World Economic Geography
advertisement

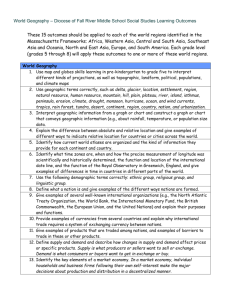
World Economy Geography Instructor: Dr. Truong Thi Kim Chuyen Email: worldeconomicgeography@gmail.com World Economy Geography Readings: Fellmann – Getis - Getis (1998). Human Geography: Landscapes of Human Activities. Brown & Benchmark. Paul Knox (2008)The geography of the world economy. You should read the materials assigned before the class, as it will facilitate your understanding. Additional readings might be assigned throughout the quarter on special topics/issues. They will be distributed in class and/or via email. Course Description Course Objectives Grades Attendance, Assignment, Seminar: 30 % Mid-term Exam: 30 % Final Exam: 40 % Course Description Course provides various dimensions of the world economy geography (WEG) in the age of globalization. In a world, the trend of global trade is increasingly vital, WEG is an imperative for all who wish to know what is happening to their global economy. Course gives the very basic concepts and terms in studying world economic geography. In economic aspects, it concerns: the varied ways of people earning, the patterns of human activities to produce, the distributed and consumed good and services, and the geographic framework of world trade and business. Course Description (cont.) The lectures will have a emphasis on geographic changes in the world economy. We will examine the geographic organization of economic activity around the world at different geographical scales (global, regional and local) as well as the relationship between geographic conditions and economic development in different states Course requires critical thinking on current economic and social problems from a geographic perspective. Expected outcome are able to: understand the basic concepts. be aware of the relationship between geographic conditions and economic development. understand the distribution and migration of human in the process of the economic growth. classify and analyze principles of location. differentiate relationships of economic interdependence of the states, Understand of the characteristics of transnational corporations (TNCs) and regional economic blocs. Course Outline Chapter 1. Introduction : Some background basics Chapter 2.Population: World Patterns and Regional Trends Chapter 3. Livelihood and Economy :primary activities Chapter 4. Livelihood and economy : From blue to gold collar Chapter 5. Patterns of Development and Change Seminars ( using Paul Knox ‘s book) 1.The changing world economy 2.Global patterns and trends 11.Services :going global? 12. International and supranational institutionalized integration