A wholesaler sells to retailers, and a
retailer sells to the final users. In addition
to using the general ledger, a business
keeps a subsidiary ledger of individual
customer accounts. Merchandising
businesses receive cash from cash sales,
payments on account, bankcard sales, and
occasionally from other types of
transactions
Glencoe Accounting
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Explain the difference between a service business and a
merchandising business.
Explain the difference between a retailer and a wholesaler.
Analyze transactions relating to the sale of merchandise.
Record sales and cash receipt transactions in a general journal.
Glencoe Accounting
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Section 14.1
Accounting for a
Merchandising Business
Key Terms
retailer
wholesaler
merchandise
inventory
sales
Glencoe Accounting
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
The Operating Cycle of
Merchandising Business
Section 14.1
Accounting for a
Merchandising Business
Retailers
Most merchandising
businesses are both
Wholesalers
retailer
A business that sells to the
final user, the consumer.
Glencoe Accounting
wholesaler
A business that sells to the
retailers.
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
The Operating Cycle of a
Merchandising Business
Section 14.1
Accounting for a
Merchandising Business
See page 383
Glencoe Accounting
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Accounts Used by a
Merchandising Business
Section 14.1
Accounting for a
Merchandising Business
A merchandising
business buys
merchandise from
a wholesaler or
manufacturer.
A merchandising
business keeps an
inventory.
A merchandising
business sells goods
to its customers.
merchandise
Goods bought to resell to
customers.
inventory
The items of merchandise a
business has in stock.
Glencoe Accounting
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Accounts Used by a
Merchandising Business
Section 14.1
Accounting for a
Merchandising Business
Inventory is represented in the general ledger by the
asset account Merchandise Inventory.
Merchandise
Inventory
Account
The normal balance of this account is a debit.
Merchandise is bought and sold during the
operating cycle.
The purchase and sale of merchandise is recorded
in separate accounts.
Glencoe Accounting
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Accounts Used by a
Merchandising Business
Section 14.1
Accounting for a
Merchandising Business
The amount of the merchandise sold is recorded in
the sales account.
Increases to sales are recorded as credits.
Sales
Account
The normal balance of the sales account
is a credit.
Sales on account affect the Accounts Receivable
account and cash sales affect the Cash in Bank account.
sales
A revenue account to record the amount of the merchandise sold.
Glencoe Accounting
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Section 14.2
Analyzing Sales
Transactions
Key Terms
sale on account
subsidiary ledger
charge customer
controlling account
credit card
sales return
sales slip
sales allowance
sales tax
credit memorandum
credit terms
contra account
accounts receivable
subsidiary ledger
Glencoe Accounting
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Sales on Account
Section 14.2
Analyzing Sales
Transactions
A sale on account is made
to a charge customer.
sale on account
The sale of merchandise that
will be paid for at a later date.
Glencoe Accounting
charge customer
A customer to whom a
sale on account is made.
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Sales on Account
Section 14.2
Analyzing Sales
Transactions
A store credit card facilitates
sales on account.
credit card
A card issued by a business
containing a customer’s name and
account number that facilitates the
sale on account.
Glencoe Accounting
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Sales on Account
Section 14.2
Analyzing Sales
Transactions
A charge sale involves:
sales slip
sales slip
A form that lists the details
of a sale.
sales tax
A tax levied by a city or
state on the retail sale of goods
and services.
sales tax
credit terms
Glencoe Accounting
credit terms
Terms that state the time
allowed for payment for a
sale on account.
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Sales on Account
Section 14.2
Analyzing Sales
Transactions
Date of the Sale
Items on a
sales slip
include:
Customer account
identification
Description, quantity, and
price of items sold
There are usually multiple copies of the sales slip with at least one for
the customer and one for accounting purposes.
Glencoe Accounting
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Sales on Account
Section 14.2
Analyzing Sales
Transactions
Sales Tax
A business periodically sends the
collection of sales tax to the state. Until
then, the amount owed is recorded in a
liability account called Sales Tax
Payable.
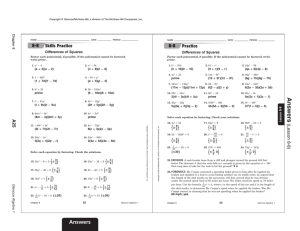
Sold $700 merchandise. Sales tax is 6%. How
much sales tax should you collect?________
What is the amount total due? ____________
Glencoe Accounting
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Sales on Account
Section 14.2
Analyzing Sales
Transactions
The credit terms are listed
on the sales slip.
