sharks: the anatomy and physiology of a predatorial machine
advertisement

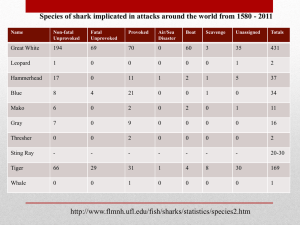
Taxonomy Kingdom – Animalia Phylum – Chordata Class – Chondrichthyes (sharks, skates, rays, sawfishes) Order – 8 orders (Lamniformes (mackerel sharks)) Family – 30 families (Lamnidae) Genus – 50+ genuses (Charcharodon) Species – 370-400+ species (carcharias) List of species External Anatomy Internal Anatomy Feeding Most are carnivorous but some are filter feeders (whale sharks, basking sharks) Tiger sharks are referred to as the “garbage guts” of the shark world Contrary to popular belief, most sharks are picky about what they eat Great whites choose only animals with blubber Respiration Most sharks have to keep moving to move water over their gills Water enters the gill chambers through the mouth or spiracles and exits through the gill slits. Blood in the gill filaments absorbs oxygen from the incoming water. Circulation 2-chambered heart Blood flows from heart to gills to body tissues back to heart Countercurrent heat exchange enables fastmoving sharks to be from 10 to 20 degrees warmer than the water around them Senses Hearing – have inner ear, attracted to low frequency sounds, can hear up to 0.6 miles Vision – excellent, 10x more light sensitive than us, attracted to shiny and thrashing, can see 50 to 100 ft. Taste – have taste buds, actually spit things out Smell – excellent, function in only smell not breathing, can detect some chemicals as small as 1 part per billion Feel – group of sensory cells along outside of body called the lateral line used to detect vibrations in the water Electroreception – Ampullae of Lorenzini detect electric fields given off by living creatures Reproduction Mating is rarely witnessed, male bites onto dorsal fin and internally fertilizes with clasper while over top of the female Can be oviparous (horn, swell sharks), ovoviviparous (mako and sand tiger sharks), or viviparous (hammerhead sharks) Gestation period is very long from 9 months up to 3 ½ years Shark Attacks You are more likely to be killed by stepping in a sand hole and having it collapse than you are by a shark Tips to avoid attacks: Don’t swim during low light periods Stay in groups Be knowledgeable about the area you swim/dive/surf in If you find one, leave it alone Avoid looking like prey Sharks are attracted to: Blood, splashing and loud noises, shiny colors International Shark Attack File Ecology and Human Uses Pilot fish, remora, and others clean parasites like copepods and flatworms off sharks Integral part of the food chain: fishes, crustaceans, mollusks, marine mammals, and other sharks Sharks, elephant seals, and killer whales have been known to eat sharks Behavior researched mainly for avoiding attacks 100 million sharks are killed every year by humans even though several species are endangered and illegal to kill Humans use sharks for: Research, recreation like fishing and viewing, and products like medicine, jewelry, tools, and mainly fin soup Shark Facts The 1st sharks appeared on Earth 400 million years ago well before the 1st dinosaur roamed the Earth Avg. life span is 25 years Sharks never stop growing Largest shark = whale shark (50 ft. long) Smallest shark = dwarf lanternshark (5-7 in. long) Fastest shark = mako shark (30 mph) Deepest diver = Portuguese shark (9,000 ft. or 1. 5 miles) Longest migration = a blue shark traveled 3,740 miles Only freshwater capable shark = bull shark (the Borneo river shark (Glyphis sp. B), the Irrawaddy river shark (Glyphis siamensis), the New Guinea river shark (Glyphis sp. C), the Ganges shark (Glyphis gangeticus), the Speartooth shark (Glyphis glyphis) Highest note heard is 800 Hertz (or G above High C on the piano), so humans can hear many high sounds that sharks cannot Lowest note heard is 10 Hertz (or 1.5 octaves below the lowest key on the piano). The lowest note a human can hear is 25 Hertz, so we miss out on some of the very low frequencies that sharks can detect Man-eaters!!! Great white shark Tiger shark Bull shark Hammerhead shark Mako shark Oceanic whitetip shark Reef sharks, lemon shark, blue shark, etc… Vocabulary Placoid scales (dermal denticles) = small outgrowths that cover the skin of a shark similar in structure to the teeth Liver = organ for energy storage and buoyancy Clasper = one of the modified, usually paired organs by which the male clasps the female during copulation Lateral line = sensitive receptors that detect gentle currents and vibrations Ampullae of Lorenzini = special sensing organs forming a network of jelly-filled canals that detect electrical fields in the water Spiracle = provide oxygenated blood directly to the eye and brain through a separate blood vessel Dorsal fin = fin on top that stabilizes and may provide protection Pectoral fin = paired fins on the side that control steering and add lift as the shark swims Caudal fin = locomotive limb at the end of a shark that propels it forward Viviparous = live birth (get nutrients from mother not an egg) Oviparous = eggs hatch outside the mother Ovoviviparous = eggs hatch inside the mother then give live birth Cloaca = opening shared by the genital organs, the urinary and intestinal tracts Spiral valve = lower portion of the digestive tract that is internally twisted or coiled to increase the surface area, which increases nutrient absorption Atrium = a large muscular chamber that serves as a one-way compartment for blood that is about to enter the ventricle Ventricle = a thick-walled muscular chamber that pumps blood Great white Tiger Bull Great Hammerhead Shortfin mako Blue Whale Basking Lemon Oceanic whitetip Nurse Pacific angel Australian wobbegong Gray reef Blacktip reef Whitetip reef Greenland Spiny dogfish Sand tiger Thresher Leopard Goblin Swell shark Horn shark Bonnethead