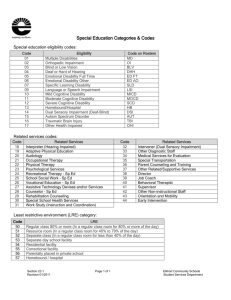
Overview of Disabilities
advertisement

Development and Characteristics of Learners Overview of Disabilities Standard # 2 Paraeducator Training 1 Local Policy Your local district’s policies regarding paraeducator job descriptions, duties, and responsibilities provide the final word! 2 Agenda Characteristics of student development Identify thirteen (13) disability categories as listed in IDEA Characteristics of the disability Issues related to the disability Discuss paraeducator’s role in supporting students with disabilities 3 Learner Outcomes Participants will be able to: Recognize importance of student development Identify thirteen disability categories List characteristics of the disability Discuss issues related to the disability Describe the paraeducator’s role in supporting students with disabilities 4 Student Support Activity Look at handout #1 Describe the student Physical development Social/emotional skills including behavior Cognitive and communication abilities Daily living skills 5 Developmental Expectations: Children learn naturally All students grow at their own developmental pace. Some students experience delays in their development. 6 To Teach Effectively… …educators must always keep in mind the dynamics and needs of the group as well as the individual characteristics and needs of each student in the group… This is where your assistance is needed. 7 How Children Develop and Learn Adults must know how students are working developmentally, as well as what makes each student unique. 8 How Children Develop and Learn Child development is the accepted body of knowledge about how students grow and learn. 9 How Children Develop and Learn Five areas of development that make up the whole child: 1.Physical 2.Cognitive 3.Speech and Language 4.Self help 5.Social/emotional 10 The Five Primary Developmental Areas Physical development – the ability to move, see, and hear Cognitive development the ability to think and learn Speech and Language development the ability to talk, express needs 11 The Five Primary Developmental Areas Self help (or adaptive development) the ability to eat, dress, and take care of themselves Social and emotional development – the ability to relate to others 12 How Children Develop and Learn These developmental areas are interrelated – development in one area affects other areas. 13 How Children Develop and Learn All students bring to school a set of unique characteristics and experiences that affect how they respond to school experiences, relate to others, and learn. 14 How Children Develop and Learn Effective teachers and other adults learn about each student in order to individualize teaching and learning. 15 Child Development and Disabilities Child development impacts the disability The disability impacts child development 17 Student Support Activity Handout #1 Review the skills and abilities of a student you know. 18 Introduction to Disability Categories Need to identify the disability: For eligibility To better match related services to student needs Match individual development levels with appropriate support 19 Thirteen disability categories as listed in IDEA • • • • • • • Autism Deaf-blindness Deafness Hearing impairment Emotional disturbance Mental retardation Multiple disabilities 20 Thirteen disability categories as listed in IDEA • • • • • • Orthopedic impairment Other health impairment Specific learning disability Speech/language impairment Traumatic brain injury Visual impairment 21 Disability Categories: Autism Autism is a developmental disorder significantly affecting verbal and nonverbal communication. Students with this disability have difficulties with communication, behavior, and social skills. 22 Characteristics of Autism Difficulties understanding spoken language Difficulties expressing needs verbally Poor pronunciation and voice control Misunderstanding social situations Problems in understanding gestures Unusual responses to touch, taste, smell, and/or sounds 23 Characteristics of Autism Clumsiness in skilled movements Aloofness and social withdrawal Resistance to change Socially embarrassing behavior May appear fearful May play differently, line up or spin objects Often better with visual skills 24 Characteristics of Autism What might you do? provide structure in routine and classroom environment prepare students for changes in routine use very concrete language make language visual observe activities to identify support needs provide choices 25 Disability Categories: Deaf-Blindness Deaf-blindness is the combination of a visual impairment and a hearing loss. Educational approaches to address only one of these problems is not be the best way to help a student learn. 26 Characteristics of DeafBlindness What might you do? • Teach through touch to help with extensive sensory loss • Hand-under-hand is an essential instructional strategy 27 Characteristics of DeafBlindness What might you do? Maximize the use of vision and hearing Learn successful procedures for “greeting” each student Help students orient themselves to classroom, bathroom, cafeteria, etc. 28 Disability Categories: Deafness Deafness is a hearing loss so severe that the student cannot get information through the sense of hearing, even with the use of amplification. 