DNA – Worksheet
advertisement
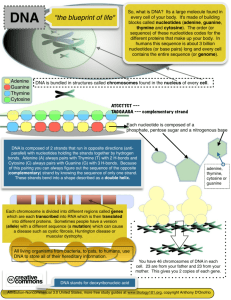
6A (RS) DNA: Identify components of DNA, and describe how information for specifying the traits of an organism is carried in the DNA What is DNA? DNA - deoxyribonucleic acid A chemical substance that’s present in the nucleus of all cells in all living organisms controls the production of proteins DNA is found in the chromosomes in the nucleus. DNA of the chromosomes is the genetic material that is passed from generation to generation(Heredity) Genetics is the study of heredity Genes are sections of DNA. Eukaryotic Chromosomes Contain DNA and proteins called histones Tightly packed DNA and proteins form chromatin During mitosis, the chromatin condenses to form tightly packed chromosomes Nucleic Acids Complex molecule that stores and communicates genetic information Two types of Nucleic Acids DNA- deoxyribonucleic acid RNA – ribonucleic acid DNA Shape Double Helix The ladder arrangement of DNA is twisted, producing the characteristic double-helix appearance DNA Structure DNA is made up of nucleotides Nucleotides Have Three Parts 1. 2. 3. Phosphate group Simple Sugar (5-carbon sugar) Nitrogen Base Ribose & Deoxyribose Ribose is a sugar, like glucose, but with only five carbon atoms in its molecule Deoxyribose is almost the same but lacks one oxygen atom Both molecules may be represented by the symbol The Nitrogen Bases The most common organic nitrogen bases are: Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Cytosine (C) Guanine (G) Pairing Nitrogen Bases Adenine forms a bond with Thymine (A-T) Adenine Thymine Cytosine bonds with Guanine (C-G) Cytosine Bases are held together by a hydrogen bond Guanine Nucleotides Phosphate Group + Deoxyribose+ one base= (or Ribose) PO4 Nucleotide adenine deoxyribose Joined nucleotides PO4 PO4 A molecule of DNA is formed by millions of nucleotides joined together in a long chain PO4 PO4 sugar-phosphate + bases backbone Do you remember what kind of chemical reaction joins monomers together by removing water? PO4 PO4 adenine thymine PO4 PO4 cytosine guanine PO4 PO4 PO4 PO4 Label the Parts