Branches Test Matching (4 pts each)
advertisement

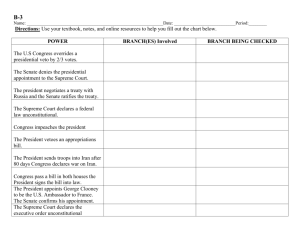
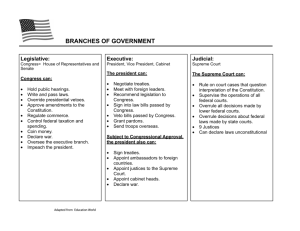
Branches Test Matching (4 pts each): 1. A proposed law. 2. A group of Senators or Representatives organized to study and make proposals for bills. 3. The most powerful man in Congress. 4. The leader who takes over in the Senate if the President of the Senate, the Vice President, is not present. 5. A count of the number of people in the state. 6. Area of a state with clearly defined boundaries and approximately equal population. 7. Opposing bill by non-stop talking until a majority of the Senate abandons or modifies it. 8. The President sends a bill back to Congress with the reasons he believes it should not become a law. 9. To bring charges against a public official. 10. The length of time for which a person is elected to office. 11. Head of the armed forces. 12. Choosing a government official. Multiple choice (3 pts each): 13. a. What is NOT a role the president plays in our government? Chief interpreter of the constitution b. Chief part leader c. Chief legislature d. Commander-in-chief 14. What presidential role involves making sure laws are carried out?(chief police officer) a. Chief Legislator b. Chief Foreign Policy Maker c. Chief Executive d. Chief of State 15. The _________________ appoints the cabinet members while the __________________ approves the appointment. a. Congress, president b. President, supreme court c. President, congress d. Supreme court, congress 16. a. How many Senators are in Congress? 25 b. 435 c. 100 17. a. Who is the presiding officer of the Senate and when can he vote? The vice-President; only if there is a tie-breaker b. The speaker of the House; he votes whenever he is present c. The Secretary of State; only if there is a tie breaker 18. The Line of Succession is detailed in the: 1st amendment a. b. 10th amendment c. 25th amendment d. 100th amendment 19. a. Why is the Gideon v. Wainright case important? If a defendant cannot afford a lawyer the state is obligated to provide one for him. b. Anyone arrested for a specific crime must be informed of certain rights c. Prison can make you famous d. Alllowed police to search houses with a warrant 20. Why is Marbury v. Madison important? a. Alllowed police to search houses with a warrant b. Anyone arrested for a specific crime must be informed of certain rights c. Prison can make you famous. d. Defined the Supreme Courts right to determine whether a law violates the constitution 21. Why is Miranda v. Arizona important? a. If a defendant cannot afford a lawyer the state is obligated to provide one for him. b. Anyone arrested for a specific crime must be informed of certain rights c. Prison can make you famous d. Alllowed police to search houses with a warrant 22. leave blank 23. What is NOT a responsibility of the U.S. Supreme Court? a. Head of the Judicial Branch b. Helps the president by giving their area of expertise c. Hears cases appealed to it from other courts. d. Interprets the law (says what the law means 24. Senators serve for ___ years while Representatives serve for ____ a. 6;2 b. 2;6 c. Life;6 d. 4,4 25. Judicial Review places emphasis on a. The supreme court must approve of nomination of Cabinet Members b. The Supreme Court can overturn a presidential veto by 2/3 vote c. The supreme court has the duty to uphold the constitution d. Looking “old and ugly” 26. How are Surpreme Court Justices hired? a. Appointed by the President b. Approved by the Cabinet c. Appointed by Congress 27. What is the maximum amount of terms a president can serve? a. As many as they want as long as people vote them in b. Two c. One d. Four 28. The purpose of the cabinet is to: a. Helps pass laws in congress b. help the President by giving their advice about their area of expertise. c. Interpret the constitution (cabinet is another name for Supreme Court Judges) d. Determine the number of representatives per state 29. What does the speaker of the house do? a. Deals with foreign dignitaries b. Takes care of the presidents press conferences c. Acts as leader of the majority party in the house of representatives 30. When would someone assume the presidency of the United States? a. The president becomes disabled b. If the president visits another country c. If the president chews gum d. If the president Vetos a law 31. A congressional district is based on ___________ and is reshaped after a ______ a. Senority; primary election b. Population; census c. Bills; appointment 32. Which presidential role involves directing relationships with other countries? a. Chief country advisor b. Chief foreign relations committee member c. Chief of State d. Chief foreign policy maker 50. Essay Question: (14 points) Checks and balances between the legislative (congress) and Executive Branch (president) “Pick from two areas below. List the powers the executive branch has over the area and what the legislative branch has:” Please write complete sentences Cabinet members Military troops War Bills becoming laws Ambassadors Treaties Federal Judges Pardons Extra Credit: (from the “How a bill becomes a law”) Name the three processes for a bill to become a law (hint: we simulated this during our 5 day group activity) and write a two sentence summary for each process. (10 points) If you can name additional supreme court justices and cabinet members I will give you 2pts for each one Key: 1. J 2. K 3. L 4. N 5.O 6.T 7.P 8.R 9.D 10.E 11.A 12.F 13.A 14.C 15.C 16.C 17.A 18.C 19.A 20.D 21.B 22.BLANK 23.B 24.A 25.C 26.A 27.B 28.B 29.C 30.A 31.B 32.D 33. John G. Roberts jr. 34. Ruth Ginsberg 35. Antonin scalia 36. Samuel alito 37. John Paul Stevens 38. Anthony M. Kennedy 39. David Hackett Souder 40. Clarence Thomas 41. Steven G. Breyer 42. Sonia Sotomeyer 43. Joe Biden vice president 44. Tim Geitner secretary of treasury 45. Leon Panetta Secretary of defense 46. Arne Duncan Secretary of Education 47. John Boehner Speaker of the house 48. Daniel Inuyie President Pro Tempore 49. Janet Napalitano secretary of homeland security a. Commander in Chief b. Line of Succession c. Warrant Arrest d. Impeachment e. Term f. Appoint to office g. Law h. Bellybuster i. Cabinet j. Bill k. Committee L. Speaker of the House m. “Big Cheese” n. President pro tempore o. Census p. Filibuster q. President Chaco-latte r. Veto s. Order of take-over t. Congressional District u. Representative Area v. Period w. Expert Coalition x. invictus