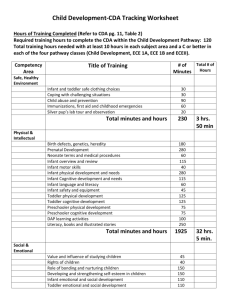
1st Six Weeks
advertisement

1 Six Weeks – Child Development st Roles and Responsibilities of Parenting Relationship skills 2 Parenting skills and responsibilities 3 Core nutrition for all ages 0 1(B) 1(A) 2(C); 3(E); 3(F); 4(E); 5(E); 6(F) Prenatal Care and Development Signs and stages of pregnancy 3 Factors affecting fetal development 2 Good nutrition and healthy practices during pregnancy 1 Medical care and technological advances 0 Labor and delivery 2 First aid and CPR skills for the expectant mother 1 2(A) 2(B) 2(B) 2(D); 2(E) 2(F) 1(D) The Infant Growth and development of the infant 3 Needs of the infant: physical, emotional, social, and intellectual 4 Nutrition and feeding of the infant 2 Impact of the infant on the family1 Protection and safety of the infant 1 Test 1.1 - 1 Test 1.2 (Six Weeks Test) – 1 = 29 days 3(D) 3(A); 1(E) 3(E) (F) 3(C) 1(E); 3(B) Dare Kirklin – FCS Teacher Week of: 8/25/14 – 8/29/14 Child Development Weekly TEKS: 1(B)- The student analyzes roles and responsibilities of parenting. The student is expected to analyze relationship skills, including money management, communication skills, and marriage preparation. 1(A)- The student analyzes roles and responsibilities of parenting, The student is expected to: investigate parenting skills and responsibilities, including child support and other legal rights and responsibilities that come with parenthood. Monday – Relationship Skills Objective: The student will be able to identify different types of relationships and the expectations associated with each type. Lesson: Have students identify different types of relationships and the importance of each. Examples might include the following: Acquaintances, social friends, best/close friends, dating partners, teacher/student, marriage partners, siblings, extended family members, parent/child, employer/employee Explain to students that different expectations are placed on people in various types of relationships. Have students think of different roles people play within various relationships. Lead students to discuss the unique role played by each type of relationship. Have students work individually or in groups to read the scenarios and away the questions on PowerPoint slides Relationships Expectations Scenarios. As students share their resources, lead them to discuss the impact of expectations on relationships. Questions for Discussion: What expectations are characteristics of each type of relationship? What are the benefits of each type of relationship? How are relationships affected by changing expectations? What are other examples of relationships where expectations may differ between the persons involved? Tuesday – Relationship Skills Objective: The student will discuss marriage preparation and explore premarital assessments. Lesson: Explain to students that the decision to marry is not one to be taken lightly. It is important for couples to discuss their ideas of marriage and determine their beliefs and values regarding issues such as communication, money management, children, etc. As a class read and discuss the Internet article American Association for Marriage and Family Therapy Consumer Update: Marriage Preparation www.aamft.org/imis15/content/consumer_updates/marriage_preparation.aspx. Divide the class into small groups. Instruct each group to explore the following websites to learn more about the premarital assessments discussed in the article. Allow groups to share what they learned about each assessment. Foccus Inc. USA www.foccusinc.com Relate Institute www.relate-institute.org/ Prepare-Enrich (sample quiz available) www.prepareenrich.com Wednesday – Parenting Skills and Responsibilities Objective: The student will define the responsibilities of parenting. Lesson: Show PowerPoint slide Parenting Responsibilities. Instruct students to define each responsibility as it relates to parenting. Ask students volunteers to share their definition with the class. Use the definitions to lead a class discussion regarding the responsibilities of parenting. Questions for Discussion: (For each responsibility listed, ask the following questions.) Why is this considered a responsibility of parenting? What are some examples of parents fulfilling this responsibility? What are possible ramifications of parents not fulfilling each responsibility? (include ramifications for parents, the child, society) Are there other responsibilities that are not listed on the teaching aid? Instruct each student to explain, in writing, how they would meet each of the parenting responsibilities listed on the PowerPoint slides. Thursday – Parenting Skills and Responsibilities Objective: The student will determine ways to fulfill parenting responsibilities. Lesson: Place signs around the classroom with the following titles: Financial, Child Guidance, Legal & Moral, Health & Safety, Physical Development, Social & Emotional Development, and Intellectual Development. Instruct students to disperse as evenly as possible to the various signs around the room. Instruct each student to list one way a parent could meet the responsibility listed on the sign. Give students a minute or two to finish. Once they are finished, ask the students to rotate to the next sign. Continue until each student has had a change to write on each sign. As a class, discuss the information gathered regarding parenting responsibilities. The student will discuss beliefs about parenting and verbally present opinions to the class. Divide the class into groups of two or three. Display PowerPoint slides Parenting – What Do You Think? Assign each statement to a group of students for discussion. Have students come to a