Chapter 11
advertisement

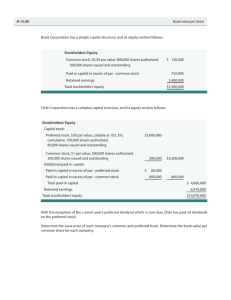
Chapter 11 ` 1 Chapter 11 Reporting and Analyzing Stockholders’ Equity After studying Chapter 11, you should be able to: Identify and discuss the major characteristics of a corporation. Record the issuance of common stock. Explain the accounting for purchase of treasury stock. Differentiate preferred stock from common stock. 2 Chapter 11 Reporting and Analyzing Stockholders’ Equity After studying Chapter 11, you should be able to: Prepare the entries for cash dividends and understand the effect of stock dividends and stock splits. Identify the items that affect retained earnings. Prepare a comprehensive stockholders' equity section. Evaluate a corporation's dividend and earnings performance from a stockholder's perspective. 3 Corporation Possess legal entity Created by law Has most of the rights and privileges of a person Classified by purpose and ownership Purpose - profit or nonprofit Ownership - publicly or privately held 4 Characteristics of a Corporation Separate legal existence Limited liability of stockholders Transferable ownership rights Ability to acquire capital Continuous life Corporation management Government regulations Additional taxes 5 Stock Certificate Shows... name of the corporation stockholder's name class and special features of the stock the number of shares owned the signatures of duly authorized corporate officials. 6 Authorized Stock... Maximum amount of stock a corporation is allowed to sell as authorized by corporate charter. Outstanding Stock... Number of shares of issued stock that are being held by stockholders. 7 Corporations Can Issue Stock... Directly to investors (typical in privately held corporations). Indirectly through an investment banking firm (customary with publicly held corporations). 8 Par Value Stock... Is capital stock that has been assigned an arbitrary value per share in the corporate charter. Is usually low because some states levy a tax on the corporation based on par value. The legal capital per share that must be retained in the business. 9 No-Par Value Stock... Capital stock that has not been assigned a value per share in the corporate charter. Stated Value of No-Par Stock Amount per share assigned by the board of directors to no-par stock. Par Value and Stated Value have NO relationship to market value. 10 Stockholders’ Equity Section of a Corporation’s Balance Sheet... Two Parts: Paid-in (contributed) capital Retained earnings (earned capital). 11 Paid-in Capital... Amount paid to corporation by stockholders for shares of ownership. Retained Earnings... Earned capital held for future use in the business. 12 Accounting for Common Stock Issues The issue of common stock affects only paid-in capital accounts. When the issuance of common stock for cash is recorded, the par value of the shares is credited to common stock. The portion of the proceeds above or below par value is recorded in an additional paid-in capital account. 13 Issuing Stock Above Par If Hydro-Slide, Inc., issues an additional 1,000 shares of the $1 par value common stock for cash at $5 per share, the entry is: Cash 5,000 Common Stock 1,000 Paid-in Capital in Excess of Par Value 4,000 14 Hydro-Slide, Inc. Balance Sheet (partial) Stockholders' equity Paid-in capital Common stock, par value Additional paid-in capital Total paid-in capital Retained earnings Total stockholders' equity $ 2,000 4,000 $ 6,000 27,000 $33,000 15 Mead, Inc. Balance Sheet (partial) Stockholders' equity Paid-in capital Common stock,$5par value, 100,000 shares issued and outstanding Retained Earnings Total stockholders’ equity $ 500,000 200,000 $ 700,000 BEFORE TREASURY STOCK TRANSACTION 16 Treasury Stock... Is a corporation's own stock that has been issued fully paid for reacquired by the corporation held in its treasury for future use. 17 Corporations Acquire Treasury Stock to... Reissue shares to officers and employees under bonus and stock compensation plans. Increase trading of company's stock in securities market in hopes of enhancing market value. Have additional shares available for use in acquisition of other companies. Reduce number of shares outstanding thereby increasing earnings per share. Prevent a hostile takeover. 