Lecture_1 - Department of Mathematics
advertisement

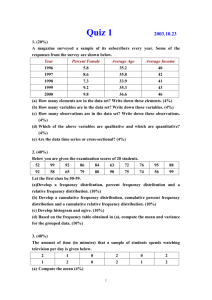
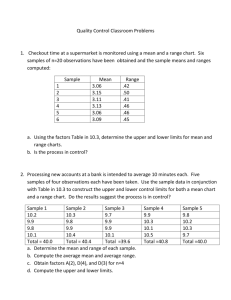
USC2001 Energy Lecture 1 Energy and Work Wayne M. Lawton Department of Mathematics National University of Singapore 2 Science Drive 2 Singapore 117543 Email matwml@nus.edu.sg http://www.math.nus/~matwml Tel (65) 6874-2749 1 WHAT IS ENERGY ? [1] The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language, Houghton Mifflin, Boston, 1992. 1 The capacity for work or vigorous activity, strength 2 Exertion of vigor or power ‘a project requiring a great deal of time and energy’ 3 Usable heat or power ‘Each year Americans consume a high percentage of the world’s energy’ 4 Physics. The capacity of a physical system to do work -attributive. energy – conservation, efficiency 2 WORK IS ENERGY [1] Appendix: PIE http://www.bartleby.com/61/roots/IE577.html (old form 5.5-7 thousand years ago) Werg – to do (suffixed form) Werg-o derivatives handiwork,boulevard,bulwark, energy, erg, ergative,-urgy; adrenergic,allergy,argon,cholinergic,demiurge, dramaturge,endergonic, endoergic,energy,ergograph,ergometer, ergonomics,exergonic,exergue, exoergic,georgic,hypergolic,lethargy,liturgy,metallurgy,surgery,synergids ynergism,thaumaturge,work Greek: ergon energos energeia Latin: energia French:energie Germanic: werkam Old High German: werc, Old English: weorc,werc (zero-grade form) Wig derivatives wrought, irk, wright (o-grade form) Worg derivatives organ, organon (= tool), orgy 3 WEIGHT LIFTING Physicists define Work Force Distance d or W F d F m g d F mg in energy units called Joules (J) Newtons (N) is the mass of an object in Kilograms (kg) 2 is the acceleration of gravity = 9.8 m / s is the distance that the object is lifted Meters (m) is force required to lift the object in Questions What is weight? Can F be exactly constant? 4 ARCHIMEDES “ Give me a place to stand and I will move the Earth” Earth load arm lightweight braggart effort arm fulcrum http://www.shu.edu/projects/reals/history/archimed.html https://www.cs.drexel.edu/~crorres/Archimedes/contents.html http://wow.osu.edu/experiments/simplemachines/levers.html Questions The Earth’s mass is 5.98E24 kg, if Archimedes’ is 65 Kg what is the geometry of his lever? What is his lever principle and what are some tools that employ it? 5 PULLEYS In the balance shown below, the heavier/lighter mass may be lifted by lowering the lighter/heavier mass. 1m 2kg 1kg 2m The objects move in opposite directions by distances that are inversely proportional to their masses ? Question What is the golden rule of mechanics? http://www.hp-gramatke.net/pmm_physics/english/page0200.htm 6 Distance Dependent Forces R 6.37 x 10 m Our formula F mg is only an approximation valid 6 The Earth’s radius is for objects whose distance r from the Earth’s centre is very close to R Isaac Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation gives mMG F 2 r where M is the Earth’s mass and G is the gravitational constant Question Why is G 6.673 x 10 -11 2 2 Nm /kg ? 7 d2 How to Compute Work F ( s ) ds where F is in the s-direction W d1 and d1 d 2 are the initial and final values of s This integral is the area between the graphs of s d , s d and y 0, y F ( s ) 1 2 y d1 d2 s Question What work is required to lift an object, having mass m, from the Earth’s surface to height d? Rd Answer mgd 2 2 W R mgR / s ds 1 d / R 8 WORK TO COMPRESS A SPRING The figure below illustrates a spring being compressed k = spring constant xi xf Initial Distance Final Distance Question What is the compression work integral? Answer Hook’s Law states that F ( x ) k ( x xi ) therefore W xf xi F ( x) dx k xf xi ( x xi ) dx 9 TUTORIAL 1 1. Compute the work to lift an object, having mass 1kg, from the Earth’s surface to ‘infinite’ height. 2. Compute the work to compress a spring by 1m if the final force equals 5N. 3. How do snakes crush prey with > 6 x their strength? 4. Compute the work to compress a volume V of gas with pressure P by a small amount dV. Compute the work to compress it to one tenth of its initial volume at constant temperature under ideal gas law assumptions. 5. Compute the work that the force of gravity does to an object having mass m as it slides a distance d along an inclined plane. How are vectors involved?10