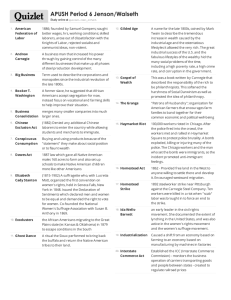
The Growth of Industry
advertisement

The Growth of Industry Goal 5 Copy and complete this chart. Labor Unions Union National Labor Union (NLU) Colored National Labor Union (CLU) Knights of Labor American Federation of Labor (AFL) American Railway Union (ARU) Industrial Workers of the World (Wobblies) Year Important People Characteristics/Significance Copy and complete this chart. Strikes Strike Year People Great Strike of 1877 Haymarket Affair Homestead Strike Pullman Company Strike X Cause Effects Strikes Strike Year Great Strike of 1877 1877 Haymarket Affair 1886 People Cause Effects Pres. Rutherford B. Hayes Baltimore & Ohio Railroad workers protested their second wage cut in two months The strike spread to other railroad lines, stopping traffic for over a week, impeding interstate commerce; Federal troops ended the strike X Protest police brutality on strikers; Bomb was thrown into a police line Police fired on workers; police officers and workers died; Public began to turn against the labor movement Strikes Strike Year People Cause Effects Wage cuts at Carnegie’s Steel Company’s Homestead plant; scabs were brought in and violence irrupted Three detective and nine workers killed; Plant was closed until the strike was broken up by the National Guard Homestead 1892 Strike Henry Clay Frick Pullman Company Strike Eugene Workers were laid off; V. Debs pay cuts without a 1893 decrease in the cost of housing; Pullman refused to negotiate with workers; ARU boycotted Pullman trains Scabs were hired and violence irrupted; Federal troops sent in; Debs jailed; Workers fired & blacklisted Labor Unions Union Year Important People Characteristics/Significance National 1866 Labor Union (NLU) William H. Sylvis First large-scale nations labor union; some local chapters refused African Americans; 1868 got Congress to legalize an eight-hour day for government workers Colored 1869 National Labor Union (CLU) Isaac Meyers Emphasized cooperation between management and labor; political reform important; Disbanded because Knights of Labor formed Knights of Labor Uriah Stephens Open to all workers, regardless of race, gender or degree of skill; equal pay and 8 hour work day; Believed strikes should be the last resort & advocated for arbitration 1869 Labor Unions Union Year Important People Characteristics/Significance American Federation of Labor (AFL) 1886 Samuel Gompers Skilled workers; Focused on collective bargaining; Used strikes as a major tactic; Won higher wages and shorter workweeks American Railway Union (ARU) 1894 Eugene V. Debs Specific to the railroad industry and included skilled and unskilled laborers; Won higher wages by using strikes Industrial Workers of the World (Wobblies) 1905 Eugene V. Debs Radical socialist labor union that wanted government control of business and property and William “Big Bill” Haywood equal distribution of wealth; Included miners, lumberers, cannery and dock workers; Included African Americans Create and complete this chart. The Expansion of Industry Invention Steam Engine Drill Bessemer Process Light bulb Typewriter / Telephone Year Inventor Significance The Expansion of Industry Invention Year Inventor Significance Drill for oil; oil used in industry Steam Engine Drill 1859 Edwin Drake Bessemer Process 1850 Henry Bessemer Removed the carbon from iron to produce steel, & William Kelly which was more flexible, lighter, and rust-resistant; Railroad boom, bridges, skyscrapers Light bulb 1876 Thomas Edison Inexpensive, convenient source of energy used in factories (factories could be located anywhere, not just near water & workers could work all hours, not just in the day Typewriter/ Telephone 1867/ 1876 Christopher Sholes/ Alexander Graham Bell New jobs for women The Age of the Railroads Effects of the Rapid Growth Of Railroads The Age of the Railroads Formation of Standard time zones Iron, steel, coal, Lumber, and glass Industries grew because The railroad needed Their products Many different Regions of America Were now linked Long distance Travel now Possible for Many Americans Some people became Very rich from Profits made in the Railroad industry Rapid Growth Of Railroads Trade among cities, Towns, and settlements Increased. Communities Grew and prospered New towns created (ex. Pullman factory, Which created sleeping cars For trains, had a town Built around it to Support its workers Answer these questions in your notebook. 1. 2. What factors made the Triangle Shirtwaist factory fire in NYC so lethal? What was the Gentlemen’s Agreement of 1907-1908? Immigration Read about what it was like to come through the inspection stations at Ellis Island and Angel Island. Write a letter home to a friend or family member telling them about your experience at either Ellis Island or Angel Island. (This can be done for homework.) Civil Service Reform Copy and answers these questions in your notebook. 1. What is patronage? Why is it bad? 2. What happened to President Garfield? 3. What did the Pendleton Civil Service Act do? Vocabulary 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Munn v. Illinois Interstate Commerce Act Andrew Carnegie Vertical integration Horizontal integration Social Darwinism John D. Rockefeller “Robber Barons” Sherman Antitrust Act Industrial Workers of the World Mary Harris Jones Ellis Island 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. Angel Island Melting pot Nativism Chinese Exclusion Act Urbanization Americanization movement Tenements Mass transit Settlement houses Jane Addams Political machine Boss Tweed Industrialization Immigration Urbanization Industrialization Emergence of Big Business late 19th century witnessed the emergence of big and powerful businesses, which monopolized their industry. The leaders of these businesses were called “Robber Barons” due to their unscrupulous business practices. The John D. Rockefeller Rockefeller started Standard Oil Company Why was oil important? Trusts Standard Oil Company was the nation’s first trust. A trust is a business arrangement in which a number of companies unite into one system. They want to destroy all competition & create monopolies. Monopolies A monopoly is when a business has complete control over an industry’s production, quality, wages paid, and prices