consensus about their statement, determining whether or not they feel it is true, and why. Have each group select a spokesperson to present the group’s opinion to the class. Friday – Parenting Skills and Responsibilities Objective: The student will discuss gender expectations in parenting. Lesson: Display PowerPoint slides Gender Expectations in Parenting. As a class, discuss the parenting responsibility listed and whether or not it is the mother’s responsibility or the father’s responsibility. Questions for Discussion: Which type of beliefs, traditional or nontraditional, best support the sharing of parenting roles? What are the advantages of having both mothers and fathers participate in parenting responsibilities? In what ways can the participation of both mothers and fathers in parenting responsibilities influence their children? When parenting tasks are not shared, what are the possible consequences for the parents and for the children? Dare Kirklin – FCS Teacher Child Development Week of:9/1/14 – 9/5/14 Weekly TEKS: (2) The student investigates components of optimal prenatal care and development. The student is expected to: (A) Identify signs and stages of pregnancy. (B) analyze environmental and hereditary factors affecting fetal development such as Mendel’s Laws of inheritance, genetics, and substances and how they affect the developing child and prenatal brain development. Monday – Labor Day – No School Tuesday – Signs and Stages of Pregnancy Objective: The student will interview a mother about signs of pregnancy experienced by her. Lesson: Have students interview their own mother or other mothers as to the physical and emotional signs of pregnancy experienced when pregnant. Compile a list and compare with the PowerPoint slide Signs of Pregnancy. Questions for Discussion: What are the physical signs a woman experiences during pregnancy? What emotional changes might the mother experience during pregnancy? What emotional changes might the father experience during pregnancy? What are physical discomforts that can accompany pregnancy? Students will watch PBS NOVA video “Life’s Greatest Miracle.” Wednesday – Signs and Stages of Pregnancy Objective: The student will create a timeline depicting prenatal development. Lesson: Show students an Internet video, Life’s Greatest Miracle http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/miracle/program.html. Have students chart a timeline of prenatal development events depicted in the video, including the time span of each stage. The timeline should include brain development and what factors may improve and/or facilitate maximum development. Thursday – Signs and Stages of Pregnancy Objective: The student will create a timeline depicting prenatal development. Lesson: Show students an Internet video, Life’s Greatest Miracle http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/miracle/program.html. Have students chart a timeline of prenatal development events depicted in the video, including the time span of each stage. The timeline should include brain development and what factors may improve and/or facilitate maximum development. Friday – Factors affecting fetal development Objective: The student will describe various birth defects. Lesson: Show the PowerPoint slides Influences on Prenatal Development as a starting point for identifying hereditary and environmental birth defects. Questions for Discussion: What is the difference between a hereditary and environmental birth defect? How can an individual know if they are the carrier of a hereditary disease? What stage of pregnancy is the most critical for the development of the fetus in regard to environmental risks? What kinds of “risky” behavior may interfere with the fetal development? Dare Kirklin – FCS Teacher Child Development Week of: 9/8/14 – 9/12/14 Weekly TEKS: (2) The student investigates components of optimal prenatal care and development. The student is expected to: (B) analyze environmental and hereditary factors affecting fetal development such as Mendel’s Laws of inheritance, genetics, and substances and how they affect the developing child and prenatal brain development. (F) analyze the process of labor and delivery. Monday – Factors affecting fetal development Objective: The student will research basic information about the incidence, causes, symptoms, prevention, treatment, and support groups for birth defects. Lesson: Explain to students that according to the Centers for Disease Control, “birth defects affect about one in every 33 babies born in the United States each year.” Some birth defects are inherited ones while many are environmental and can be prevented. Students should be aware the effects of risky behaviors on unborn babies so they are able to make wised decisions about their own health and the health of their unborn babies. Distribute the teaching aid Birth Defects. Have students go to the website Center for Disease Control Birth Defects Home Page www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/jump/pregnancy.html to find the answers to the questions on the teaching aid. Instruct students to record the answers on the teaching aid. Questions for Discussion: What is a birth defect? What are the most common birth defects? Do genetic factors play a role in causing birth defects? What effect does alcohol during pregnancy have on the fetus? Smoking? Illegal drugs? Vaccines? When are the critical periods when birth defects may happen? What is the role of health care providers, genetic counselors, or geneticists in the detection and treatment of birth defects? Where can information be found about birth defects and care for a child who may have a birth defect? Tuesday – Factors