What does n/30 mean?
Net amount must be paid in
30 days.
See page 388
Glencoe Accounting
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
The Accounts Receivable
Subsidiary Ledger
Section 14.2
Analyzing Sales
Transactions
What is the accounts receivable
subsidiary ledger?
accounts receivable subsidiary ledger
A separate ledger that contains accounts for each
charge customer; it is summarized in the Accounts
Receivable controlling account in the general ledger.
Glencoe Accounting
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
The Accounts Receivable
Subsidiary Ledger
Section 14.2
Analyzing Sales
Transactions
See page 389
controlling account
An account that serves as a control on the accuracy of
the account balances in the subsidiary ledger; its
balance must equal the total of all account balances in
the subsidiary ledger.
Glencoe Accounting
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
The Accounts Receivable
Subsidiary Ledger
Section 14.2
Analyzing Sales
Transactions
Subsidiary Ledger Account Form
See page 389
subsidiary ledger
A ledger with detailed data that
is summarized in a controlling
account in the general ledger.
Glencoe Accounting
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Recording Sales
on Account
Section 14.2
Analyzing Sales
Transactions
Recorded at the time
of sale
Recording a sale
on account
Revenue must be
realizable
Glencoe Accounting
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Recording Sales
on Account
Section 14.2
Analyzing Sales
Transactions
Business Transaction
On December 1 The Starting
Line sold merchandise on
account to Casey Klein for
$200 plus sales tax of $12,
Sales Slip 50.
See page 390
Glencoe Accounting
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Recording Sales
on Account
Section 14.2
Analyzing Sales
Transactions
Business Transaction
On December 3 The Starting Line sold merchandise on account to South
Branch High School Athletics for $1,500, Sales Slip 51.
Why no tax? Schools are tax exempt
See page 391
Glencoe Accounting
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Recording Sales
on Account
Section 14.2
Analyzing Sales
Transactions
A merchant performs a
sales return for customers
who are unhappy with their
purchases.
A sales allowance may be
issued by the merchant if
merchandise is damaged
prior to purchase.
sales return
Any merchandise returned
for credit or a cash refund.
sales allowance
A price reduction granted
for damaged goods kept
by the customer.
Glencoe Accounting
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Recording Sales
on Account
Section 14.2
Analyzing Sales
Transactions
Credit Memorandum
See page 392
credit memorandum
A form that lists the details of a sales return
or sales allowance.
Glencoe Accounting
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Recording Sales
on Account
Section 14.2
Analyzing Sales
Transactions
The Sales Returns and Allowances account is a contra account.
contra account
An account whose balance is a
decrease to its related account.
Glencoe Accounting
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Recording Sales
on Account
Section 14.2
Analyzing Sales
Transactions
Sometimes a cash refund is given and the Cash in Bank
account is credited instead of Accounts Receivable.
Glencoe Accounting
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Posting to the Accounts
Receivable Subsidiary Ledger
Section 14.2
Analyzing Sales
Transactions
Business Transaction
On December 4 The
Starting Line issued Credit
Memorandum 124 to
Gabriel Ramos for the
return of merchandise
purchased on account,
$150 plus $9 sales tax.
See page 393
Glencoe Accounting
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Posting to the Accounts
Receivable Subsidiary Ledger
Section 14.2
Analyzing Sales
Transactions
See page 394
Glencoe Accounting
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Posting to the Accounts
Receivable Subsidiary Ledger
Section 14.2
Analyzing Sales
Transactions
See page 394
Glencoe Accounting
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Using the Schedule of
Accounts Receivable
Section 16.2
The Cash
Receipts Journal
To prove the accounts receivable subsidiary ledger,
accountants prepare a schedule of accounts receivable.
schedule of accounts receivable
A list of each charge customer, the balance in the
customer’s account, and the total amount due from
all customers.
Glencoe Accounting
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Using the Schedule of
Accounts Receivable
Section 16.2
The Cash
Receipts Journal
Possible
Errors in the
Subsidiary
Ledger
Failing to Post a
Transaction
Miscalculating an
Account Balance
Proving the accounts receivable subsidiary ledger does not ensure
that transactions were posted to the correct customer account.
