Daily TAKS Connection: DNA
advertisement

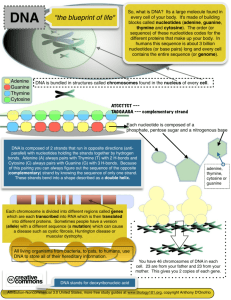
Daily TAKS Connection: DNA BIO(6): The student knows that the structures and functions of nucleic acids in the mechanisms of genetics. The student is expected to: (A) Describe components of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), and illustrate how information for specifying the traits of an organism is carried in the DNA. Foldable Instructions Construct a folded book foldable titled “DNA” Materials: Foldable handout (2 pages) Scissors Pen Colored pencils/crayons Instructions: Hamburger fold the foldable handouts Cut 2 cm slits from the edges of the fold of the handout that has page 2 (as marked) Cut along the fold line of the other sheet of paper beginning and ending about 2 cm from each end (as marked). Burrito fold and insert paper from step 2 into the hole and open, forming a book. Notes: “What is DNA?” Record the following notes on page 1 of your foldable: DeoxyriboNucleic Acid Function: blueprint for life; determines traits of an organism Composition: Double-stranded Strands are made of nucleotides – a single unit of DNA. Contain a phosphate group, a sugar, and a nitrogen base. Arranged in a double helix Location in every cell: nucleus Question 1 (Answer questions on page 6.) In all plant and animal cells, the nucleus contains long molecules of DNA. Which of the following best describes the function of DNA? a. DNA provides the shape and structure of the nucleus. b. DNA packages materials for transport through the nucleus. c. DNA carries materials into and out of the nucleus. d. DNA contains the blueprint for producing the whole organism. Question 2 All of the following are found in a DNA molecule except — a. carbon dioxide b. deoxyribose c. nitrogen d. phosphate Question 3 Which molecule is most responsible for determining an organism’s eye color, body structure, and cellular enzyme production? a. Complex starch b. Fatty acid c. Carbohydrate d. Deoxyribonucleic acid Question 4 Proteins are produced according to a special code found in the control center of the cell. Which of these molecules carries this code? a. DNA b. ADP c. Phosphate d. Lipid Notes: “DNA Base Pairing” Record the following notes on page 2 of your foldable: Four nitrogenous bases Adenine Thymine Cytosine Guanine Base pairing adenine complements (pairs with) thymine cytosine complements guanine Sequence of bases (nucleotides) determines traits “Base Pairing Practice” On page 3 of your foldable, determine the complement strand of DNA for each strand shown below: ATACGCCCTTGAG _________________ GCCCTATATTGCG _________________ GTGTCCCAGGGG _________________ Question 5 In DNA, which of the following determines the traits of an organism? a. Amount of guanine b. Number of sugars c. Sequence of nucleotides d. Strength of hydrogen bonds Question 6 Erwin Chargaff studied the DNA of organisms within a single species. Chargaff discovered that the amount of adenine is about equal to the amount of thymine. Which of these explains why the ratio of adenine to thymine is nearly 1:1? a. Adenine and thymine pair with each other. b. Adenine binds with phosphates, while thymine binds with nitrates. c. Adenine and thymine are identical in chemical composition. d. Adenine bases contain a form of thymine. Question 7 “Cytosine—guanine—thymine—guanine” describes — a. nucleotides within an RNA strand b. a sequence of bases within a DNA section c. points of DNA separation during protein synthesis d. tRNA codons for specific amino acids Notes: “Replication” Record the following notes on page 4 of your foldable: Replication An exact copy of the DNA is made Takes place in the nucleus Notes “Steps of Replication” (record on page 5) 1. DNA unwinds and the two strands separate. 2. DNA polymerase (an enzyme) adds the complementary base pairs to each side. 3. Result: two identical molecules of DNA, each with one new and one old strand of DNA Question 8 DNA molecules separate into single strands, which are then used to construct two identical strands of DNA. This process ensures that the — a. cytoplasm is in equilibrium b. mitochondria are genetically identical to the chloroplasts c. parent cells use little ATP d. daughter cells are genetically identical to the parent cells