affecting fetal development Objective: The student will research basic information about the incidence, causes, symptoms, prevention, treatment, and support groups for birth defects. Lesson: Explain to students that according to the Centers for Disease Control, “birth defects affect about one in every 33 babies born in the United States each year.” Some birth defects are inherited ones while many are environmental and can be prevented. Students should be aware the effects of risky behaviors on unborn babies so they are able to make wised decisions about their own health and the health of their unborn babies. Distribute the teaching aid Birth Defects. Have students go to the website Center for Disease Control Birth Defects Home Page www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/jump/pregnancy.html to find the answers to the questions on the teaching aid. Instruct students to record the answers on the teaching aid. Questions for Discussion: What is a birth defect? What are the most common birth defects? Do genetic factors play a role in causing birth defects? What effect does alcohol during pregnancy have on the fetus? Smoking? Illegal drugs? Vaccines? When are the critical periods when birth defects may happen? What is the role of health care providers, genetic counselors, or geneticists in the detection and treatment of birth defects? Where can information be found about birth defects and care for a child who may have a birth defect? Wednesday – Good Nutrition and Healthy Practices During Pregnancy Objective: The student will summarize healthy practices during pregnancy. Lesson: Show students the PowerPoint slides Factors Influencing Prenatal Care. Discuss with students why each of the factors is vital to a successful pregnancy and the proper growth and development of the fetus. Questions for Discussion: What are some important nutrients needed during pregnancy? Why? Why should junk food be eliminated during pregnancy? What is the importance of early medical care? Why should a strenuous exercise program be avoided during pregnancy? For further discussion have students go to Staying Healthy During Pregnancy http://kidshealth.org/parent/pregnancy_newborn/pregnancy/preg_health.html and answer the questions on the teaching aid Staying Healthy During Pregnancy. Thursday – Labor and Delivery Objective: The student will describe the process of labor and delivery. Lesson: Show the PowerPoint Process of Labor and Delivery, slides 1-5, and discuss with students the vocabulary related to the process of labor and delivery. Instruct students to complete the teaching aid Process of Labor and Delivery as information on the slides is being discussed. Show the PowerPoint Process of Labor and Delivery, slides 6-7, and discuss with students Three Signs That Labor Is About to Occur and The Three Stages of Labor. Have students take notes on the teaching aid What Happens During Labor and Delivery. Finally, show the PowerPoint Process of Labor and Delivery, slides 8-9, and discuss with students the Four Types of Pain Relief that are available during labor. Questions for Discussion: Which of the three stages of labor is likely to be the longest? Why? Which of the three stages of labor is likely to be the most painful to the mother? Why? How much time does the mother have from the onset of contractions until the birth of the baby? What does 10 centimeter dilation mean? What are the benefits of pain relief during labor? What may be risks of the various types of pain relief during labor? Why do you suppose many women choose to have no pain relief during labor and delivery? Friday – Labor and Delivery Objective: The student will summarize the three stages of labor and delivery, the risks involved, and treatment of complications during the stages of labor and delivery. Lesson: Show the interactive website Nova: Anatomy of Childbirth www.pbs.org/teachers/connect/resources/6311/preview on the screen. Have students take notes on the three stages of labor and delivery, risks that may occur during each stage, and treatment for complications that may occur during each stage of labor and delivery. Lead students to discuss their reactions to the labor and delivery process. Dare Kirklin – FCS Teacher Child Development Week of: 9/15/14 – 9/19/14 Weekly TEKS: (1) The student analyzes roles and responsibilities of parenting. The student is expected to (D) demonstrate first aid and cardiopulmonary resuscitation skills. (3) The student investigates strategies for optimizing the development of infants of diverse backgrounds, including those with special needs. The student is expected to: (D) identify Monday – First aid and CPR skills for the expectant mother Objective: The student will examine Heimlich maneuver and CPR procedures used for pregnant women. Lesson: Explain to students that first aid and CPR procedures must be adapted for use on pregnant women. Have students work in pairs to research the Heimlich maneuver and CPR used when a woman is pregnant. Compare those procedures with how they are preformed when the victim is not pregnant. Test Review 1.1 Tuesday – Test Objective: The student will be tested on taught material. Lesson: Test 1.1 Wednesday – Growth and development of the infant Objective: The student will describe the growth, development, and maturation of the infant. Lesson: Show the PowerPoint slide Infant Growth Vocabulary. Have students give other examples of growth and development. Questions for Discussion: How are growth and development related? What growth has to occur before the infant can hold up the head? What growth has to occur before the infant can crawl? Show the PowerPoint slides Types of Development explaining the