Week of 10-15-2013
advertisement

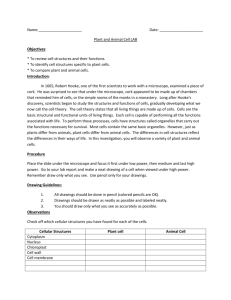
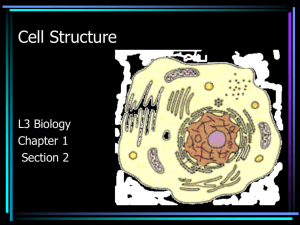
Week of 10-15-2013 Ms. Tate D110 Biology/Pre-Ap International Scholars Academy Tuesday 10-15 Study Skills 2nd Pd 1. Students will watch the Amanda Todd Story video on YouTube (8 min.) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vOHXGNx-E7E 2. Writing: Reflection Paper ( include your reactions to the film. 3. Think-Pair- Share 4. Students will watch the teen reaction video via YouTube (15 min.) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VF6cmddWOgU 5. Discussion: Compare your reactions to those teens from the film 6. Bullying Rap/Song/Poem Activity Tuesday 10-15-13 Biology 3rd-5th, 7th 8th Objective: Compare the structures and functions of different types of biomolecules, including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids; identify and investigate the role of enzymes 1. Exam: Biomolecules/Enzymes 2. Start Working on Homework: Microscope Functions and Parts ( use page 1070 in the biology book as a guide)- (30L) Reminders: Enzyme Lab report will be checked in class tomorrow; Microscope Worksheet MUST be completed or you may NOT participate in lab. Wednesday 10-16 Study Skills STUDY SKILLS LESSON 3 & 4 • Interview a Word Why not turn vocabulary acquisition into a game? Using the Interview a Word strategies, students will review and summarize learning to develop concepts and comprehension. • Select key words important to understanding a concept or unit. • Discretely give each student a word. • Write the interview questions on the board. • Have students “become” the word and write answer to questions. • Without revealing the word, the teacher or a student acts as Interviewer and asks the questions. After the interview, the class guesses the word. Wednesday 10-16-13 Biology Class Objective: • Distinguish between eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Agenda: 1. Bell Ringer 10 ( 8 min to complete, 5 min to review)- (30R) 2. Notes: Cell Theory / Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes – (31L) 3. Door Ticket: Venn Diagram (31R)-Compare and Contrast the two cell types by completing the Venn diagram on the front board in your journal. Homework: Cell Organelles Worksheet ( this is your vocabulary as well (32L). It is due by Friday. Have the microscope worksheet and your enzyme report ready. Cell Theory and Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote What is a Cell? • Cell – Basic unit of living things. Organisms are either: • Unicellular – made of one cell such as bacteria and amoebas. OR • Multicellular – made of many cells such as plants and animals. Scientists to Remember • Robert Hooke (1665) – Observed “cells” in cork • Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1674) – Father of Microscopy – Saw tiny living things in pond water. Cell Theory • Confirmed discoveries that all scientists believe to be true about cells: – 1. Cells are the basic unit of life. – 2. All living things are made of cells. – 3. New cells are produced from existing cells. Microscopes • Light Microscope – magnifies tiny organisms up to 1,000 times. -Uses light and lenses. -We use these. • Electron Microscope – magnifies up to a million times. -Uses electrons. The Discovery of Cells before nucleus true nucleus Eukaryotes 1. Has a nucleus with a nuclear envelope 2. Bigger and more complex than prokaryotes 3. Have membrane bound Organelles (golgi, ER, lysosomes…etc) 4. DNA – double-stranded and forms chromosomes (highly organized) 5. Can be uni- OR multicellular organisms 6. Ex: animals, plants, fungi Prokaryotes 1. NO nucleus 2. NO membrane bound organelles (just ribosomes) 3. ALL are unicellular 4. Smaller than eukaryotic cells 5. Forerunner to eukaryotic cells (smaller and more simple) 6. DNA – single strand and circular 7. Ex: ALL Bacteria Similarities 1. Contain all four biomolecules (lipids, carbs, proteins, and nucleic acids) 1. Have ribosomes 2. Have DNA 3. Similar Metabolism 4. Can be unicellular 5. Have cell/plasma membranes or cell wall Eukaryote VS. Prokaryote