Glencoe Accounting
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Demonstration Problems 1-2 Connect
Glencoe Accounting
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Section 14.3
Analyzing Cash
Receipt Transactions
Key Terms
cash receipt
cash sale
cash discount
sales discount
Glencoe Accounting
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Cash Transactions
Section 14.3
Analyzing Cash
Receipt Transactions
Cash Sales
Four Kinds of Cash Receipts
• Sales are recorded on two tapes
• The register tape lists the total cash
sales and tax collected
Charge
Customer
Payments
• Businesses record cash received
on account from charge customers
on pre-numbered receipts
Bankcard
Sales
• Can be processed manually or
electronically
• Debit and credit card sales are
recorded like cash sales
Other Cash
Receipts
• Cash may be received from
– Bank loans
– Sale of assets other than
merchandise
Glencoe Accounting
cash receipt
The cash received by a
business in a single
transaction.
cash sale
A transaction in which the
business received full
payment for the
merchandise sold at the
time of the sale.
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Cash Discounts
Section 14.3
Analyzing Cash
Receipt Transactions
A cash discount,
or sales
discount, is an
advantage to
both the buyer
and the seller.
The buyer receives
merchandise at a
reduced cost.
The seller receives
cash quickly.
cash discount or sales discount
The amount a customer can deduct from the total owed for purchased
merchandise if payment is made within a certain time; also called sales discount.
Glencoe Accounting
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Calculating Cash Discounts
Invoice #
Terms
Amount of
Sale
978
2/10, n/30
$3,000.00
333
1/10, n/30
450.00
663
n/30
501
2/15, n/60
Glencoe Accounting
Sales Tax
Total Sale
Discount
$3,000.00
_________
$27.00
477.00
_________
4,970.00
29.82
4,999.82
_________
1,260.00
75.60
1,335.60
_________
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Recording Cash Receipts
Section 14.3
Analyzing Cash
Receipt Transactions
Charge Customer Payments
Recording
Cash from Four
Sources
Cash Discount Payments
Cash Sales
Bankcard Sales
Glencoe Accounting
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Recording Cash Receipts
Section 14.3
Analyzing Cash
Receipt Transactions
Charge Customer Payments
Business Transaction
On December 5 The Starting
Line received $212 from Casey
Klein to apply to her account,
Receipt 301.
See page 399
Glencoe Accounting
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Recording Cash Receipts
Section 14.3
Analyzing Cash
Receipt Transactions
Cash Discount Payments
Business Transaction
On December 12 The Starting
Line received $1,470 from
South Branch High School
Athletics in payment of Sales
Slip 51 for $1,500 less the
discount of $30, Receipt 302.
See page 400
Glencoe Accounting
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Recording Cash Receipts
Section 14.3
Analyzing Cash
Receipt Transactions
Cash Sales
Business Transaction
On December 15 The Starting
Line had cash sales of $3,000
and collected $180 in sales
taxes, Tape 55.
See page 401
Glencoe Accounting
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Recording Cash Receipts
Section 14.3
Analyzing Cash
Receipt Transactions
Bankcard Sales
Business Transaction
The Starting Line had
bankcard sales of $700
and collected $42 in
related sales taxes on
December 15, Tape 55.
See page 402
Glencoe Accounting
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Recording Cash Receipts
Section 14.3
Analyzing Cash
Receipt Transactions
Other Cash Receipts
Business Transaction
On December 16, The Starting Line received $30 from Mandy Harris, an
office employee. She purchased a calculator that the business was no
longer using, Receipt 303.
See page 403
Glencoe Accounting
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Internet Sales
Section 16.2
The Cash
Receipts Journal
Use an Internet merchant
account for credit and debit
card payments or an online
payment service.
Internet
Sales
Steps must be taken to make
sure online sales transactions
are secure.
Glencoe Accounting
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Question 1
List the operating cycle for a merchandising business.
Step 1:
Purchase goods for resale
Step 2a: Sell goods for cash (skip to step 4).
Step 2b: Sell goods on account.
Glencoe Accounting
Step 3:
Collect cash from accounts.
Step 4:
Pay expenses.
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Question 1
A customer bought merchandise on February 1 totaling $1,800.00. As an
incentive to get this customer to pay early, you offer terms of 1/20, n/30.
The customer pays on February 15. Calculate the following:
$1,800.00
Total sale amount
__________
$18.00
Amount of discount __________
$1,782.00
Net cash received
__________
Now indicate whether you would debit or credit the following accounts.
Credit
Accounts Receivable
__________
Credit
Customer’s subsidiary account __________
Debit
Sales Discounts
__________
Debit
Cash in Bank
__________
Glencoe Accounting
Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
End of