The Second New Deal
advertisement

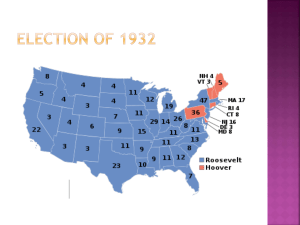
FROM THE MOUTH OF ROOSEVELT We find our population suffering from the old inequalities, little changed by our past sporadic remedies. In spite of our effort and in spite of our talk, we have not weeded out the over privileged and we have not effectively lifted up the underprivileged....We have...a clear mandate from the people, that Americans must forswear the conception of the acquisition of wealth which, through excessive profits, creates undue private power over private affairs and, to our misfortune, over public affairs as well. In building toward this end we do not destroy ambition, nor do we seek to divide our wealth into equal shares on stated occasions. We continue to recognize the greater ability of some to earn more than others. But we do assert that the ambition of the individual to obtain for him and his a proper security, a reasonable leisure, and a decent living throughout life is an ambition to be preferred to the appetite for great wealth and great power. HOW IS THE 2ND NEW DEAL DIFFERENT FROM THE FIRST NEW DEAL? Whereas the First New Deal focused on all three R’s (Relief, Recovery and Reform), and provided immediate help toward the Recovery of the ailing Depression economy, The Second New Deal focused on Reform and Relief, especially to directly help minorities, the poor, and the elderly (those people in society most vulnerable). ND 2 HOW IS THE NEW DEAL THE SAME AS THE NEW DEAL? • BOTH Relied on Deficit Spending. The Federal Deficit ran up from 461 million in 1932 to 4.4 Billion in 1936. • So What? SOCIAL SECURITY ACT • August 14, 1935 • Pension System for Retirees – based upon an automatic collection of taxes from employers and employees throughout working people’s careers, then paid monthly to retirees over the age of 65. • Eventually expanded to include widows, young children of deceased workers, unemployed, and people hurt on the Job. WPA Works Progress Administration A make-work agency. Created a huge number of very diverse jobs. Included public works as well as programs in the arts. _____ The Works Progress Administration's Federal Art Project (WPA/FAP) 5,300 Artists were hired to create art such as large murals (2,500 in all) to decorate buildings and downtown areas. WPA Mural Inside Coit Tower In San Francisco Showing Scenes Of The Gold Rush And Men Panning For Gold Nuggets Alfred Crimi, Modern Surgery and Anesthesia, Harlem Hospital FEDERAL WRITER’S PROJECT Hired 6,000(+) writers to write things like guide books for every state in the Union. More importantly writers recorded the Oral histories of various minority groups. Ex. The Slave Narratives. WAGNER ACT (AKA: National Labor Relations Act) ORGANIZED LABOR Because the Wagner Act recognized the right of employees to join unions and gave workers the right to collectively bargain, there was a spike in union activity (3 million union members in 1933 to 10 million in 1941), and strikes became a frequent occurrence in the Depression Decade. Fair Labor Standards Act (1938) – created minimum wage (.40/hr), and time and ½ for overtime; maximum workweek (40 hours); and child labor restrictions (under 16) THE SUPREME COURT SHOOTS DOWN NEW DEAL IDEAS In 1935 the Supreme Court killed the National Recovery Act and a key piece of legislation from the Agricultural Adjustment Act. Roosevelt was worried that they would rule more of the New Deal Unconstitutional. COURT-PACKING Roosevelt’s 1937 plan was to add up to six new judges to the supreme court since so many of the judges were already “elderly and overworked”. These new judges would of course have been New Deal supporters How does this make Roosevelt look? ADD TO STUDY GUIDE: 7. Women during the New Deal/ Eleanor Roosevelt 8. African- Americans during the New Deal/ New Deal Coalition 9. Native Americans during the New Deal/ the Environment 10. Popular Culture during the 1930’s (Movies, Radio, Literature) 11. Expanding Role of Government and the Presidency during the New Deal