Geography 101
advertisement

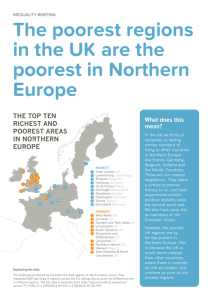
International Environmental Problems and Policy Office hours PROFESSOR ZOLTÁN GROSSMAN 258 Phillips Hall 10:00-10:50 am MWF 836-4471 E-mail: grossmzc@uwec.edu Web: www.uwec.edu/grossmzc Regions of the “World Village” East Asians South Asians Africans European Latin Amer. North Amer. Oceania • • • • • • • 333 East Asians 274 South Asians 132 Africans 120 Europeans 86 Latin Americans 50 North Americans 5 from Oceania Where we live • 452 in town Urban Rural • 548 in country Ages • 310 children Under 14 15-65 Over 65 • 70 elderly • 610 between Demographics • 22 children born • 9 people die • One-third of deaths are children under 5. • Numbers of elderly increasing rapidly. Human Population at 6 billion Food shortages/famines •Water quality •Fossil fuel burning •Air and water pollution •Landscape destruction •Loss of biodiversity • Languages • 500 speak one of six languages 6 languages 6,000 languages – – – – – – Chinese English Hindi Spanish Russian Arabic • 500 speak one of 6,000 languages Household income • Average annual income $4,890 Less than $650 $650$35,000 Over $35,000 • 600 poor • 300 marginal • 100 well-off Ownership/consumption • 200 richest villagers own and consume 80% of goods 200 richest 800 others • Other villagers own and consume remaining 20% Affluent lifestyles Material World: A Global Family Portrait Iceland Guatemala Japan Land use Cropland Pasture Forest Noneconomic • Average of 6 acres for each person – – – – 700 acres cropland 1400 acres pasture 1900 acres woodland 2000 acres desert, other noneconomic land Land ownership The richest 270 people control: 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Cropland Grain for food People fed Fertilizer Richest 270 Other 730 – 40% of the cropland – 72% of the foodgrain but feeds 27% of the people – 83% of the fertilizer United States Population • 45 people live in U.S. United States Other countries • 955 live elsewhere United States Consumption • Oil 26% • Aluminum 24% •Copper 20% •Nickel 19% •Steel 13% United States Share of World Pollution • Toxic wastes 50% • Nitrogen oxides 26% •Carbon dioxide 26% •Sulfur oxides 25% •Chloroflurocarbons 22% Rich/poor divisions • Wealthy countries tend to be located in the Northern Hemisphere. • About 1/5 of world population live in countries with per capita income > $25,000.00 (U.S.). – Poor people exist here as well. • Gap between rich and poor continues to increase. – Wealthiest 200 people in the world have combined wealth of $1 trillion - more than total wealth of poorest half (3 billion) of the world’s population. Environmental challenges • Wealthy countries exploit natural resources in poor countries (often through corporations). • Elites in poor countries often cooperate with wealthy countries and interests. • Poor exploit natural resources, because socio-economic conditions (dictated by rich countries and domestic elites) create a struggle for survival. • Poor in wealthy countries also face economic blackmail. Philadelphia Infant Mortality Red area high than at least 28 Third World countries, including: Jamaica Cuba Costa Rica Malaysia Panama Sri Lanka South Korea Taiwan Uruguay Argentina Chile Adult Literacy • 310 adults can read and write Literate Illiterate • 310 adults cannot read or write • Girls half as likely as boys to attend school Access to TV • 10% without access Access to TV No access • 90% with access Access to fresh water • 30% of rural residents without access Rural access No rural access • 7% of urban residents without access Women and girls • Two-thirds of manual labor 120 100 Total numbers Manual labor Wages 80 60 40 20 0 Female Male • One-tenth of wages Property • One-hundredth of property % of poor • Make up 70% of the poor. Life expectancy • Not age lived to, but affected by infant mortality rates. 90 80 70 Average age Richest families Poorest families 60 50 40 30 20 • Richest familes: women 80, men 78 • Poorest families: 48 for both 10 0 Female Male “North/South” Divisions • Poor countries tend to be located in Southern Hemisphere. • World Bank estimates more than 1.3 billion people (1/5 world population) live in acute poverty of < $1 (U.S.) per day. – 70% women and children – Self-Sustaining • Daily survival necessitates over-harvesting resources thus degrading chances of long-term sustainability. Former world “divisions” • First World - Industrialized, market-oriented democracies of Western Europe, North America. • Second World - Centrally-planned socialist countries such as former USSR. • Third World - Ex-colonial nations such as India, Malaysia, Iran, etc. • Fourth World - Poorest nations (and indigenous communities within wealthy nations). Current world system • Core - Industrialized, market-oriented democracies of Western Europe, North America, East Asia, Australia. • Periphery - Poor, ex-colonial nations such as Kenya, Bolivia, Pakistan, etc. • Semi-periphery - Partially industrialized ex-colonial nations (South Africa, Brazil, Mexico, South Korea, etc.) Indigenous peoples • Indigenous (Native) people are often least powerful, most neglected people in the world. – At least half the world’s 6,000 distinct languages are dying. – Indigenous homelands may harbor vast percentage of world’s biodiversity. – Recognizing Native land rights and political rights may often be a solid ecological safeguard. – Who is “Indigenous”? Human Development Index • United Nations releases Human Development Index (HDI). Based on social factors - ranges from 0-1.0. – In 2000: Canada had highest with 0.96 and Sierra Leone had lowest with 0.19. • Aggregate numbers hide many important inequity issues: – Gender – Race Sustainable Development • “Meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.” • Benefits must be available to all humans, not just sub-set of privileged group. • Economists: continual growth for people • Ecologists: non-renewable resources, limited waste capacity Signs of hope • Progress had been made on many fronts. – Population has stabilized in many industrialized countries; population growth slowing in others. – Incidence of life-threatening diseases has been reduced in some countries. – Average life expectance nearly doubled. World Summit on Sustainable Development • Johannesburg, South Africa, Aug.-Sept. 2002 • Ten years after 1992 Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil (Rio + 10). • International grassroots NGOs used as opportunity for networking. WSSD websites Earth Summit 2002 Girona Declaration www.earthsummit2002.org http://www.xs4all.nl/~ceo/un/gironadecl.html UN site Global Indaba www.johannesburgsummit.org www.globalindaba.org.za Linkages Independent Media Center www.iisd.ca/wssd/portal.html http://southafrica.indymedia.org/ Radio Earth Summit http://www.radioearthsummit.org/ Ideas for class website?