Picture Study Skills 10-17-13 Study Hall Day You may: Work on homework/class work Study quietly Read quietly Work on a project or presentation If it is NOT on the list, you may NOT do it in class Thursday 10-17-13 Objective: To observe different cell types; understand that there are specialized cells with specific functions; explain how to and create a wet mount slide 1. Pro Vs. Eukaryote/ Cell Theory ( review) 2. Station Rotation ( Cells) – 32R- 34R 32R- Sta 1, 33L- Sta 2, 33R- Sta 3, 34L- Sta 4, 34R- Sta 5 1. Clean Up Reminders: Cell Organelle sheet due tomorrow ( 3rd-5th, Bio Review Sheet due tomorrow); Paste Cell Pictures in Journal Due: Enzymes and Microscope sheet Lunch SSR Amsterdam http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EOMXqcHt5ts Cities – The Real Berlin http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FEH1Z4NwRLo German Food • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bX9bsp4SSNY TGIFriday 10-18-13 Objective: understand that cells have specialized parts called organelles with specific functions; Be able to identify the structure and explain the function of each cell organelle; distinguish between plant, animal and bacteria cells Agenda 1. Due: Cell Organelles (review)- 10 min (32L) 2. Cell City Analogy -10 min (35L) 3. Continue Station Rotation (32R-34R) 32R- Sta 1, 33L- Sta 2, 33R- Sta 3, 34L- Sta 4, 34R- Sta 5 4. Clean Up Homework: Cell City Analogy Project (due next Friday 10/25)- Rubrics given (keep up with them) Due: Bio Review and Cell Organelles Extra Credit: Create a Two 3D cell models (with labels). This is due Tuesday at the START of class. Creating the model will also aide you in studying the structures of the cell. You can do 2 of the 3 : an animal cell, a plant cell or a bacteria cell. You must also tell whether the cell is classified as prokaryotic or eukaryotic. ---This will drop 1 quiz and 1 homework/daily grade. Homework Review Organelle CELL WALL Description Rigid, tough, made of cellulose Function Protects and supports the cell Animal, Plant or Both Plant CELL MEMBRANE Thin, covering, protects cells Protects the cell, performs active transport and passive transport, moves materials in and out of the cell, communication Both CYTOPLASM Jelly like substance that contains organelles Pads and supports organelles inside the cell. Moves by cyclosis Both NUCLEUS Dense, ball shaped structure, contains DNA Controls all of the cell’s activities Both NUCLEAR MEMBRANE Thin covering over the nucleus Covers and protects the nucleus Both NUCLELOUS Small dark area in the nucleus Produces ribosome’s Both CHROMATIN In the nucleus, made of DNA and protein, contains genes Provides instructions for the cells activities, (growth, reproduction) Both ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM Clear, tubular system of tunnels throughout the cell Transports materials like proteins around the cell Both Continued…. RIBOSOME Small specks made of RNA. Makes proteins Found in cytoplasm or on the endoplasmic reticulum Both MITOCHONDRIA Location in the cytoplasm, bean shaped Supplies energy or ATP for the cell through cell respiration using glucose and oxygen Both VACUOLE Large open storage area, smaller in animal cells Storage tank for food, water, wastes or enzymes Both CHLOROPLAST Green structures that contain chlorophyll Captures sunlight and uses it to produce food through photosynthesis Plant GOLGI BODY Small bags with tubes connecting them Packages and secrets proteins for use in and out of the cell Both LYOSOME Small, round structures, containing enzymes Digests older cell parts, food or other objects Both CENTRIOLE Small cylindrical Used with the spindle apparatus during mitosis Animal Extra Credit: Create a Two 3D cell models (with labels). This is due Tuesday at the START of class. Creating the model will also aide you in studying the structures of the cell. You can do 2 of the 3 : an animal cell, a plant cell or a bacteria cell. You must also tell whether the cell is classified as prokaryotic or eukaryotic. ---This will drop 1 quiz and 1 homework/daily grade.