29 Characteristics of Deafness • • • • • May exhibit unintelligible or no speech Possible speech and/or language delays Usually use hearing aids May use assistive listening devices May use sign language 30 Characteristics of Deafness What might you do? Help the student learn to operate their listening device Meet with interpreter to share homework, vocabulary 31 Characteristics of Deafness What might you do? Look at environment for best seating Work with others to follow good communication behavior Facilitate student learning 32 Disability Categories: Hearing Impairment Hearing impairment means an impairment in hearing, whether permanent or fluctuating, that adversely affects a child’s educational performance. It is not as severe as deafness. 33 Characteristics of Hearing Impairment • May exhibit unintelligible or no speech • Possible speech and/or language delays • Usually use hearing aids • May use assistive listening devices • May use sign language 34 Characteristics of Hearing Impairment What might you do? Optimize learning environment Organize their instructional materials Communicate clearly Promote self-advocacy 35 Activity Look at Handout #3 Consider the disabilities that we have just discussed: autism, deaf-blind, deafness, and hearing impairment. Answer the three questions on the handout relating to these disability categories. 36 Disability Categories: Emotional Disturbance A condition exhibiting one or more of the following characteristics which occur over a period of time, and to a marked degree, which affect a child’s ability to learn: difficulty building or maintaining interpersonal relationships inappropriate behavior or feelings The inability to learn cannot be explained by intellectual, sensory or health factors 37 Characteristics of Emotional Disturbance Immaturity (inappropriate crying, temper tantrums, poor coping skills) Possible learning difficulties (academically performing below grade level) 38 Characteristics of Emotional Disturbance Students with the most serious emotional disturbances may exhibit: distorted thinking excessive anxiety, bizarre motor acts abnormal mood swings 39 Characteristics of Emotional Disturbance What might you do? Keep rules short Check for understanding Provide verbal cues to students to remind them to prepare for changing classes or going home Give written cues such as schedules or To Do Lists Remain patient! 40 Disability Categories: Mental Retardation Students with this disability have impaired mental development which adversely affects their educational performance, and who exhibit impaired adaptive behavior in learning, maturation, or social development. 41 Characteristics of Mental Retardation Intelligence testing score of 70 or below Difficulties with learning, communication, social, academic, vocational, and independent living skills Varies: mild, moderate, severe, profound 42 Characteristics of Mental Retardation What might you do? Make instruction and practice more concrete and personally relevant by relating them to tasks and experiences the student understands Provide additional practice on skills Provide skill practice and lots of repetition Break down tasks in to small units-prompts 43 Characteristics of Mental Retardation What might you do? Provide social skill instruction Repeat instructions or activity descriptions; Keep directions simple 44 Disability Categories: Multiple Disabilities Students with multiple disabilities have more than one disabling condition. 45 Characteristics of Multiple Disabilities Students with severe or multiple disabilities may exhibit a wide range of characteristics, depending on the combination and severity of disabilities, and the person’s age. There are, however, some traits they may share, including: 46 Characteristics of Multiple Disabilities Limited speech or communication Difficulty in basic physical mobility Trouble generalizing skills from one situation to another; and/or A need for support in major life activities (e.g., self-care, leisure, community use, vocational). 47 Disability Categories: Multiple Disabilities What might you do? Provide physical support in daily activities: dressing, feeding, toileting Learn positioning techniques Use safe lifting techniques Ask for training in specialized areas (tube feeding, seizures)! 48 Disability Categories: Orthopedic Impairment Student with this disability have skeletal or physical problems which may be first seen at birth (e.g., cerebral palsy, spina bifida), may be the result of disease (e.g., meningitis), or may be the result of an accident (e.g., amputation). 49 Disability Categories: Orthopedic Impairment What might you do? Learn to accommodate the classroom environment Use assistive devices for writing skills and communication Consider logistics and plan for inclusion 50 Disability Categories: Other Health Impairment Students with this disability have limited or heightened sensitivities to their environment, or limited strength or endurance caused by health problems like asthma, diabetes, or epilepsy. 