difference between cephalocaudal and proximodistal development of the body. Remind students of the prenatal growth process by asking the following questions: Questions for Discussion: Why was the head of the fetus most prominent in the first months of development? Why did the spinal cord develop before the fingers and toes? How can the laws of development be seen as the child matures? How will the laws continue during the child’s growth and development? Show the PowerPoint slides Principles of Development listing the five principles of development. Have students give examples of each of the five principles. Questions for Discussion: How are the principles related to growth and development of the infant? What circumstances may help an infant to develop quicker? Why must an infant be able to have control of the trunk before being able to roll over? Why must an infant be able to walk before being toilet trained? Thursday – Growth and development of the infant Objective: The student will assess skill development for infants. Lesson: Distribute to students the teaching aid Timeline for Skills Development. Instruct students to search Internet resources or print resources to complete the timeline with examples of the types of skill development which should be taking place during that stage and examples of activities or strategies that parents or caregivers can use to encourage skill development in that area. Questions for Discussion: What are some positive influences for this particular skill to be accomplished? How will attainment of this skill lead to the next skill? Why do the skills come in a progression? Friday – Growth and development of the infant Objective: The student will discuss the principles of brain development and how to increase an infant’s brain wiring. Lesson: Show students the PowerPoint slides Brain Development of the Infant, and lead a discussion on the principles of brain development and how the “use it or lose it” principle can be implemented by parents and caregivers to increase the infant’s brain wiring. Questions for Discussion: How can parents and caregivers increase the number of dendrites attached to the neurons? What kinds of messages can parents and caregivers give to the infant that will stimulate transmission of information? What may happen to the infant’s brain if parents do not smile, talk, or touch the infant? If learning opportunities are not taken by parents and caregivers, what may happen to the infant’s brain development? Dare Kirklin – FCS Teacher Child Development Week of: 9/22/14 – 9/26/14 Weekly TEKS: (1) The student analyzes roles and responsibilities of parenting. The student is expected to: (E) assess the safety of purchases for children such as cribs, toys, clothing, and food. (F) explain factors that contribute to literacy. (3) The student investigates strategies for optimizing the development of infants of diverse backgrounds, including those with special needs. The student is expected to: (A) explain the physical, emotional, social, and intellectual needs of the infant. (E) select and use appropriate standard international units to identify nutritional needs for infants such as caloric requirements, protein, lipids, carbohydrates, and proton control. (F) research the advantages of breast feeding. Monday – Needs of the infant: physical, emotional, social, and intellectual Objective: The student will describe physical characteristics of the newborn. Lesson: Show the PowerPoint slide Characteristics of the Newborn. Have students work in pairs to gather information about the appearance of the newborn. Resources may be the Internet or printed materials. Instruct students to write the information on note cards to present to the class with the newborn characteristics on one side and the information about the characteristic on the other side. Questions for Discussion: Why is the newborn’s head in the shape of a cone? Will the red rash go away? What caused it? Why are the fingers and toes not as pink as the chest and inner part of the torso? Why are the newborn’s legs tucked into the body? What is the whitish substance on the eyelashes, eyebrows, and hair? Why is the newborn’s head so large? Tuesday – Needs of the infant: physical, emotional, social, and intellectual Objective: The student will determine needs of the infant. Lesson: Have students close their eyes and pretend they are newborn babies. Allow students to call out what their individual needs are while either the teacher or another student is scripting the answers on the board. Answers should include things, such as food, clothing, shelter, water, love, touch, etc. Show students the PowerPoint slides Needs of the Infant to determine how many of those basic needs the students knew and to discuss the ones students did not mention. Questions for Discussion: Why is it important to touch and cuddle with the newborn? What consequences might there be for the newborn who is not fed properly? How might improper nutrition affect emotional, social, and intellectual development as well as the physical development of the newborn? How might the lack of touch and nurturing affect the newborn’s emotional and social development? Wednesday – Needs of the infant: physical, emotional, social, and intellectual Objective: The student will describe bonding opportunities between parents and infants. Lesson: Write the word “bonding” on the board. Ask students for their definition of the word. After a short discussion, have students pair with one other student who they do not know well. Have pairs of students go to a different part of the room or separate tables, and give them five minutes to talk to each other relating information they do not know