Digestive System and Excretory System
advertisement

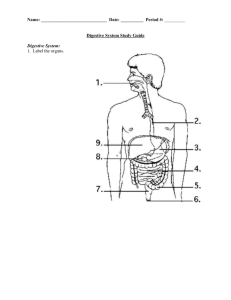
Digestive System and Excretory System Process of Digestion Function: - help convert or break down foods into simpler molecules that can be absorbed and utilized by the cells Two types of digestion: 1. mechanical – physical breakdown by tearing or grinding 2. chemical – breakdown of food with enzymes or substances that dissolve Organs of Digestion • Pathway of digestion: • Mouth (pharynx) • Esophagus • Stomach • Small Intestine • Large Intestine • Rectum • Anus Organs of Digestion • Mouth – food enters and undergoes both mechanical and chemical digestion - Teeth will tear and mash food particles for break down - Salivary glands produce saliva that contains enzymes that will dissolve food (sugars and amylase) • Esophagus – long tube that connects mouth to the stomach - no digestion takes place in the esophagus - peristalsis is the rhythmic contractions that take place to move food down to the stomach Organs of Digestion • Stomach – large muscular sac where both mechanical and chemical digestion take place - contractions of wall churn and mix food - Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) chemically breaks down bolus and activates an enzyme called pepsin that will break down proteins - makes the environment acidic - kills some microorganisms Organs of Digestion • Small Intestine – long narrow tubing where chemical digestion and absorption take place - coiled and compacted to fit, but measures 4 times the height of the individual - consists of the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum - materials that pass undigested in small intestine go to appendix, that mainly stores cellulose Organs of Digestion • Large intestine – larger diameter tubing that measures equal to the height of an individual - primary function is to remove water from undigested material - solid waste will then leave colon and pass through the rectum and exit the body Accessory Organs • Liver, Gallbladder, and Pancreas are organs that aid in chemical digestion - liver produces bile which breaks down fats - gallbladder stores and releases bile - pancreas produces alkaline buffers to combat acidic environment - all are accessory because no actual food passes through these organs - fluids produced by these organs are released into the duodenum of the small intestine Excretory System • Excretion is the process in which the body eliminates metabolic wastes • Excretion is a homeostatic process of the body • Skin and lungs are other organs that are considered part of excretory system for removing wastes Kidneys Kidneys are the main organ of excretion - remove waste products - maintain blood pH - regulate water content of the blood - act as a filter for separating toxic substances (nitrogen) and converting it to urea - also send needed products back into bloodstream Elimination of Wastes • Pathway of waste: 1. Waste products are filtered and separated in the kidney 2. Waste moves to the ureters which connect to the bladder 3. Bladder is an inflatable sac that fills with a little less than 2 liters of fluid (urine) 4. Waste leaves bladder and enters urethra to be removed from the body