51 Disability Categories: Other Health Impairment What might you do? Be sure you are aware of serious health problems Get clear direction on what you need to do in an emergency Monitor safety and health 52 Activity Look at Handout #3 continued Consider the disabilities that we have just discussed: emotional disturbance, mental retardation, multiple disabilities, orthopedic impairment, and other health impairment. Answer the three questions on the handout relating to these disability categories. 53 Disability Categories: Specific Learning Disability Learning disability is a general term that describes specific kinds of learning problems. A learning disability can cause a person to have trouble learning and using certain skills. The skills most often affected are: reading, writing, listening, speaking, reasoning, and math. 54 Characteristics of Specific Learning Disability Students may have difficulty: Taking in, remembering, and producing information Understanding, connecting and relating new information Planning, organizational, study and problemsolving skills Social skills and self-esteem 55 Characteristics of Specific Learning Disability What might you do? Adapt the physical environment Provide organizational changes in areas such as time, instructional methods, or materials 56 Disability Categories: Specific Learning Disability What might you do? Use advance organizers (outlines, study guides, focus questions) to structure classroom Allow more time for assignments, projects 57 Disability Categories: Speech/Language Impairment Difficulty with one of the following: Producing speech sounds or whole words Receptive and expressive language skills Conversational skills May be related to other disabilities such as mental retardation, autism or cerebral palsy 58 Characteristics of Speech/Language Impairment Speech Disorders: interruption in flow or rhythm of speech problems with the way sounds are formed difficulties with the pitch, volume, or quality of the voice 59 Characteristics of Speech/Language Impairment Language Disorders: inability to express ideas inappropriate grammatical patterns reduced vocabulary inability to follow directions 60 Characteristics of Speech/Language Impairment What might you do? Adapt the physical environment Provide many opportunities for student to interact verbally or through alternate means (pictures, symbols, etc.) With student who stutters, use nonverbal listening skills 61 Disability Categories: Traumatic Brain Injury A traumatic brain injury (TBI) is an injury to the brain caused from a blow to the head. This injury can change how a person acts, moves, and thinks. A traumatic brain injury can also change how a student learns and acts in school. 62 Characteristics of Traumatic Brain Injury Students with TBI may have one or more difficulties, including: Sensory issues Physical disabilities Headaches Fatigue Seizures Paralysis… 63 Characteristics of Traumatic Brain Injury Difficulties with thinking Short and long term memory Concentration Social, behavioral, or emotional problems Mood, emotional changes Relating to others 64 Characteristics of Traumatic Brain Injury What might you do? Provide a structured environment Shorten homework assignments Use lots of drill and practice Break instruction into smaller amounts of time 65 Characteristics of Traumatic Brain Injury What might you do? Allow student to keep extra set of books at home Be clear on classroom rules & expectations …repeat them often… check for understanding 66 Disability Categories: Visual Impairment Students with this disability are blind or have low vision. The terms partially sighted, low vision, legally blind, and totally blind are used in the educational context to describe students with visual impairments. 67 Characteristics of Visual Impairment Students with Visual Impairment: have little reason to explore environment missing opportunities to learn Are unable to imitate social behavior Do not understand nonverbal cues May have obstacles to independence 68 Characteristics of Visual Impairment What might you do? Use concrete materials and tactile aids like relief maps, math manipulatives, and raised-line paper for writing Encourage hands-on learning Help students “see”, e.g. incidental learning 69 Characteristics of Visual Impairment What might you do? Produce modified materials on a Expect and support active participation and engagement in learning 70 Activity Look at Handout #3 one more time Consider the disabilities that we have just discussed: specific learning disability, speech/language impairment, traumatic brain injury, and visual impairment. Answer the three questions on the handout relating to these disability categories. 71 Student Support Activity Look at your Student Support Activity Handout #1 Using your notes from Handout #3 complete the section on ideas for supporting your student. 72 What have we talked about? The importance of student development Thirteen disability categories Characteristics of the disability Issues related to the disability The Paraeducator’s role in supporting students with disabilities 73 Afterschool Videoconferences: Check www.pattan.net 74