Rhetorical Devices

Becker/Tegethoff
Rhetorical Devices
10 points
Name: ____________________________________
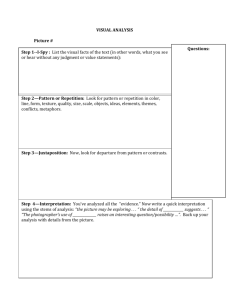
Directions: Most all of the rhetorical devices below needs a definition, fill-in-the-blank, and /or example. It’s your job to find the missing hole and fill it! Today, we are going to work through this packet. Feel free to work with a partner. When you find a great example either in a youTube clip or online example/text, you’re encouraged to share with others or with the whole class.
Sources: www.Americanrhetoric.com
http://www-pub.naz.edu:9000/~csick4/english_site/balance.html
http://www.virtualsalt.com/rhetoric.htm#Procatalepsis
Devices of Repetition:
Epimone: Repetition of a question to dwell on a point. This is often seen in drama.
Example: Taxi Driver “You talkin’ to me? Because I see you, you talkin’ to me?”
Anaphora:
Example:
Epistrophe:
Example:
Epanalepsis:
Example: “The king is dead, long live the king!”
Assonance: The repetition of vowel sounds (a, e, i, o, u) between words within a sentence, lyric, or line.
Example: “Hear the mellow wedding bells/ Golden bells!/ What a world of happiness/ their harmony foretells!...” -Edgar Allen Poe “Bells
Consonance:
Example: “And frightful a nightfall folded rueful a day/ Nor rescue, only rocket and lightship, shone/ And lives at last were washing away…”
-“The Wreck of the Deutschland” by Gerald Hopkins
Devices of Transition:
Word Bank:
Metabasis
Procatalepsis
Hypophora
__________________________: One or more questions is/are asked and then answered, often at length, by one and the same speaker; raising and responding to one's own question(s).
Example:
__________________________: In anticipation of objection, the speaker raises the objection and responds to it to permit an argument from moving forward.
Example: It is usually argued at this point that if the government gets out of the mail delivery business, small towns like Podunk will not have any mail service. The answer to this can be found in the history of the Pony Express . . .
___________________________: Consists of a brief statement that acknowledges what has been said and what will follow. It functions as a transitional summary that links sections of speaking together.
Example:
Devices of Emphasis:
Word Bank:
Climax
Enumeratio
Asyndeton:
Example:
_______________________: arranging a list of consequences in increasing priority
Example:
_________________________: to enumerate the consequences, causes, or effects
Example: “…Much will be said about my father the man, the storyteller, the lover of costume parties, a practical joker, the accomplished painter. He was a lover of everything French: cheese, wine, and women. He was a mountain climber, navigator, skipper, tactician, airplane pilot, rodeo rider, ski jumper, dog lover, and all-around adventurer…” –Eulogy for Ted Kennedy Sr.
Devices of Balance
Parallelism-
Similarity of structure in a pair or series of related words, phrases, or clauses.
Example:
Antithesis/Chiasmus:
Example:
"You forget what you want to remember, and you remember what you want to forget"(Cormac McCarthy, The Road, 2006).
Devices of Clarity
Word Bank:
Distinctio
Exemplum
______________________: An explicit reference to a particular meaning or to the various meanings of a word, in order to remove or prevent ambiguity.
Example:
_______________________: To provide an anecdote that can be real, fictitious, brief, or extended to illustrate a point
Example:
***************************************************************************************
Other figures of speech to keep in mind:
Sententia: The use of a maxim or conventional wisdom to sum up a situation.
Example: "So, I'm happy tonight. I'm not worried about anything. I'm not fearing any man. 'Mine eyes have seen the glory of the coming of the Lord.'"
-- Martin Luther King, Jr., I've Been to the Mountaintop
Transposition: The inversion of normal order of words.
Example: “Why should their liberty than ours be more?” –Comedy of Errors,
Shakespeare
Litotes: An understatement when an idea is expressed by a denial of its opposite, principally through double negatives
Example: The prison is not terribly good.
Metaphor: A figure of speech in which a word or phrase is applied to an object or action to which it is not literally applicable.
Example: The AP Calculus test is a bear.
Simile: A figure of speech in which a word or phrase is applied to another using like or as.
Example: Shrek: Ogres are like onions. Donkey: They stink? Shrek: Yes. No!
Donkey: They make you cry? - Shrek