about each other. Bring students back together and discuss with students what they learned about each other during that five minute period. Explain to students that talking is a way people with verbal skills can bond. Since infants do not speak and use words, it is up to the parent to talk to the baby and give the infant opportunities to hear language and voices which allows for early bonding. Show the Internet video Simple Ways to Bond With Your Baby http://video.about.com/babyparenting/Ways-to-bond-with-your-baby.htm. Ask students for examples from the video of how they think the bonding process is developed for the parents and newborn. Answers should include skin to skin contact, eye to eye communication, talking during everyday tasks, reading, singing, and gently moving arms and legs. Questions for Discussion: What is the importance of touch to the bonding process between parents and newborns? What are some opportunities to talk to the newborn? What may happen to the bonding process if the newborn has to be isolated in an intensive care unit for a period of time? What may be some long-term effects of the lack of parent/newborn bonding? Thursday – Needs of the infant: physical, emotional, social, and intellectual Objective: The student will develop toys and/or activities for infants. Lesson: Show PowerPoint slides Piaget’s Cognitive Theories. Lead a discussion with students about Jean Piaget’s four stages on intellectual development. Emphasize the sensorimotor stage, which is the stage of infancy. Show students the Power Point slides Play Activities, Toys, and Equipment for Infants. Have students work individually, in pairs, or in groups to create a toy and/or play activity for an infant. Have students present the toy or activity to the class and discuss what type/s of learning can take place for the infant with this toy or activity. Friday – Nutrition and feeding of the infant Objective: The student will compare breast feeding and bottle feeding. Lesson: Have students work with a partner to brainstorm the advantages and disadvantages of breast feeding and bottle feeding. Show the PowerPoint slides Breast Feeding vs. Bottle Feeding to compare lists. Discuss advantages and/or disadvantages on the slide that the students did not have on their lists. Baby Food Tasting Exercise Dare Kirklin – FCS Teacher Child Development Week of: 9/29/14 – 10/3/14 Weekly TEKS: (3) The student investigates strategies for optimizing the development of infants of diverse backgrounds, including those with special needs. The student is expected to: (E) select and use appropriate standard international units to identify nutritional needs for infants such as caloric requirements, protein, lipids, carbohydrates, and proton control. (F) research the advantages of breast feeding. (C) draw conclusions regarding the impact of the infant on the family in areas such as roles, finances, responsibilities, and relationships. (B) generate ideas and gather information relevant to care and protection of infants such as child care options, abuse, guidance, services and agencies, immunizations, and appropriate health care. Monday – Nutrition and feeding of the infant Objective: The student will summarize when and why new foods should be added to an infant’s diet. Lesson: Discuss the concept of weaning an infant off the bottle and onto more solid foods. Show the PowerPoint slide Weaning. Have students formulate ideas as to what factors are involved in an infant’s readiness to move from the bottle to other foods. Show the PowerPoint slides Nutritional Needs of the Infant depicting when certain foods are introduced to an infant and what nutrition those foods bring the infant. Discuss with students the definition of malnutrition (faulty nutrition due to inadequate or unbalanced intake of nutrients or their assimilation or utilization) and undernutrition (deficient bodily nutrition due to inadequate food intake or faulty assimilation) and how each may occur when moving infants from bottle to solid foods and as children grow and develop. After discussion is complete, distribute teaching aid Moving on to Solid Foods for students to complete individually. Tuesday – Impact of the infant on the family Objective: The student will draw conclusions regarding the impact of the infant on the family in areas, such as roles, finances, responsibilities, and relationships. Lesson: Explain to students that with the advent of an infant many responsibilities and relationships change. Infants require a great deal of time from the parents or caregivers, money to provide for the many needs, and nurturing. As a new parent, relationships with others and roles in the family may change. Distribute the teaching aid Impact of the Infant on the Family to students. Instruct students to complete the activity as if they just had the infant and their own life and family life will be affected by role changes, financial changes, responsibility changes, and relationship changes. Wednesday – Protection and safety of the infant Objective: The student will choose appropriate child care for various situations. Lesson: Show the PowerPoint slides Types of Child Care Services. Discuss with students each type of child care service, its purpose, age of the children served, services provided, and possible cost of services. Distribute teaching aid Child Care Scenarios. Based on what students have learned, have them provide solutions for the scenarios. Thursday – Test Review Objective: The student will complete a test review of material learned this six weeks. Lesson: Test 1.2 review. Friday – Test 1.2 Objective: The student will be tested on what they have learned the 1 six weeks. Lesson: Test 1.2 st