charged. The Sherman Anti-trust Act prevented the creation of monopolies by making it illegal to establish trusts that interfere with free trade. Andrew Carnegie Andrew Carnegie founded a steel company in Pittsburgh, PA (THINK: Pittsburgh Steelers). Steel was important to the railroad industry. He was a millionaire philanthropist who began the public library system. He used vertical and horizontal integration to build his steel empire. Andrew Carnegie Vertical Integration A business buys out all of its suppliers EX: McDonalds would buy out the makers of: Buns (Merita Bread Company) Ketchup (Heinz) Meat (Smithfield Meats) French Fries (Idaho) Horizontal Integration A business buys out all of its competitors For example, McDonald’s would buy out: Burger King KFC Taco Bell Sonic Social Darwinism Social Darwinism was a philosophy of this time period which drew from Darwin’s theory of evolution. Put in terms of society, Social Darwinism states that it is acceptable for businesses to be big and controlling, because society is all about the “survival of the fittest”. The weak help the strong survive & thrive. Problems for Workers Many problems were faced by workers in factories: Long hours Low pay No benefits (health insurance, sick leave) Dangerous working conditions Child labor Video Questions- “A Child on Strike” 1. 2. What was your reaction to Camella Teoli’s accident? What labor practices are taken for granted today that were not afforded to people living in 1910? Workers Unite Workers united and formed labor unions, which demanded improved working conditions Labor unions would strike (work stoppages by union members as a form of protest) Key labor unions included: National Labor Union Industrial Workers of the World (Wobblies) American Railway Union American Federation of Labor (founded by Samuel Gompers) Knights of Labor Immigration New Immigrants Assimilate Immigrants came to America to work in factories. They often faced culture shock, confusion & anxiety resulting in becoming a part of a new culture that you do not understand. America became a melting pot, a mixture of different people and cultures who blend together and abandon their native language and culture. Immigration Stations Ellis Island, New York (Statue of Liberty) was the inspection station for European immigrants. Angel Island, San Francisco, CA was the inspection station for Asian immigrants. In 1887, the Chinese Exclusion Act was passed which banned entry of all Chinese immigrants, except students, teachers, merchants, tourists, and government officials. Video Questions- “From China to Chinatown: Fong See’s American Dream” 1. 2. How did Fong See overcome the difficulties facing Asian immigrants in America during his lifetime? What did Lisa See learn about living in a diverse society from her greatgrandfather’s experience? Urbanization Urban Problems Problems 1. Housing Shortages 2. Transportation 3. Water 4. Sanitation 5. Crime 6. Fire Causes- Explain the Problem Solutions Urban Problems Problems Causes Solutions 1. Housing Shortages So many people came to the cities with few housing options: 1. House of the outskirts of townbut, how would they get into the city for work? 2. Tenements that were crowded & unsanitary NYC passed a law that set standards for plumbing and ventilation 2. Transportation A large number of people needed to move within the city Mass transit developed, such as street cars & electric subways 3. Water Need for safe drinking water as populations grew, because there was inadequate piped water or none at all; Diseases spread Built public waterworks to handle more people; Filtration was introduced Urban Problems Problems Causes Solutions 4. Sanitation Horse manure piles; sewage in open gutters; smoke from factories; no trash collection Sewer lines & sanitation departments established 5. Crime Poverty led to crime such as pick pocketing and theft Established police forces 6. Fire Limited water supply; Wooden dwelling; Use of candles & kerosene heaters posed fire hazards; Deadly fire in Chicago & after the San Francisco earthquake Full time fire departments established; Automatic fire sprinklers invented; Replace wood buildings with brick, stone, and concrete Urban Reforms A movement called the Social Gospel preached salvation through service to the poor Settlement houses were created, as community centers for people in urban areas, especially immigrants. Settlement houses provided educational, cultural, and social services. Jane Addams Hull House, Chicago The Gilded Age The time period from 1877-early 1900s is known as the “Gilded Age”. Writer Mark Twain coined this term. Gilded is something covered in a thin layer of gold to make it look nice & shiny. This expression was used to imply that the time period appeared to be prosperous, but that appearance was just covering up the poverty and corruption of society. Political Machines A new power structure emerged in the cities to take control, called political machines. The political machine was an unofficial entity that kept a certain political party in power. Political machines were headed by a “boss” who may or may not hold a political office himself. William “Boss” Tweed, Tammany Hall Boss of the NYC Democratic Party The Purpose of the Political Machines Political machines provided services to the city, such as police & fire departments. In exchange for votes, the political machines would provide jobs and other services for immigrants. Government Corruption Many political machines and government officials became corrupt as their power grew. Graft (using political influence for personal gain) & “kickbacks” (taking money from government construction projects) were common. Ex. Boss Tweed built a NYC Courthouse which actually cost $3 million, but the taxpayers were charged $13 million TEST REVIEW Industrialization-Immigration-Urbanization Industrialization: new technologies led to industrialization; robber barons; Rockefeller & Carnegie; Social Darwinism; monopolies; horizontal/vertical integration; trusts- Sherman Antitrust Act= no monopolies Immigration: Ellis/Angel Island; discrimination; melting pot/assimilation; why they came?; exploitation (problems) of worker; emergence of labor unions Urbanization: urban problems; reforms; settlement houses; political machine