Plant Pigments
advertisement

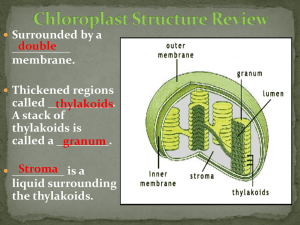
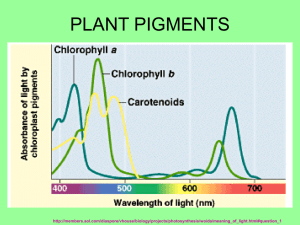
Investigation #5 Plant Pigments and Photosynthesis Plant Pigments: Purpose: Rate of Photosynthesis Purpose: Pre-Lab Questions •What are pigments? •What is the electromagnetic spectrum? •Why are leaves green? •What colors do you expect to see? •How does paper chromatography work? •What variables affect the rate of photosynthesis in living leaves? •Design a controlled experiment to test one of the variables from PLQ#6. Materials: -Chromatography paper -Solvent (Petroleum ether/acetone solvent) -Pencil -Ruler -Coin -Different kinds of leaves Procedure Step 1: Prepare chromatography papers. Draw a fine pencil line across the strip about 1.5 cm from one end. Step 2. Use the ribbed edge of the coin to push the plant cells into the chromatography paper. Step 3: Set the chromatograph paper in the solvent. Step4 : Stop the chromatogram and record (Sketch) your results. When the solvent "front" is within 2-3 cm from the top of the paper, remove the chromatogram. Use a pencil to quickly mark the location of the solvent front. Step 5: Identify your pigments. Calculate the Rf value (described below) for each pigment. •Rf value = distance from origin to pigment distance from origin to solvent front Data Table Leaf 1- Spinach Color Pigment1 Pigment2 Pigment3 Pigment4 Rf Value Name of the Pigment Photosynthetic pigments • • Pigments absorb different λ of light chlorophyll – absorb violet-blue/red light, reflect green chlorophyll a (blue-green): light reaction, converts solar to chemical E chlorophyll b (yellow-green): conveys E to chlorophyll a Caroten (yellow, orange): photoprotection, broaden color spectrum for photosynthesis Xanotophyll (Yellow)