18 Purchase of Treasury Stock On February 1, 2004, Mead acquires 4,000 shares of its stock at $8 per share. Treasury Stock Cash 32,000 32,000 19 Treasury Stock The Treasury Stock account would increase by the cost of the shares purchased $32,000. The original paid-in capital account, Common Stock, would not be affected because the number of issued shares does not change. Treasury stock is deducted from total paidin capital and retained earnings in the stockholders' equity section of the balance sheet. 20 Mead, Inc. Balance Sheet (partial) Stockholders' equity Paid-in capital Common stock,$5par value, 100,000 shares issued and 96,000 outstanding Retained Earnings Total stockholders’ equity Less: Treasury Stock Total stockholders’ equity $ 500,000 200,000 700,000 32,000 $ 668,000 AFTER TREASURY STOCK TRANSACTION 21 Preferred Stock... Capital stock that has contractual preferences over common stock in certain areas. Dividends Assets in the event of liquidation Preferred stockholders do not have voting rights. 22 Preferred Stock Assume Corporation issues 10,000 shares of $10 par value preferred stock for $12 cash per share. Cash 120,000 Preferred Stock Paid-in Capital in Excess of Par Value--Preferred Stock 100,000 20,000 (Preferred stock may have either a par value or no-par value.) 23 Dividend Preferences Preferred stockholders have the right to share in the distribution of corporate income before common stockholders. The first claim to dividends does not guarantee dividends. 24 Cumulative Dividend... Is a feature of preferred stock entitling the stockholder to receive current and unpaid prior-year dividends before common stockholders receive any dividends. 25 Dividends in Arrears... Are preferred dividends that were scheduled but were not declared during a given period. Are not a liability. No liability exists until a dividend is declared by board of directors. Must be disclosed in the notes to the financial statements. 26 Dividends in Arrears Scientific-Leasing has 5,000 shares of 7%, $100 par value cumulative preferred stock outstanding. The annual dividend is $35,000 (5,000 x $7 per share). Dividends are 2 years in arrears Dividends in arrears ($35,000 x 2 years) Current-year dividends Total preferred dividends $ 70,000 35,000 $105,000 27 Liquidation Preference Is a feature that gives preferred stockholders preference to corporate assets in the event of liquidation. 28 Dividend... Is a distribution by a corporation to its stockholders on a pro rata basis. Pro rata means that if you own 10% of the common shares, you will receive 10% of the dividend. Dividend forms: cash stock 29 Cash Dividend Is a pro rata distribution of cash to stockholders. A corporation must have 2 things to pay cash dividends: Retained earnings Adequate cash 30 Cash Dividend In many states, payment of dividends from legal capital is illegal. Payment of dividends from paid-in capital in excess of par is legal in some states. Payment of dividends from retained earnings is legal in all states. Companies are frequently constrained by agreements with lenders to pay dividends only from retained earnings. 31 Entries for Cash Dividends Three dates are important in connection with dividends: the declaration date the record date the payment date Mo n th a n d ye a r 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 32 Monda y Tue sd a y We dne sd a y Thu rs da y Frid a y S a turda y S un da y 00 The Declaration Date... Is the date the board of directors declares the cash dividend. Commits the corporation to a binding legal obligation that cannot be rescinded. On December 1, 2004, the directors of Media General declare a $.50 per share cash dividend on 100,000 shares of $10 par value common stock. The dividend is $50,000 (100,000 x $.50). 12/1 Retained Earnings Dividends Payable 50,000 50,000 33 The Record Date... The date ownership of the outstanding shares is determined for dividend purposes. Dec 20 No Entry Necessary. The Payment Date... The date dividend checks are mailed. January 20 is the payment date for Media General. Jan 20 Dividends Payable Cash 50,000 50,000 34 A Stock Dividend... Is a pro rata distribution of the corporation's own stock to stockholders. Is paid in stock. Results in a decrease in retained earnings and an increase in paid-in capital. Does not decrease total stockholders' equity or total assets. Is often issued by companies that do not have adequate cash to issue a cash dividend. 