection source • land survey • GPS • aerial imagery represented at a “geographic scale” Geographic Information Science approach to using GISystems what to do & how to do it GIS History Table, page 6 1960’s & 1970’s - mainframe computers 1980’s to mid 1990’s - mainframe & minicomputers mid 1990’s to present - PCs & workstations GIS data types geodetic control network: surface location topographic base: point elevation graphical overlays: thematic data representation vector: point, lines, polygons raster: grid cells surface metadata information about the data key when sharing data GIS technology hardware organization • intranet: servers & client computer stations • PCs • internet considerations • processing power • file size (very large) • data access GIS technology software proprietary open standard companies ESRI • ArcInfo & ArcView • ArcGIS Intergraph MapInfo Application of GIS table - p 12 academic business government industry military Users of GIS Specialist: includes programmers, designers, developers General Users: planners, scientists, administrators (us) Viewers: everyone (our “clients”) Core concepts figure: p 17