Chapter 9
advertisement

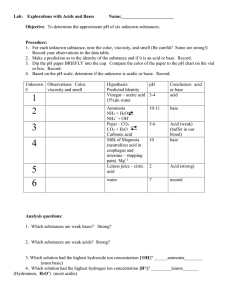
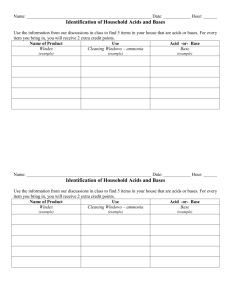
Chapter 9 Acids and Bases Autoionization of water • Equation • Hydronium ion –No free H+, Autoionization • Dynamic equilibrium • Problem • Write the equilibrium expression for the autoionization of water. • • In pure water at 25oC, Therefore… • Kw = • How much ion is present, relatively speaking? A lot or a little? • If [H+] increases… what must happen to [OH-]? What are Acids/Bases? Acids • Produce H+ • • Neutralize bases to produce salt water • Bases • Produce OH• • Neutralize acids to produce salt water • Indicators • • • • • Litmus, blue and red Universal Phenolphthalein Red cabbage juice Phenol red Strong Acids • No equilibrium • • • HCl • • HI • • • HClO4 Strong Bases • No equilibrium • • • • Ba(OH)2 • • Practice I • What is the concentration of hydronium ion in a 0.0400 M solution of HNO3? Practice II • What is the [OH-] in a solution of KOH that ha a concentration of 0.320 M? Practice III • What is the [H+] in a 0.400 M solution of H2SO4? Practice IV • What is the [OH-] in a solution of HCl that has a [H+]= 0.00300 M? Practice V • What is the [H+] in a 0.0500 M Ba(OH)2? pH • Logarithmic scale • • • pH pH • So… if [H+] = –pH = – –Pure water pH • To find [H+] given pH, use + –[H ] = pH scale 1 Acid 7 14 Neutral Base pOH • Calculated the same way, but using [OH-] • pH + pOH = – From Kw = Weak Acids and Bases • If the acid/base is not one of the strong, it is considered weak • Majority of acids and bases • React with water, Practice I • Write the equilibrium expression for formic acid reacting with water • Keq = Practice II • Repeat the above for NH3 reacting with water • Keq = • Also called Conjugate Acids and Bases • Write the reaction between nitrous acid, HNO2 and water – • Write the reaction between nitrite ion and water – Ka and Kb • Multiply • Cancel items that cancel • What do you get? • Practice • What is Ka for carbonate ion if Kb = 2.19 x 10-4 pKa and pKb • • • Determining Ka from pKa – Polyprotic acids • Write the dissociations for H3PO4, a weak acid. There are three steps • Ka1 = 5.93 e-3 • Ka2 = 6.32 e-8 • Ka3 = 4.84 e-13 Salts and Hydrolysis • Ions of a strong acids or bases • Ions of weak acids and bases Practice • Predict whether each of the following will make an acidic, basic, or neutral solution. – Mg(NO)3 – K2CO3 – NH4NO3 Buffers • Resist changes in pH • • Why do companies make buffered aspirin? – – Buffer system • Conjugate acid/base pair • • • Concentrations of each must be about equal Sponge factor • One ion acts as a sponge for • One ion acts as a sponge for • Greater concentration of acid and base, greater the ability to resist pH changes Henderson-Hasselbalch • pH = pKa + log [Base] [Acid] • • Tells you what changes in pH will happen with addition of acid or base Practice • Calculate the pH of a solution that is 0.00600 M acetic acid and 0.0080 M sodium acetate. • What is the pH if the concentration of acetic acid is changed to 0.0090 M? Practice • Determine the buffer system ions to use to have a system pH of 6.1 +/0.3 Carbon Dioxide • • • • • CO2(aq) + H2O(l) H2CO3(aq) H2CO3(aq) + H2O(l) H3O+(aq) + HCO3pKa Used in blood to maintain pH at 7.45 How? Blood buffer system • Use Henderson-Hasselbalch • pH = pKa + log [HCO3-(aq)] [CO2(aq) + H2CO3(aq)] Blood buffer system • pKa = • pH-pKa = • So… the rest of the equation must equal 1 • Log 10 = • Therefore the ratio of HCO3/(CO2+H2CO3) = Blood buffer system • CO2 is constantly being replaced by metabolic processes and is present in the blood • • Blood buffer system • CO2 is constantly lost • If CO2 is removed too fast… problems arise – Smokers • Inhale CO2 • – Look at Henderson-Hasselbalch – Respiratory Acidosis • When CO2 not removed or is added from the environment • • pH falls • • Death Equations • CO2(aq) + H2O(l) H2CO3(aq) • H2CO3(aq) + H2O(l) H3O+(aq) + HCO3• • LeChatlier’s principal Respiratory Alkalosis • CO2 removed too fast • • Hyperventilation • Metabolic Acidosis • • Body attempts to compensate by adding CO2 • • Help buffer system by adding HCO3- Metabolic Alkalosis • • • Eating too many Rolaids • • Add NH4Cl Titration • • • • Lab experiment React an acid and base to form water Measure the endpoint with indicator Use MaVa = MbVb Practice • What volume of 0.200 M NaOH is needed to completely neutralize 40.00 mL of 0.0855 M HCl? Practice II • What volume of 0.250 M KOH is needed to neutralize 50.0 mL of 0.250 M H2SO4? Practice III • What is the concentration of HCl if 35.00 mL of the acid are neutralized by 61.50 mL of 0.500 M NaOH?