35 Stock Dividends You have a 2% ownership interest in Cetus Inc., owning 20 of its 1,000 shares of common stock. In a 10% stock dividend, 100 shares (1,000 x 10%) of stock would be issued. You would receive two shares (2% x 100), but your ownership interest would remain at 2% (22 /1,100). You now own more shares of stock, but your ownership interest has not changed. 36 Reasons for Stock Dividends To satisfy stockholders' dividend expectations without spending cash. To increase marketability of its stock by increasing number of shares outstanding and decreasing market price per share. To emphasize that a portion of stockholders' equity has been permanently reinvested in business and is unavailable for cash dividends. 37 Stock Dividends A small stock dividend (less than 20%-25% of the corporation's issued stock) is recorded at the fair market value per share. A large stock dividend (greater than 20%-25% of the corporation's issued stock) is recorded at par or stated value per share. 38 Stock Dividends Medland Corporation has $300,000 in retained earnings and declares a 10% stock dividend on its 50,000 shares of $10 par value common stock. The current fair market value of the stock is $15 per share. Retained Earnings 75,000 Common Stock Dividends 50,000 Distributable Paid-in Capital in Excess 25,000 of Par Value 39 Stock Split... Is the issuance of additional shares of stock to stockholders accompanied by: A reduction in the par or stated value. An increase in number of shares. A stock split does not have any effect on total paid-in capital, retained earnings, and total stockholders' equity. 40 Stock Split Because a stock split does not affect the balances in stockholders' equity accounts, it is not necessary to journalize a stock split. 41 Retained Earnings... Is net income that is retained in the business. The balance in retained earnings is part of the stockholders' claim on the total assets of the corporation. Retained earnings does not represent a claim on any specific asset. 42 Deficit... Is a debit balance in retained earnings and is reported as a deduction in the stockholders' equity section of the balance sheet. 43 Retained Earnings Restrictions... Are legal, contractual or voluntary circumstances that make a portion of retained earnings currently unavailable for dividends. 44 AMAZON.COM Balance Sheet (Partial) December 31, 2000 (in thousands) Stockholders Equity With Deficit Stockholders' equity Paid-in capital Common Stock $ 3,571 Paid-in capital in excess of par value 1,322,479 Total paid-in capital 1,326,050 Accumulated Deficit 2,293,301 Total stockholders’ equity (deficit) $ (967,251) 45 Kmart, Inc. Balance Sheet (Partial) (in millions) Stockholders Equity Section Stockholders' equity Common stock, $.01 par value; 1,500,000,000 shares authorized -250,000,000; 503,294,515 shares issued $ 503 Capital in excess of par value 1,695 Retained earnings 1,261 Total stockholders' equity $ 3,459 46 SARA LEE CORPORATION Statement of Cash Flows (partial) For the Year Ended June 30,2001 (in millions) Cash flow from Financing Activities Issuance of common stock $ Purchase of common stock Payment of dividends Borrowing of long-term debt Repayment of long-term debt Short-term (repayments)borrowing Net cash used in financing activities 104 (643) (486) 1,023 (390) (1,914) (2,306) The Payout Ratio = CASH DIVIDENDS DECLARED ON COMMON STOCK NET INCOME … measures the percentage of earnings distributed in the form of cash dividends to common stockholders. 48 Return on Equity Ratio = NET INCOME - PREFERRED STOCK DIVIDENDS AVERAGE COMMON STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY ...measures the profitability from the stockholders’ point of view. 49 Advantages of Bond Financing Over Common Stock 50 The Dividend Yield = DIVIDENDS DECLARED PER SHARE OF COMMON STOCK STOCK PRICE AT END OF YEAR …reports the rate of return an investor earned from dividends. 51 Earnings Per Share = NET INCOME - PREFERRED STOCK DIVIDENDS AVERAGE COMMON SHARES OUTSTANDING ...measures the net income earned on each share of common stock. 52 Price-Earnings Ratio = MARKET PRICE PER SHARE OF STOCK EARNINGS PER SHARE In order to make a meaningful comparison of earnings across firms, use the price-earnings ratio. The price-earnings ratio reflects the market’s assessment of a company's future earnings. 53