The Cell
advertisement

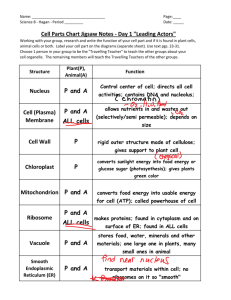
The cell ; It is the smallest structural and functional unit in living organisms. There are two types of cells ; 1-Prokaryotic cells , such as in Bacteria & Archaea. 2- Eukaryotic cells ,such as in animal and plant cells. The first living organisms to evolve. Are primarily distinguished by the fact that they lack a membrane-bound nucleus, thus the genetic material is found naked in the cytoplasm. They are small in size 1-10µm. They are single celled. They have simple internal structures. They contain no cell organelles (only the ribosomes which are not considered as cell organelles.) Reproduce by means of binary fission, duplicating their genetic material and then essentially splitting to form two daughter cells identical to the parent Most important feature is that they contain a well defined nucleus meaning that the genetic material is separated from the rest of the of the cell by a nuclear membrane. Are larger in size 10-100µm. Are found in single and multicellular organisms. It has a complex internal structure (contains a large number of cell organelles) Reproduces by Meisos or Mitosis. Nucleus;It is surrounded by a double layered nuclear membrane which contains pores to allow exchange of material between nucleus and rest of the cell. Contains the genetic material. Nucleolus Is the site For rRNA Synthesis. Endoplasmic reticulum; - Tubular network fused to nuclear membrane - Goes through cytoplasm onto cell membrane - Stores, separates, and serves as cell's transport system - Smooth type: lacks ribosomes - Rough type ;ribosomes embedded in surface can Synthesize protein. Golgi apparatus; - Important in packaging and secretion of cell products. - A membrane structure found near nucleus - Composed of numerous layers forming a sac. Mitochondria; Second largest organelle with unique genetic structure. - Double-layered outer membrane with inner folds called cristae - Energy-producing chemical reactions and ATP production site. Lysosome Contains digestive enzymes to digest proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates - Transports undigested material to cell membrane for removal. Chloroplasts A plastid usually found in plant cells - Contain green chlorophyll where photosynthesis takes place. Vacuoles Membrane-bound sacs for storage, digestion, and waste removal in plant cells. Ribosomes; Site of protein biosynthesis. Stationary ribosomes are bound to the RER. Free ribosomes in cytoplasm. Not surrounded by plasma membrane and is made up of rRNA and protein. Plasma membrane Outer membrane of cell that controls cellular traffic. - Made up of a phosphiolipid bilayer and proteins that span through the membrane and allow passage of materials. Example E.Coli Component Percent total weigh Approxmate No of Molecular species Water 70 1 Proteins 15 3000 DNA 1 1 RNA 6 1000 Carbohydrates 3 50 Lipids 2 40 Building-block molecules&intermediat es 2 500 Inorganic ions 1 12 Nucleic acids Viruses structure : protein coat + genetic material ( DNA or RNA ) Viruses do not have a cellular structure.